Design and validation of analytical methods for quantitative determination of active ingredients in extemporal combined medicine in spray form
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.294919Keywords:
spray, phenylephrine hydrochloride, nitrofural, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, quantitative determination, liquid chromatographyAbstract
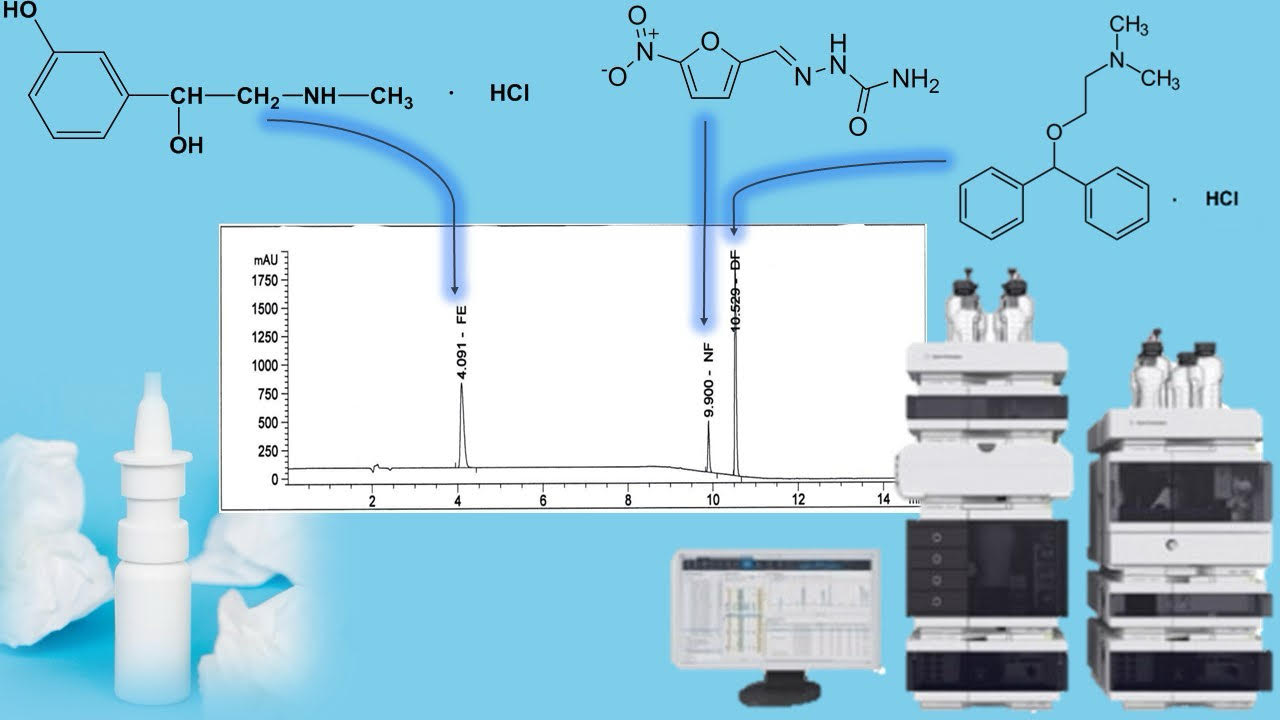
The aim of the work was the development and study of the validation characteristics of the method of quantitative determination of phenylephrine hydrochloride, nitrofural and diphenhydramine hydrochloride when they are simultaneously present in an extemporaneous combined medicinal product in the form of a spray using liquid chromatography method.
Materials and methods. Agilent 1260 liquid chromatographs, equipped with a diode-matrix and UV detector from the company "Agilent technologies", USA. Chromatographic columns 250×4.6 mm filled with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (Zorbax StableBond SB-Aq, Agilent company), mobile phase - 0.1 % aqueous solution of trifluoroacetic acid R - methanol R, elution mode - gradient; mobile phase speed – 1.2 ml/min; the detection wavelength is 220 nm.
Results. The determined chromatographic conditions ensure proper separation of the peaks of the substances to be determined: phenylephrine hydrochloride, nitrofural and diphenhydramine hydrochloride in their joint presence, and do not have a negative effect on the quantitative assessment of their content. Validation tests were conducted to confirm the suitability of the analytical method for the performance of the task - control of the quantitative content of active substances in the combined medicinal product in the form of a spray. The determined validation characteristics indicate that the method is characterized by appropriate specificity, linearity, correctness and convergence in the range of application for phenylephrine hydrochloride (range 0.499-0.749 mg/ml, ΔZ=0.44 ≤ max ΔZ=3.20, d=0.22 ≤ max d=1.02, a=0.01 max a=5.1, r = 0.9997 min r= 0.9924), nitrofural (range 0.154-0.231 mg/ml, ΔZ=0.44 ≤ max ΔZ=3.20, d=0.62 ≤ max d=1.02, a=0.0006 max a=5.1, r = 0.9996 min r= 0.9924) and diphenhydramine hydrochloride (range 0.499-0.749 mg/ml, ΔZ=0.50 ≤ max ΔZ=3.20, d=0.05 ≤ max d=1.02, a=0.076 max a=5.1, r = 0.9999 min r= 0.9924).
Conclusions. An analytical technique for the quantitative determination of phenylephrine hydrochloride, nitrofural and diphenhydramine hydrochloride when simultaneously present in an extemporaneous combined medicinal product in the form of a spray by the method of high-performance liquid chromatography was developed. The determined validation parameters confirm the correctness of the methodology. The proposed HPLC technique was used to study the chemical stability of the spray for the treatment of allergic rhinitis
References
- Polovko, N. P. , Zuykina, E. V. (2018). Condition of the extemporal formulation in Ukraine and the problems of the present. Coliection of scientific works of staff member of Shupyk NHU of Ukraine, 32, 294–307.
- Savchenko, L. P., Heorhiiants, V. A. (2020). Vyhotovlennia likiv u aptekakh: indyvidualnyi pidkhid iz vikovymy tradytsiiamy. Zdorovia Ukrainy 21 storichchia, 11 (480).
- Sulistiyo, J. (2023). Assay of Diphenhydramine HCl in Syrup by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 13 (6), 141–144. doi: http://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v13i6.5885
- Al-Salman, H. N. K., Alassadi, E. A. S., Fayadh, R. H., Hussein, H. H., Jasim, E. Q. (2020). Development of The Stable, Reliable, Fast and Simple RP-HPLC Analytical Method for Quantifying Diphenhydramine-Hcl (DPH) In Pharmaceuticals. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 12 (4), 4457–4467. doi: http://doi.org/10.31838/ijpr/2020.12.04.608
- Mamina, О., Kabachny, V., Tomarovska, T., Bondarenko, N. (2020). Determination of diphenhydramine by HPLC method in biological liquids. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (26), 18–24. doi: http://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2020.210728
- British Pharmacopoeia 2023rd ed. (2023). The British Pharmacopoeia Secretariat. London. Available at: https://www.pharmacopoeia.com/
- Wang, K., Kou, Y., Wang, M., Ma, X., Wang, J. (2020). Determination of Nitrofuran Metabolites in Fish by Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Photodiode Array Detection with Thermostatic Ultrasound-Assisted Derivatization. ACS Omega, 5 (30), 18887–18893. doi: http://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02068
- Nagarjuna, P., Tharun Kumar, B., Nalluri, B. N. (2020). Simultaneous Analysis of Phenylephrine HCl and Ketorolac Tromethamine in Bulk and Injectable Formulations by RP-HPLC-PDA Method. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 10 (4-s), 39–45. doi: http://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v10i4-s.4204
- Dewani, A. P., Patra, S. (2015). A single HPLC-DAD method for simultaneous analysis of paracetamol, phenylephrine, caffeine and levocetirizine in bulk powder and tablet formulation: application to invitro dissolution studies. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 60 (4), 2736–2739. doi: http://doi.org/10.4067/s0717-97072015000400019
- Bachute, M. T., Shanbhag, S. V., Turwale, S. L. (2021). Simultaneous determination of four active pharmaceuticals in tablet dosage form by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 18 (10), 2161–2166. doi: http://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v18i10.23
- Shaalan, R. A., Belal, T. S. (2010). HPLC-DAD Stability Indicating Determination of Nitrofurazone and Lidocaine Hydrochloride in Their Combined Topical Dosage Form. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 48 (8), 647–653. doi: http://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/48.8.647
- KNOWLEDGE Database. Available at: https://www.edqm.eu/en/knowledge-database Last accessed: 27.05.2023
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride. 01/2016:0023, Ph.Eur. 11.0 (2016). Available at: https://pheur.edqm.eu/home Last accessed: 27.05.2023
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride capsules, USP43. Available at: https://www.uspnf.com/ Last accessed: 27.05.2023
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride oral solution, USP43. Available at: https://www.uspnf.com/ Last accessed: 27.05.2023
- Nitrofural, 01/2022:1135, Ph.Eur., 11.0. Available at: https://pheur.edqm.eu/home Last accessed: 27.05.2023
- Phenylephrine hydrochloride, USP43. Available at: https://www.uspnf.com/ Last accessed: 21.05.2023
- Derzhavna farmakopeia Ukrainy. Dopovnennia 4 (2.4) (2020). Kharkiv: Derzhavne pidpryiemstvo «Ukrainskyi naukovyi farmakopeinyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 600.
- Derzhavna Farmakopeia Ukrainy. Vol. 1. Kharkiv: Derzhavne pidpryiemstvo «Ukrainskyi naukovyi farmakopeinyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 1028.
- ICH guideline Q2(R2) on validation of analytical procedures Step 2b (2022). European Medicines Agency, 39.
- ICH Q1A (R2) Stability testing of new drug substances and drug products Step 5 (2003). European Medicines Agency, 20.
- ST-N MOZU 42-3.3:2004 Likarski zasoby. Nastanova z yakosti. Vyprobuvannia stabilnosti (2012). Kyiv: Ministerstvo okhorony zdorovia Ukrainy. Available at: https://compendium.com.ua/uk/clinical-guidelines-uk/standartizatsiya-farmatsevtichnoyi-produktsiyi-tom-1/st-n-mozu-42-3-3-2004/
- ICH guideline Q8 (R2) on pharmaceutical development Step 5 (2017). European Medicines Agency, 24.
- ICH guideline Q14 on analytical procedure development Step 2b (2022). European Medicines Agency, 65.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Valeriia Cherniakova, Artem Myhal, Vitalii Rudiuk, Yaroslav Studenyak, Oleksandr Kryvanych, Nataliia Bevz, Victoriya Georgiyants

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






