Formulation of mouth-dissolving tablets containing a spray-dried solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble fenoprofen calcium dihydrate and its characterization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.302788Keywords:
fenoprofen calcium dihydrate, spray drying, β-cyclodextrin, skimmed milk powder, mouth-dissolving tablets, anti-inflammatoryAbstract
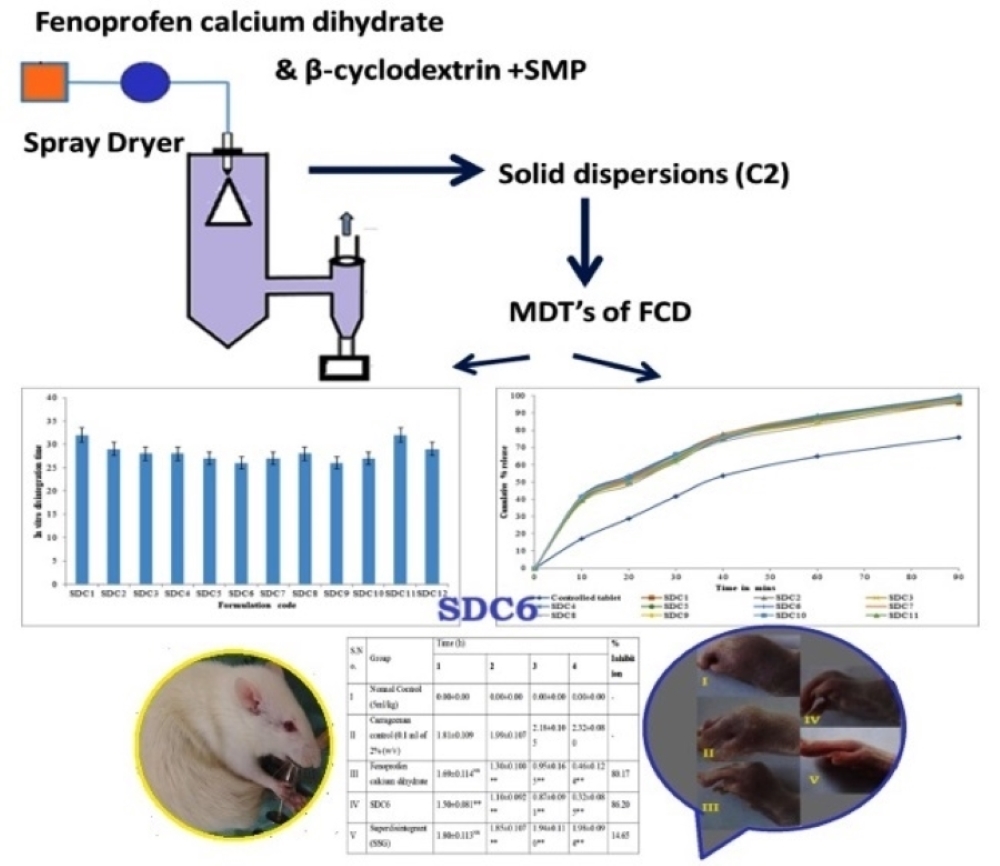
The aim and objective of this investigation focus on the formulation of mouth-dissolving tablets of Fenoprofen calcium dihydrate spray dried solid dispersions.
Materials and methods. Spray drying is a well-recognized manufacturing technique that can be used to create amorphous solid dispersions, which are an effective delivery method for poorly water-soluble pharmaceuticals such as Fenoprofen calcium dihydrate (FCD). In addition to skimmed milk powder (SMP) and FCD, the carrier β-cyclodextrin was used to produce solid dispersions.
Results and discussion. The production of solid dispersions yielded reproducible results. Solid dispersion with β-cyclodextrin and skimmed milk powder is one way to increase disintegration time by increasing the water solubility of inadequately water-soluble FCD. In-vitro dissolution experiments of FCD mouth-dissolving tablets revealed significant differences. Stability studies should evaluate drug product characteristics that are susceptible to change during storage and are anticipated to impact quality, safety, and efficacy to demonstrate that the optimal formulations remain stable over the course of the study. The results of stability experiments were statistically significant at p<0.05 using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet's test. During in-vivo anti-inflammatory experiments, the formulation SDC6 demonstrated a greater percentage of inhibition than the purified drug and super disintegrant, and the results were statistically significant using one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni test.
Conclusions. The solid dispersions were prepared with β-cyclodextrin, and skimmed milk powder improved the solubility of the poorly water-soluble fenoprofen calcium dihydrate. In vitro dissolution experiments of fenoprofen calcium dihydrate mouth dissolving tablets and controlled tablets revealed significant differences
References
- Hannan, P., Khan, J., Khan, A., Safiullah, S. (2016). Oral dispersible system: A new approach in drug delivery system. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 78 (1), 2. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.180244
- Achal, C., Chaudhary, B., Redasani, V. K., Bhagat, P., Mahadik, R. (2023). On Overview of Fast dissolving tablet. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development, 11 (3), 190–193. https://doi.org/10.22270/ajprd.v11i3.1276
- Ajay, S., Mankar, S. (2023). Mouth Dissolving Tablet: A Novel Approach for Drug Delievery. International journal of current research and innovations in pharma sciences, 1 (2), 84–95. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8019368
- Masih, A., Kumar, A., Singh, S., Tiwari, A. K. (2017). Fast dissolving tablets: a review. International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research, 9 (2), 8–18. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijcpr.2017v9i2.17382
- Bera, A., Mukherjee, A. (2013). A detailed study of mouth dissolving drug delivery system. Acta Chimica and Pharmaceutica Indica, 3 (1), 65–93.
- Khan, D., Kirby, D., Bryson, S., Shah, M., Rahman Mohammed, A. (2022). Paediatric specific dosage forms: Patient and formulation considerations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 616, 121501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121501
- Madhumathi, I., Hemalatha, B., Padmalatha, K. (2022). Fast Dissolving Tablets: A Review. Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 12 (2), 183–189. https://doi.org/10.52711/2231-5713.2022.00031
- Jire, D. S., Gosavi, N. S., Badhe, R. B., Jagdale, D. H. (2021). Mouth Dissolving Tablet: A Novel Drug Delivery System. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 11 (3), 180–186. https://doi.org/10.52711/2231-5691.2021.00033
- Tambe, S., Jain, D., Meruva, S. K., Rongala, G., Juluri, A., Nihalani, G. et al. (2022). Recent Advances in Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Preformulation, Formulation Strategies, Technological Advancements and Characterization. Pharmaceutics, 14 (10), 2203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102203
- Miller, D. A., Ellenberger, D., Porfirio, T., Gil, M. (2022). Spray-drying technology. Formulating poorly water soluble drugs. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 377–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88719-3_10
- Patel, K., Shah, S., Patel, J. (2022). Solid dispersion technology as a formulation strategy for the fabrication of modified release dosage forms: A comprehensive review. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 30 (1), 165–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-022-00440-0
- Chen, Z., Yang, K., Huang, C., Zhu, A., Yu, L., Qian, F. (2018). Surface Enrichment and Depletion of the Active Ingredient in Spray Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutical Research, 35 (2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-018-2345-1
- Bhujbal, S. V., Mitra, B., Jain, U., Gong, Y., Agrawal, A., Karki, S. et al. (2021). Pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersion: A review of manufacturing strategies. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 11 (8), 2505–2536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.014
- Sawicki, E., Beijnen, J. H., Schellens, J. H. M., Nuijen, B. (2016). Pharmaceutical development of an oral tablet formulation containing a spray dried amorphous solid dispersion of docetaxel or paclitaxel. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 511 (2), 765–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.068
- Surampalli, G., Nanjwade, B. K., Patil, P. A., Chilla, R. (2014). Novel tablet formulation of amorphous candesartan cilexetil solid dispersions involving P-gp inhibition for optimal drug delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Delivery, 23 (7), 2124–2138. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.945017
- Sarfraz, R., Khan, H., Mahmood, A., Ahmad, M., Maheen, S., Sher, M. (2015). Formulation and evaluation of mouth disintegrating tablets of atenolol and atorvastatin. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 77 (1), 83. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.151602
- Aulton, M. E., Taylor, K. M. (2007). Aulton’s pharmaceutics. The design and manufacture of medicines, 3, 176–178.
- Laitinen, R., Suihko, E., Bjorkqvist, M., Riikonen, J., Lehto, V.-P., Jarvinen, K., Ketolainen, J. (2009). Perphenazine solid dispersions for orally fast-disintegrating tablets: physical stability and formulation. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 36 (5), 601–613. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639040903386690
- Pawar, H., Varkhade, C., Jadhav, P., Mehra, K. (2014). Development and evaluation of orodispersible tablets using a natural polysaccharide isolated from Cassia tora seeds. Integrative Medicine Research, 3 (2), 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2014.03.002
- Tashan, E., Karakucuk, A., Celebi, N. (2020). Development of Nanocrystal Ziprasidone Orally Disintegrating Tablets: Optimization by Using Design of Experiment and In Vitro Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech, 21 (3). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-020-01653-9
- Sheikh, F. A., Aamir, M. N., Shah, M. A., Ali, L., Anwer, K., Javaid, Z. (2020). Formulation design, characterization and in vitro drug release study of orodispersible film comprising BCS class II drugs. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 33, 343–353.
- Hasan, A., Abd Elghany, M., Sabry, S. (2020). Design and characterization of intra-oral fast dissolving tablets containing diacerein-solid dispersion. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 10 (6), 44–53. https://doi.org/10.7324/japs.2020.10607
- Singh Narwariya, S., Jain, S. (2022). Physicochemical In vivo Anti-Inflammatory effect of Tablet containing Fenoprofen. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 15 (10), 4413–4415. https://doi.org/10.52711/0974-360x.2022.00739
- Singh, A., Van den Mooter, G. (2016). Spray drying formulation of amorphous solid dispersions. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 100, 27–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.12.010
- Maheshwari, R., Todke, P., Kuche, K., Raval, N., Tekade, R. K. (2018). Micromeritics in pharmaceutical product development. Dosage form design considerations. Academic Press, 599–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-814423-7.00017-4
- Salah Attia, M., Ali Hasan, A., Ghazy, F.-E. S., Gomaa, E. (2021). Solid Dispersion as a Technical Solution to Boost the Dissolution Rate and Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, 55 (2s), s327–s339. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.55.2s.103
- Amin, P., Prabhu, N., Wadhwani, A. (2006). Indion 414 as superdisintegrant in formulation of mouth dissolve tablets. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 68 (1), 117. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.22983
- Mohanachandran, P. S., Sindhumol, P. G., Kiran, T. S. (2011). Superdisintegrants: an overview. International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research, 6 (1), 105–109.
- Pahwa, R., Gupta, N. (2011). Superdisintegrants in the development of orally disintegrating tablets: a review. International journal of pharmaceutical sciences and research, 2 (11), 2767–2780.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Shailendra Singh Narwariya, Suman Jain, Alagusundaram Muthumanickam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






