Study of the effect of ethanol on the properties of poloxamer 338 solutions by rotational viscometry and spin probe method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.306365Keywords:
poloxamer 338 (Р338), ethanol, solution, gel, viscosity, micelle, spin probe, EPR spectrum, spectrum parametersAbstract
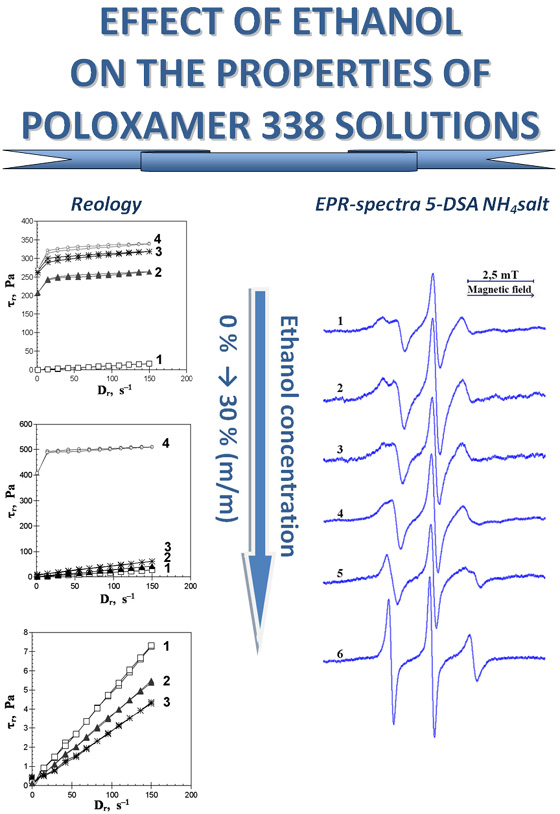
The aim. Study the properties of 20 % solutions of poloxamer 338 (P338) in water and mixed solvents water-ethanol using rotational viscometry and the spin probe method at various temperatures.
Materials and methods. 20 % m/m solutions of P338 in water and water – ethanol mixtures were the objects of research. The solutions were studied by rotational viscometry at various temperatures; the flow behaviour, lower yield stress (t0) and dynamic or apparent viscosity (η) were determined. Spin probes based on fatty acids, which differ in molecular structure, solubility, and radical localization, were added to the solutions. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were obtained to determine their type and parameters.
Results. Depending on the content, ethanol affects the rheological properties of 20 % solution of P338. The solution was demonstrated to be able to thermally induce sol → gel transition at 32 °C when ethanol content is 5 % m/m. The rheological parameters of the gel at 32 °C and 37 °C exhibit an increase (in comparison to the gel without ethanol), accompanied by a reduction in the packing density of polypropylene oxide (PPO) chains within the cores of P338 micelles. At an ethanol content of 10 % m/m, the gel formation temperature rises to 40 °C. At ethanol content of 15 % m/m and above, 20 % P338 solutions do not form gels at temperatures between 25 °C and 40 °C. The values of rotational correlation times (τ) and the order parameter (S) of fatty acid-based spin probes were observed to decrease with increasing ethanol content up to 30 % m/m; in the case of the ammonium salt of 5‑doxylstearic acid (5-DSA NH4 salt), the anisotropic EPR spectra transform, becoming a superposition of two triplets and subsequently a triplet. P338 solutions retain their ability to undergo thermally induced sol ↔ gel transitions as long as the EPR spectra of this probe exhibit anisotropy at temperatures ranging from 25 °C to 37 °C. As the concentration of ethanol in the solution increases, the solvation of the cores of P338 micelles by the dispersion medium of the solution also increases.
Conclusions. It was demonstrated that ethanol, when added to the 20 % P338 solution, results in changes to the rheological properties of this solution. However, at the ethanol content of 5-10 % m/m, the ability of P338 to thermally induce sol → gel transition remains unaltered. The rheological properties of the 20 % P338 solution exhibit a correlation with the observed change in EPR spectra types for the 5-DSA NH4 salt. As the ethanol content in the solution increases, the solvation of P338 micelle cores by the dispersion medium increases, accompanied by decreased density and orderliness of the PPO chains packing in the micelle cores
References
- The European Pharmacopoeia (2022). European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare of the Council of Europe. Strasbourg: Sedex, 6105.
- Sheskey, P. J., Hancock, B. C., Moss, G. P., Goldfarb, D. J. (Eds.) (2020). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. London: Pharm. Press, 1296.
- Delgado, D. R., Martínez, F. (2014). Preferential solvation of sulfadiazine, sulfamerazine and sulfamethazine in ethanol+water solvent mixtures according to the IKBI method. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 193, 152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2013.12.021
- Lee, S.-K., Ha, E.-S., Jeong, J.-S., Kim, S., Park, H., Kim, J.-S. et al. (2022). Determination and correlation of solubility of efinaconazole in fifteen mono solvents and three binary mixed solvents at various temperatures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 349, 118148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118148
- Bezuhlaia, E. P., Melnykova, E. N., Zhemerova, E. H., Liapunov, A. N., Zynchenko, Y. A. (2016). Efficacy of antimicrobial preservation of certain hydrophilic non-aqueous solvents in aqueous solutions and gels. Farmakom, 1, 51–59.
- Hyde, A. E., Ohshio, M., Nguyen, C. V., Yusa, S., Yamada, N. L., Phan, C. M. (2019). Surface properties of the ethanol/water mixture: Thickness and composition. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 290, 111005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111005
- Bielawska, M., Chodzińska, A., Jańczuk, B., Zdziennicka, A. (2013). Determination of CTAB CMC in mixed water+short-chain alcohol solvent by surface tension, conductivity, density and viscosity measurements. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 424, 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.017
- Kirschner, J., Gomes, A. H. A., Marinho, R. R. T., Björneholm, O., Ågren, H., Carravetta, V. et al. (2021). The molecular structure of the surface of water–ethanol mixtures. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23 (19), 11568–11578. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp06387h
- Belda, R., Herraez, J. V., Diez, O. (2004). Rheological study and thermodynamic analysis of the binary system (water/ethanol): Influence of concentration. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 42 (5), 467–479. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319100410001700850
- Hoga, H. E., Torres, R. B., Volpe, P. L. O. (2018). Thermodynamics properties of binary mixtures of aqueous solutions of glycols at several temperatures and atmospheric pressure. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 122, 38–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2018.02.022
- Idrissi, A., Jedlovszky, P. (2021). Effect of the alkyl chain and composition on the thermodynamics of mixing of small alcohols and water. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 338, 116777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116777
- Pashayev, B. G., Aliyev, L. P., Hajiyeva, Sh. N. (2024). Viscous flow and structural properties in water-ethanol-urea systems. Advanced Physical Research, 6 (1), 29–35. https://doi.org/10.62476/apr61.35
- Pal, J., Patla, A., Subramanian, R. (2021). Thermodynamic properties of forming methanol-water and ethanol-water clusters at various temperatures and pressures and implications for atmospheric chemistry: A DFT study. Chemosphere, 272, 129846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129846
- Finneran, I. A., Carroll, P. B., Allodi, M. A., Blake, G. A. (2015). Hydrogen bonding in the ethanol–water dimer. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 17 (37), 24210–24214. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp03589a
- Marinho, R. R. T., Walz, M.-M., Ekholm, V., Öhrwall, G., Björneholm, O., de Brito, A. N. (2017). Ethanol Solvation in Water Studied on a Molecular Scale by Photoelectron Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 121(33), 7916–7923. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b02382
- Larkin, J. A. (1975). Thermodynamic properties of aqueous non-electrolyte mixtures I. Excess enthalpy for water + ethanol at 298.15 to 383.15 K. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 7 (2), 137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9614(75)90261-x
- Dutton, S. E., Mastin, E. M., Blake, G. A. (2023). Chirped pulse Fourier-transform microwave spectroscopy of alcohol and water tetramers. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 25 (8), 5960–5966. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cp05022f
- Bezuglaya, E., Krasnopyorova, A., Liapunova, A., Zinchenko, I., Lyapunov, N., Sytnik, O. (2023). Influence of physicochemical properties and structure of mixed solvents propylene glycol – macrogol 400 on their in vitro release. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (41), 4–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.274468
- Yang, W.-Z., Fan, G.-Q., Zhang, T.-T., Li, D.-B., Pei, L.-L., Huang, R.-Y. et al. (2019). Determination of the solubility and thermodynamic properties of albendazole in a binary solvent of ethanol and water. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 59 (1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319104.2019.1660979
- Zhang, C., Jouyban, A., Zhao, H., Farajtabar, A., Acree, W. E. (2021). Equilibrium solubility, Hansen solubility parameter, dissolution thermodynamics, transfer property and preferential solvation of zonisamide in aqueous binary mixtures of ethanol, acetonitrile, isopropanol and N,N-dimethylformamide. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 326, 115219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115219
- He, Q., Zheng, M., Zhao, H. (2019). Baicalin solubility in aqueous co-solvent mixtures of methanol, ethanol, isopropanol and n-propanol revisited: solvent–solvent and solvent–solute interactions and IKBI preferential solvation analysis. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 58 (6), 820–832. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319104.2019.1660981
- Zheng, M., Chen, G., Chen, J., Farajtabar, A., Zhao, H. (2019). Solvent effect and preferential solvation of cefpiramide in cosolvent plus water mixtures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 276, 318–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.027
- Akay, S., Kayan, B., Jouyban, A., Martínez, F. (2021). Solubility and dissolution thermodynamics of 5-fluorouracil in (ethanol + water) mixtures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 333, 116038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116038
- Sarkar, B., Lam, S., Alexandridis, P. (2010). Micellization of Alkyl-Propoxy-Ethoxylate Surfactants in Water-Polar Organic Solvent Mixtures. Langmuir, 26 (13), 10532–10540. https://doi.org/10.1021/la100544w
- Ivanova, R., Alexandridis, P., Lindman, B. (2001). Interaction of poloxamer block copolymers with cosolvents and surfactants. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 183-185, 41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0927-7757(01)00538-6
- Ivanova, R., Lindman, B., Alexandridis, P. (2002). Effect of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Glycols on the Stability of the Liquid Crystalline Gels Formed by Poloxamer 407 in Water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 252 (1), 226–235. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8417
- Soni, S. S., Brotons, G., Bellour, M., Narayanan, T., Gibaud, A. (2006). Quantitative SAXS Analysis of the P123/Water/Ethanol Ternary Phase Diagram. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110 (31), 15157–15165. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp062159p
- Zhao, Y., Ma, S.-M., Li, B., De Nicola, A., Yu, N.-S., Dong, B. (2019). Micellization of Pluronic P123 in Water/Ethanol/Turpentine Oil Mixed Solvents: Hybrid Particle–Field Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Polymers, 11 (11), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111806
- Bodratti, A., Alexandridis, P. (2018). Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 9 (1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9010011
- Alkilani, A., McCrudden, M. T., Donnelly, R. (2015). Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics, 7 (4), 438–470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
- Lyapunov, N., Bezuglaya, E., Liapunov, O., Lysokobylka, O. (2023). Study of aqueous solutions of poloxamers by rotational viscometry and spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (44), 4–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.285933
- Berliner, L. (Ed.) (1979). Metod spinovykh metok. Teoriia i primenenie. Moscow: Mir, 635.
- Likhtenshtein, G. I. (1974). Metod spinovykh zondov v molekuliarnoi biologii. Moscow: Nauka, 256.
- Kuznetcov, A. N. (1976). Metod spinovogo zonda (Osnovy i primenenie). Moscow: Nauka, 210.
- Derzhavna Farmakopeia Ukrainy. Vol. 1 (2015). Kharkiv: Derzhavne pidpryiemstvo «Ukrainskyi naukovyi farmakopeinyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 1128.
- Bezuglaya, E., Lyapunov, N., Chebanov, V., Liapunov, O. (2022). Study of the formation of micelles and their structure by the spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (38), 4–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.263054
- Cabana, A., Aı̈t-Kadi, A., Juhász, J. (1997). Study of the Gelation Process of Polyethylene Oxidea–Polypropylene Oxideb–Polyethylene OxideaCopolymer (Poloxamer 407) Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 190 (2), 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1997.4880
- Prud’homme, R. K., Wu, G., Schneider, D. K. (1996). Structure and Rheology Studies of Poly(oxyethylene−oxypropylene−oxyethylene) Aqueous Solution. Langmuir, 12 (20), 4651–4659. https://doi.org/10.1021/la951506b
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oleksii Liapunov, Elena Bezuglaya, Anna Liapunova, Oleksii Lysokobylka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






