Xylometazoline base suitable for use in lipophilic drug products: development of production technology and analytical methods for quality control
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.310656Keywords:
xylometazoline, technology, essential oils, stability, liquid chromatography, lipophilicity, chlorides, validation, synthesisAbstract
The aim: development of the technology for obtaining the base of xylometazoline, suitable for the development of formulations in combination with essential oils. Development and validation of methods of control of related substances and assay of the obtained base of xylometazoline. Study of the stability of the obtained xylometazoline base under long-term and accelerated conditions.
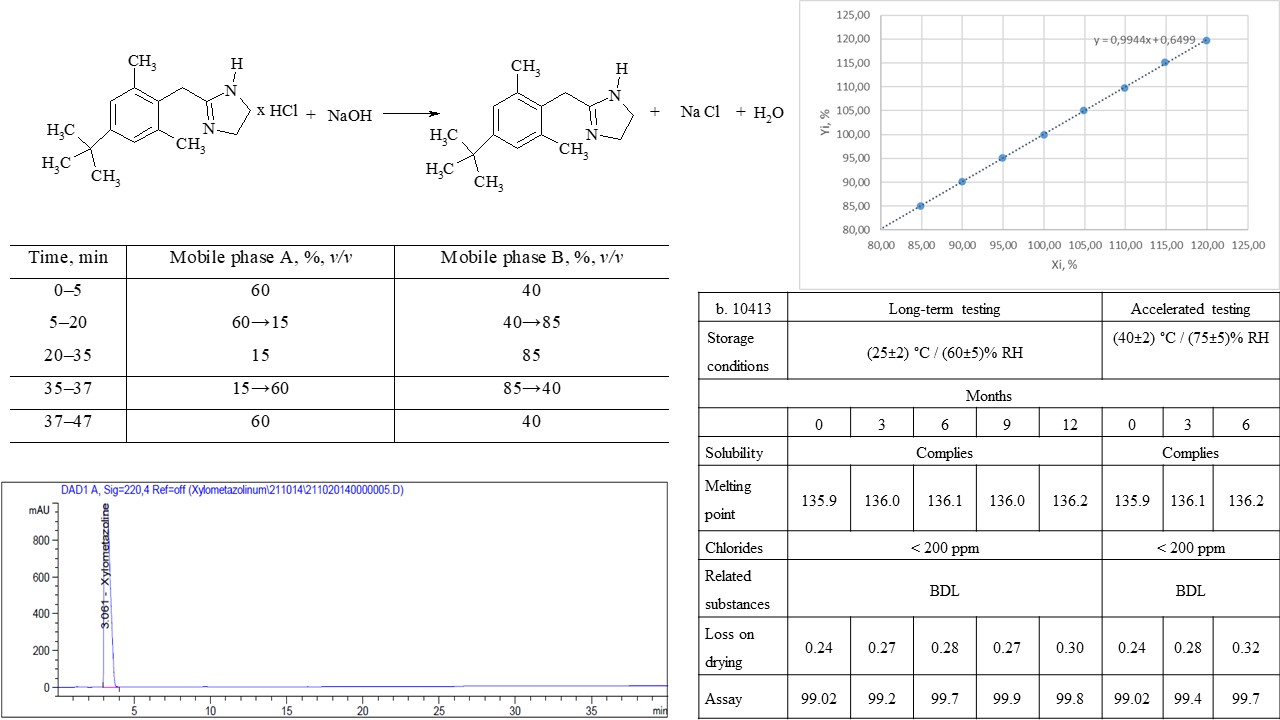
Materials and methods: experimental samples of xylometazoline base were obtained from commercially available xylometazoline hydrochloride and aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. The quality control of the obtained substance was carried out in accordance with the requirements of the internal specification. The analysis of raw materials of xylometazoline hydrochloride was carried out in accordance with the monograph of the European Pharmacopoeia on xylometazoline hydrochloride (Ph. Eur. 10.1, 1162 (01/2008)).
Results: a technology for obtaining xylometazoline base from xylometazoline hydrochloride by the action of a 2 % solution of a strong base, namely sodium hydroxide, was developed. Developed and validated methods of quality control of the obtained xylometazoline base according to indicators of related substances and assay. The stability of the substance was studied for 1 year; the results of control under accelerated research conditions meet the requirements of the specification, which allows for establishing a shelf life of 2 years.
Conclusions: the technology for obtaining xylometazoline base and quality control methods based on the monograph of the European Pharmacopoeia on xylometazoline hydrochloride was developed. The developed technology ensures the proper quality of the substance in accordance with the requirements of the internal specification. Analytical methods "related substances" and "assay" meet the established criteria during validation. The obtained results were later used to develop a medicine based on xylometazoline and eucalyptus oil – Eukazolin, nasal drops
References
- Haenisch, B., Walstab, J., Herberhold, S., Bootz, F., Tschaikin, M., Ramseger, R., Bönisch, H. (2010). Alpha‐adrenoceptor agonistic activity of oxymetazoline and xylometazoline. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 24 (6), 729–739. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00805.x
- Graf, C., Bernkop-Schnürch, A., Egyed, A., Koller, C., Prieschl-Grassauer, E., Morokutti-Kurz, M. (2018). Development of a nasal spray containing xylometazoline hydrochloride and iota-carrageenan for the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion caused by rhinitis and sinusitis. International Journal of General Medicine, 11, 275–283. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s167123
- Graf, P., Eccles, R., Chen, S. (2009). Efficacy and safety of intranasal xylometazoline and ipratropium in patients with common cold. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 10 (5), 889–908. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656560902783051
- Kehrl, W., Sonnemann, U. (2000). Verbesserung der Wundheilung nach Nasenoperationen durch kombinierte Anwendung von Xylometazolin und Dexpanthenol. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie, 79 (3), 151–154. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2000-295
- EP1446119B1 (2006). Compositions comprising ipatropium and xylometazoline for treatment of the common cold. Published: 01.03.2006.
- Pat. CN1832726A (2009). Aqueous pharmaceutical solution containing oxymetazoline and/or xylometazoline. Published: 26.08.2009.
- Challier, C., Mártire, D. O., García, N. A., Criado, S. (2017). Visible light-mediated photodegradation of imidazoline drugs in the presence of Riboflavin: Possible undesired effects on imidazoline-based eye drops. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 332, 399–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.09.009
- Arnott, J. A., Planey, S. L. (2012). The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 7 (10), 863–875. https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.2012.714363
- Hinchcliffe, M., Illum, L. (1999). Intranasal insulin delivery and therapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 35 (2-3), 199–234.
- Chouhan, S., Sharma, K., Guleria, S. (2017). Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils – Present Status and Future Perspectives. Medicines, 4 (3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4030058
- Kalemba, D., Kunicka, A. (2003). Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Essential Oils. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 10 (10), 813–829. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867033457719
- Marzoug, H. N. B., Romdhane, M., Lebrihi, A., Mathieu, F., Couderc, F., Abderraba, M. et al. (2011). Eucalyptus oleosa Essential Oils: Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of the Oils from Different Plant Parts (Stems, Leaves, Flowers and Fruits). Molecules, 16 (2), 1695–1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16021695
- Takahashi, T., Kokubo, R., Sakaino, M. (2004). Antimicrobial activities of eucalyptus leaf extracts and flavonoids from Eucalyptus maculata. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 39 (1), 60–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765x.2004.01538.x
- Bachir, R. G., Benali, M. (2012). Antibacterial activity of the essential oils from the leaves of Eucalyptus globulus against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2 (9), 739–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2221-1691(12)60220-2
- Kumari, P. K., Akhila, S., Rao, Y. S., Devi, B. R. (2019). Alternative to artificial preservatives. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 10 (1), 99–102.
- Kheirkhah Rahimabadi, S., Tabatabaee Bafroee, A. S., Khalili Hadad, B. (2022). Development of a Natural Preservative System in Fluticasone Propionate Nasal Spray Formulation Using Eucalyptus globulus Essential Oil. Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products, 17 (4). https://doi.org/10.5812/jjnpp-127106
- Caimmi, D., Neukirch, C., Louis, R., Malard, O., Thabut, G., Demoly, P. (2020). Effect of the Use of Intranasal Spray of Essential Oils in Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis: A Prospective Study. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 182 (3), 182–189. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510592
- European Pharmacopoeia (2023). Strasbourg: Council of Europe.
- Pat. CN101928247A (2012). Method for synthesizing xylometazoline hydrochloride compound. Published: 09.05.2012.
- Pat. CN103351343A (2013). Synthetic method for xylometazoline hydrochloride (2013). Published: 16.10.2013.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Tetiana Solominchuk, Vitalii Rudiuk, Nataliia Smielova, Alinа Deyneka, Tetiana Nesteruk, Victoriya Georgiyants

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






