Study of phenolic compounds of umbellate wintergreen herb and their influence on biochemical indicators of blood and urine in the rat model of chronic kidney disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.310744Keywords:
Chimaphila umbellata (L.), phenolic compounds, antioxidant effect, chronic kidney disease, neuroprotective effectAbstract
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract are a common problem in people of all ages. Kidneys filter blood, removing water-soluble waste from the body, maintain water-salt balance, stabilize blood pressure and PH level. Intoxication, hypothermia, injuries and other causes lead to problems with the kidneys - inflammatory disease, urolithiasis, etc. Therefore, the development of effective herbal remedies that affect the etiopathogenic factors of diseases is urgent.
The aim. Study of the profile of phenolic compounds of umbellate wintergreen, study of antioxidant and nephroprotective properties of umbellate wintergreen extract on the model of chromate-induced renal failure (chronic kidney disease) in rats.
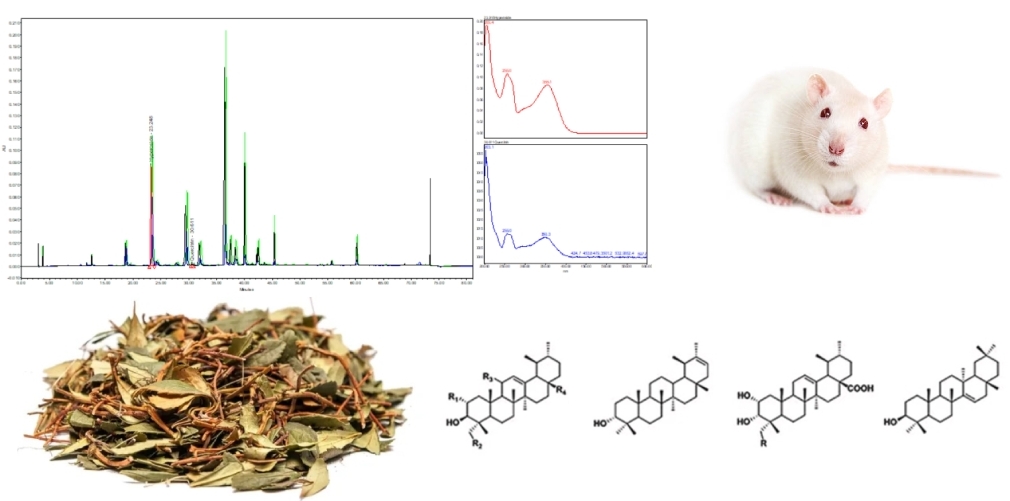
Materials and methods. Phenolic compounds were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a Waters e2695 Alliance HPLC system in combination with a 2998 PDA detector (Waters, Milford, MA, USA).
Study of in vitro antioxidant activity by HPLC method for 50 % extract of umbellate wintergreen herb. A Waters 2695 chromatograph (Waters, USA) equipped with a Waters 996 diode-matrix detector was used.
To determine the nephroprotective effect, 60 outbred sexually mature rats (males), divided into six groups, were studied. Based on the results of biochemical studies, creatinine clearance and urea clearance were calculated in experimental animals.
Results. 8 phenolic compounds - apigenin, hyperoside, quercitrin, rutin, quercetin, gallic acid, guaiaverine and isoquercetin - were identified and quantified in umbellate wintergreen by HPLC. Based on the results of a preliminary assessment of the antioxidant contribution of individual phenolic compounds to the overall effectiveness of the umbellate wintergreen grass extract, a significant effect of caffeic acid derivatives and quercetin was determined.
The use of Chimaphila umbellata extract in experimental animals was marked by the normalization of diuresis, a decrease in the total protein content of urine by 1.8 times. The effect of the use of umbellate wintergreen extract was expected to be dose dependent.
Conclusions. The profile of umbellate wintergreen phenolic compounds was investigated by HPLC, and their antioxidant effect was determined. In the conditions of the development of renal failure in rats, the studied extract of Chimaphila umbellata improved the physical condition of the animals, reduced their mortality, improved the excretory function of the kidneys, normalized nitrogen and protein metabolism, contributed to the protection of the structure of the kidney tissue, and therefore had a positive effect on the course of nephropathy
References
- Grams, M. E., Levey, S. A., Coresh, J.; Yu, A. S. L., Chertow, G. M., Luyckx, V. A., Marsden, P. A., Skorecki, K., Taal, M. W., Wasser, W. G. (Eds.) (2020). Epidemiology of Kidney Disease. Brenner and Rector’s The Kidney. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 616-639.e5.
- Wang, H., Naghavi, M., Allen, C., Barber, R. M., Bhutta, Z. A., Carter, A. et al. (2016). Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet, 388, 1459–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1
- Luyckx, V. A., Tonelli, M., Stanifer, J. W. (2018). The global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development goals. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 96 (6), 414-422D. https://doi.org/10.2471/blt.17.206441
- Shebeko, S. K., Chernykh, V. V., Zupanets, K. O. (2020). Nephroprotective Effect of the Herbal Composition BNO 2103 in Rats with Renal Failure. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 88 (4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88040047
- Ali, U., Khan, M. M., Khan, N., Haya, R. tul, Asghar, M. U., Abbasi, B. H. (2023). Chimaphila umbellata; a biotechnological perspective on the coming-of-age prince’s pine. Phytochemistry Reviews, 23 (1), 229–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-023-09880-1
- Ivanauskas, L., Uminska, K., Gudžinskas, Z., Heinrich, M., Georgiyants, V., Kozurak, A., Mykhailenko, O. (2023). Phenological Variations in the Content of Polyphenols and Triterpenoids in Epilobium angustifolium Herb Originating from Ukraine. Plants, 13 (1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13010120
- Marksa, M., Radušienė, J., Jakštas, V., Ivanauskas, L., Marksienė, R. (2015). Development of an HPLC post-column antioxidant assay forSolidago canadensisradical scavengers. Natural Product Research, 30 (5), 536–543. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1027703
- Mykhailenko, O., Korinek, M., Ivanauskas, L., Bezruk, I., Myhal, A., Petrikaitė, V. et al. (2020). Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Ukrainian Iris Species: A Fresh Look on Their Antioxidant Content and Biological Activities. Molecules, 25 (19), 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194588
- Kozhemiakin, Yu. M., Khromov, O. S., Filonenko, M. A., Saifetdynova, H. A. (2002). Naukovo-praktychni rekomendatsii z utrymannia laboratornykh tvaryn ta roboty z nymy. Kyiv: Avitsena, 156.
- Stefanov, O. V. (Ed.) (2001). Doklinichni doslidzhennia likarskykh zasobiv (metodychni rekomendatsii). Kyiv: Avitsena, 528.
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. OJEU2010 (2010). L276, 33–79.
- Instruktsiia dlia medychnoho zastosuvannia preparatu LESPEFRYL (LESPEFRIL). Normatyvno-derektyvni dokumenty MOZ Ukrainy (2021). Available at: https://mozdocs.kiev.ua/likiview.php?id=52052
- Kovregin, O., Prokopiuk, V., Lytkin, D., Vladymyrova, I. (2024). Study of the influence of the extract of pipsissewa on cell cultures. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 3 (49), 78–85. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.307291
- Nair, A., Jacob, S. (2016). A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 7 (2), 27–31. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-0105.177703
- Shtryhol, S. Iu., Lisovyi, V. M., Zupanets, I. A. et al. (2009). Metody eksperymentalnoho modeliuvannia urazhennia nyrok dlia farmakolohichnykh doslidzhen. Kharkiv: Vyd-vo NFaU, 48.
- Jadhav, R., Jadhav, N., Patil, C., Chaudhari, K., Wagh, J., Surana, S. (2010). Diuretic and natriuretic activity of two mistletoe species in rats. Pharmacognosy Research, 2 (1), 50–57. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.60576
- Naumenko, A. N., Gorelaya, M. V., Babiy, S. O. (2017). Biochemical composition of urine in rats with developed Guerin’s carcinoma and administration of cisplatin. Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems, 8 (1), 11–14. https://doi.org/10.15421/021702
- Vilkhova, I. V., Mateshuk-Vatseba, L. R., Kantser, O. V., Podoliuk, M. V., Bekesevych, A. M., Hresko, N. I. (2021). Changes in biochemical parameters of nitrogen renal function of rats with long-term administration of therapeutic doses of nalbuphine. Bulletin of Medical and Biological Research, 3 (1), 54–61. https://doi.org/10.11603/bmbr.2706-6290.2021.1.12088
- Indrayan, A., Malhotra, K. R. (2018). Medical biostatistics. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 685.
- Yu, Y., Elshafei, A., Zheng, X., Cheng, S., Wang, Y., Piao, M. et al. (2021). Chemical constituents of Chimaphila japonica Miq. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 95, 104219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2020.104219
- Stan, D., Enciu, A.-M., Mateescu, A. L., Ion, A. C., Brezeanu, A. C., Stan, D., Tanase, C. (2021). Natural Compounds With Antimicrobial and Antiviral Effect and Nanocarriers Used for Their Transportation. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.723233
- Newman, D. J., Cragg, G. M. (2020). Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. Journal of Natural Products, 83 (3), 770–803. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oleksiy Kovregin, Dmytro Lytkin, Olha Mykhailenko, Liudas Ivanauskas, Tetiana Yudkevych, Inna Vladymyrova, Larisa Khodak, Volodymyr Starikov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






