Structural-fragment analysis of active pharmaceutical ingredients of antiepileptic drugs in group N03A of the Ukrainian pharmaceutical market and their pharmacophoric features
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2025.337842Keywords:
antiepileptic drugs, APIs, FBDD, pharmacophore, structural clustering, ADME, Tanimoto similarity, NaV, GABA-A, SV2A, carbonic anhydrase, Ukrainian pharmaceutical marketAbstract
Epilepsy affects approximately 50 million people globally, with one-third of patients remaining resistant to available therapies, emphasizing the need for new and safer anticonvulsants. Although fragment-based and in silico approaches are effective for drug discovery, a unified structural analysis of antiepileptic APIs on the Ukrainian market remains unexplored.
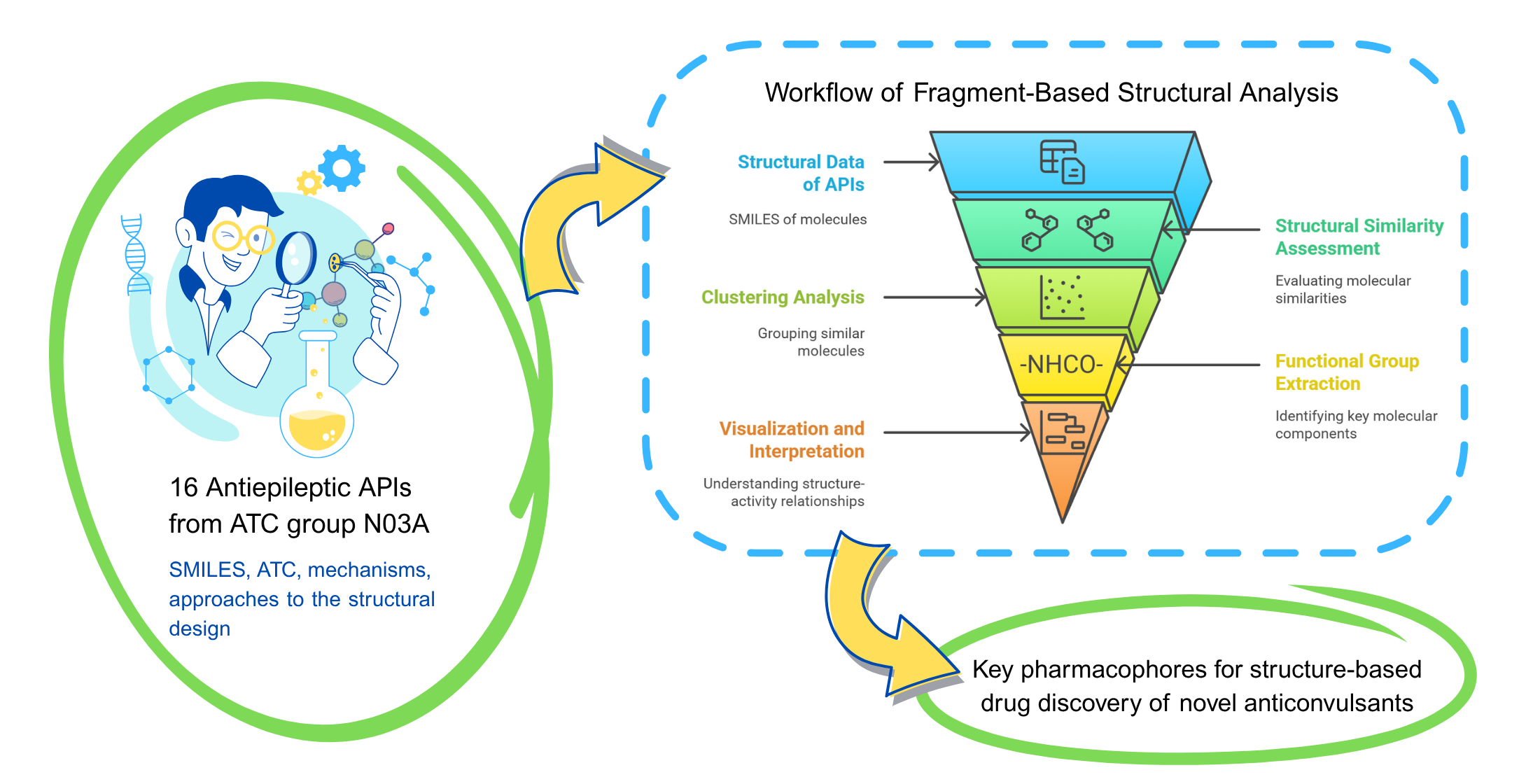
The aim of the study. To analyze 16 antiepileptic APIs registered in Ukraine using fragment-based methods to identify shared pharmacophoric features, structural similarities, and correlations between structural fragments and ADME properties (including drug-likeness patterns for structure-property insights) as a basis for rational anticonvulsant design.
Materials and methods. Data were collected from the State Register of Medicinal Products of Ukraine and Compendium (June 2025) using ATC code N03A. Literature review used PubMed, PubChem, DrugBank, Scopus, Elicit, and ResearchRabbit. Structural analysis was performed using Python libraries.
Results. The study classified 16 active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) into structural clusters (e.g., barbiturates, dibenzazepines, amino acid derivatives) based on Tanimoto similarity coefficients and ECFP4 molecular fingerprints. Commonly identified fragments included carbonyl, amino, amide, carboxyl groups, and aromatic rings. ADME profiling revealed consistent relationships between structural features and physicochemical properties: high lipophilicity in benzodiazepines and good absorption characteristics in gabapentinoids. This analysis was performed to identify structure-dependent ADME patterns, providing a basis for fragment-based design of novel anticonvulsants.
Conclusions. Despite chemical diversity, the analyzed APIs exhibit shared spatial pharmacophore arrangements with recurring groups supporting activity at NaV, CaV, GABA-A, SV2A, and GABA-T. ADME profiling and structure–property correlations provide a basis for pharmacophore fragment modelling and CNS-oriented fragment-library design to enable rational discovery. Future design should leverage the identified pharmacophoric fragments to build multitarget molecules within a CNS ADME window
Supporting Agency
- The study was carried out within the framework of the research project “ Search for novel potential anticonvulsant agents for the treatment of post-traumatic epilepsy in military personnel and the civilian population”, funded by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine (Project registration number: 0125U001794).
References
- Epilepsy (2024). World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
- Sinha, S., Dubey, M., Misal, S., Alavala, R. R., C. S., R.; Rao G., S. K., Alavala, R. R. (Eds.) (2025). Computational Analyses of the Mechanism of Action of Antiepileptic Agents. Applications of Computational Tools in Drug Design and Development. Singapore: Springer, 885–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-4154-3_24
- Wu, Z., Chen, S., Wang, Y., Li, F., Xu, H., Li, M. et al. (2024). Current perspectives and trend of computer-aided drug design: a review and bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Surgery, 110 (6), 3848–3878. https://doi.org/10.1097/js9.0000000000001289
- Karaküçük-İyidoğan, A., Başaran, E., Tatar-Yılmaz, G., Oruç-Emre, E. E. (2024). Development of new chiral 1,2,4-triazole-3-thiones and 1,3,4-thiadiazoles with promising in vivo anticonvulsant activity targeting GABAergic system and voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs). Bioorganic Chemistry, 151, 107662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107662
- State Register of Medicinal Products of Ukraine. Available at: http://www.drlz.com.ua
- Compendium. Available at: https://compendium.com.ua
- Tsyvunin, V., Shtrygol’, S., Havrylov, I., Shtrygol’, D. (2021). Low-dose digoxin enhances the anticonvulsive potential of carbamazepine and lamotrigine in chemo-induced seizures with different neurochemical mechanisms. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 6 (34), 58–65. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2021.249375
- Tsyvunin, V., Shtrygol’, S., Prokopenko, Y., Georgiyants, V., Blyznyuk, N. (2016). Influence of dry herbal extracts on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in mice: screening results and relationship “chemical composition – pharmacological effect.” ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (1), 18–28. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2016.71518
- Tsyvunin, V., Shtrygol’, S., Havrylov, I., Shtrygol’, D., Reus, A. (2022). SGLT-2 inhibitors as potential anticonvulsants: empagliflozin, but not dapagliflozin, renders a pronounced effect and potentiates the sodium valproate activity in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 5 (39), 83–90. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.266065
- Kamiński, K., Zagaja, M., Łuszczki, J. J., Rapacz, A., Andres-Mach, M., Latacz, G., Kieć-Kononowicz, K. (2015). Design, Synthesis, and Anticonvulsant Activity of New Hybrid Compounds Derived from 2-(2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)propanamides and 2-(2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamides. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 58 (13), 5274–5286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00578
- Nath Pandeya, S. (2012). Semicarbazone – a versatile therapeutic pharmacophore for fragment based anticonvulsant drug design. Acta Pharmaceutica, 62 (3), 263–286. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10007-012-0030-1
- Krasowski, M. D., McMillin, G. A. (2014). Advances in anti-epileptic drug testing. Clinica Chimica Acta, 436, 224–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.06.002
- Serdaroğlu, G., Ortiz, J. V. (2016). Ab Initio Calculations on some Antiepileptic Drugs such as Phenytoin, Phenbarbital, Ethosuximide and Carbamazepine. Structural Chemistry, 28 (4), 957–964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-016-0898-3
- Ugale, V. G., Bari, S. B., Khadse, S. C., Reddy, P. N., Bonde, C. G., Chaudhari, P. J. (2020). Exploring Quinazolinones as Anticonvulsants by Molecular Fragmentation Approach: Structural Optimization, Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation Studies. ChemistrySelect, 5 (10), 2902–2912. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201904776
- Abram, M., Jakubiec, M., Kamiński, K. (2019). Chirality as an Important Factor for the Development of New Antiepileptic Drugs. ChemMedChem, 14 (20), 1744–1761. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201900367
- Kwan, P., Brodie, M. J. (2004). Phenobarbital for the Treatment of Epilepsy in the 21st Century: A Critical Review. Epilepsia, 45 (9), 1141–1149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.12704.x
- Cozanitis, D. A. (2004). One Hundred Years of Barbiturates and Their Saint. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 97 (12), 594–598. https://doi.org/10.1177/014107680409701214
- Bialer, M. (2012). How did phenobarbital’s chemical structure affect the development of subsequent antiepileptic drugs (AEDs)? Epilepsia, 53 (s8), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12024
- Murayama, N., Shimada, M., Yamazoe, Y., Sogawa, K., Nakayama, K., Fujii-Kuriyama, Y., Kato, R. (1996). Distinct Effects of Phenobarbital and Its N-Methylated Derivative on Liver Cytochrome P450 Induction. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 328 (1), 184–192. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1996.0159
- Bush, M. T., Sanders, E. (1967). Metabolic Fate of Drugs: Barbiturates and Closely Related Compounds. Annual Review of Pharmacology, 7 (1), 57–76. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.07.040167.000421
- SanMartin, R., Churruc, F. (2011). Drug Discovery in Epilepsy: A Synthetic Review. Novel Treatment of Epilepsy. https://doi.org/10.5772/24991
- Rowe, E. J., Weinswig, M. H. (1964). Synthesis of N-Substituted and N,N′-Disubstituted Benzyl Derivatives of 5,5-Disubstituted Barbiturates. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 53 (2), 226–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600530229
- Nims, R. W., Syi, J. L., Wink, D. A., Nelson, V. C., Thomas, P. E., Jones, C. R. et al. (1993). Hepatic cytochrome P450 2B-type induction by ethyl/phenyl-substituted congeners of phenobarbital in the rat. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 6 (2), 180–187. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx00032a007
- Vida, J. A., Hooker, M. L., Samour, C. M., Reinhard, J. F. (1973). Anticonvulsants. 4. Metharbital and phenobarbital derivatives. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 16 (12), 1378–1381. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00270a013
- Ernst, B., Clark, G., Grundmann, O. (2015). The Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Relationships of Barbiturates – From the Past to the Future. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 21 (25), 3681–3691. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612821666150331131009
- Ho, I. K., Harris, R. A. (1981). Mechanism of Action of Barbiturates. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 21 (1), 83–111. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000503
- Leeb-Lundberg, F., Olsen, R. W. (1982). Interactions of barbiturates of various pharmacological categories with benzodiazepine receptors. Molecular Pharmacology, 21 (2), 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-895x(25)14607-5
- Vieira, A. A., Gomes, N. M., Matheus, M. E., Fernandes, P. D., Figueroa-Villar, J. D. (2011). Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of 5-chloro-5-benzobarbiturates as new central nervous system depressants. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 22 (2), 364–371. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0103-50532011000200024
- Jursic, B. S., Neumann, D. M., Bowdy, K. L., Stevens, E. D. (2004). Simple, efficient, high yield syntheses of substituted and unsubstituted 5‐benzoylbarbituric acids, and their corresponding schiff base phenylhydrazones. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 41 (2), 233–246. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.5570410214
- Perekhoda, L. (2020). The application of PASS-computer program and molecular docking for the search of new anticonvulsants. Annals of Mechnikov’s Institute, 4, 55–60. Available at: https://journals.uran.ua/ami/article/view/208223
- Okujava, V. M., Chankvetadze, B. G., Rukhadze, M. D., Rogava, M. M., Tkesheliadze, N. B. (1991). Use of normal-phase microcolumn high-performance liquid chromatography for the study of hydrolytic stability, metabolic profiling and pharmacokinetics. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 9 (6), 465–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/0731-7085(91)80248-8
- Patocka, J., Wu, Q., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K. (2020). Phenytoin – An anti-seizure drug: Overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 142, 111393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Poupaert, J. H., Vandervorst, D., Guiot, P., Moustafa, M. M. M., Dumont, P. (1984). Structure-activity relationships of phenytoin-like anticonvulsant drugs. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 27 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00367a015
- Deodhar, M., Sable, P., Bhosale, A., Juvale, K., Dumbare, R., Sakpal, P. (2009). Synthesis and evaluation of phenytoin derivatives as anticonvulsant agents. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 33 (3), 367–373. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-0711-18
- Henderson, J. D., Dayton, P. G., Israili, Z. H., Mandell, L. (1981). A nonmetabolized analog of phenytoin. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 24 (7), 843–847. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00139a015
- Philip, A. E., Poupaert, J. H., Chevé, G., Muccioli, G., Lambert, D., McCurdy, C. R. (2007). Structure-activity relationship of phenytoinergic antiepileptic drugs related to ameltolide. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 16 (3), 130–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-007-9016-9
- Keppel Hesselink, J. M., Kopsky, D. J. (2017). Phenytoin: 80 years young, from epilepsy to breast cancer, a remarkable molecule with multiple modes of action. Journal of Neurology, 264 (8), 1617–1621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8391-5
- Pal, R., Singh, K., Khan, S. A., Chawla, P., Kumar, B., Akhtar, M. J. (2021). Reactive metabolites of the anticonvulsant drugs and approaches to minimize the adverse drug reaction. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 226, 113890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113890
- Loscher, W. (2002). Basic Pharmacology of Valproate. CNS Drugs, 16 (10), 669–694. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-200216100-00003
- Blaheta, R. A., Cinatl, J. (2002). Anti‐tumor mechanisms of valproate: A novel role for an old drug. Medicinal Research Reviews, 22 (5), 492–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.10017
- Landmark, C. J., Johannessen, S. I. (2008). Modifications of Antiepileptic Drugs for Improved Tolerability and Efficacy. Perspectives in Medicinal Chemistry, 2. https://doi.org/10.1177/1177391x0800200001
- Mishra, M. K., Kukal, S., Paul, P. R., Bora, S., Singh, A., Kukreti, S. et al. (2021). Insights into Structural Modifications of Valproic Acid and Their Pharmacological Profile. Molecules, 27 (1), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010104
- Acheampong, A. A. (1985). Quantitative structure-anticonvulsant activity studies of valproic acid analogues. [Doctoral dissertation, University of British Columbia]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.14288/1.0096534
- Palaty, J. (1995). Unsaturated analogues of valproic acid: Structure activity relationships and interaction with GABA metabolism. [Doctoral Dissertation; University of British Columbia]. Available at: https://open.library.ubc.ca/collections/ubctheses/831/items/1.0088895
- Shields, W. D., Pellock, J. M. (2011). Vigabatrin 35 years later – from mechanism of action to benefit-risk considerations. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 124, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2011.01606.x
- Zhao, L.-X., Park, J. G., Moon, Y.-S., Basnet, A., Choi, J., Kim, E. et al. (2004). Design, synthesis and anticonvulsive activity of analogs of γ-vinyl GABA. Il Farmaco, 59 (5), 381–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.farmac.2004.01.011
- Michael, K. B. (2022). Study of long-term visual function and plasma biomarkers in patients with epilepsy receiving Vigabatrin. [Doctoral Dissertation; University of Glasgow]. Available at: https://theses.gla.ac.uk/82953/
- Tong, X. (2007). The pharmacokinetics and neuropharmacological action of the new antiepileptic drugs vigabatrin and levetiracetam. [Doctoral Thesis; University of London]. Available at: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1445126/
- Guberman, A. (1996). Vigabatrin. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Journal Canadien Des Sciences Neurologiques, 23 (S2), S13–S17. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100020928
- Alrashood, S. T. (2016). Carbamazepine. Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology, 133–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.podrm.2015.11.001
- McLean, M. J., Schmutz, M., Wamil, A. W., Olpe, H. ‐R., Portet, C., Feldmann, K. F. (1994). Oxcarbazepine: Mechanisms of Action. Epilepsia, 35 (s3), S5–S9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1994.tb05949.x
- Almeida, L., Soares-da-Silva, P. (2007). Eslicarbazepine Acetate (BIA 2-093). Neurotherapeutics, 4 (1), 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2006.10.005
- Gerlach, A. C., Krajewski, J. L. (2010). Antiepileptic Drug Discovery and Development: What Have We Learned and Where Are We Going? Pharmaceuticals, 3 (9), 2884–2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3092884
- Das, N., Dhanawat, M., Shrivastava, S. K. (2012). An overview on antiepileptic drugs. Drug discoveries & therapeutics, 6 (4), 178–193. https://doi.org/10.5582/ddt.2012.v6.4.178
- Chung, S. S., Kelly, K., Schusse, C. (2011). New and Emerging Treatments for Epilepsy: Review of Clinical Studies of Lacosamide, Eslicarbazepine Acetate, Ezogabine, Rufinamide, Perampanel, and Electrical Stimulation Therapy. Journal of Epilepsy Research, 1 (2), 35–46. https://doi.org/10.14581/jer.11008
- Rocamora, R. (2015). A review of the efficacy and safety of eslicarbazepine acetate in the management of partial-onset seizures. Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders, 8 (4), 178–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756285615589711
- Arzimanoglou, A., Ben‐Menachem, E., Cramer, J., Glauser, T., Seeruthun, R., Harrison, M. (2010). The evolution of antiepileptic drug development and regulation. Epileptic Disorders, 12 (1), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2010.0303
- Macdonald, R. L. (1989). Antiepileptic Drug Actions. Epilepsia, 30 (s1), S19–S28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1989.tb05810.x
- Wilde, M., Auwärter, V., Moosmann, B. (2021). New psychoactive substances – Designer benzodiazepines. WIREs Forensic Science, 3 (6). https://doi.org/10.1002/wfs2.1416
- Batlle Rocafort, E. (2018). Benzodiazepines and derivatives. Overview, analysis and synthesis. Available at: https://core.ac.uk/outputs/158608492/?source=4
- Arora, N., Dhiman, P., Kumar, S., Singh, G., Monga, V. (2020). Recent advances in synthesis and medicinal chemistry of benzodiazepines. Bioorganic Chemistry, 97, 103668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103668
- Teli, S., Teli, P., Soni, S., Sahiba, N., Agarwal, S. (2023). Synthetic aspects of 1,4- and 1,5-benzodiazepines usingo-phenylenediamine: a study of past quinquennial. RSC Advances, 13 (6), 3694–3714. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra06045k
- Leppik, I. E. (2004). Zonisamide: chemistry, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetics. Seizure, 13, S5–S9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2004.04.016
- Shimizu, M., Uno, H., Ito, T., Masuda, Y., Kurokawa, M. (1996). Research and Development of Zonisamide, a New Type of Antiepileptic Drug. Yakugaku Zasshi, 116 (7), 533–547. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi1947.116.7_533
- Gidal, B. E., Resnick, T., Smith, M. C., Wheless, J. W. (2024). Zonisamide: A Comprehensive, Updated Review for the Clinician. Neurology. Neurology Clinical Practice, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1212/cpj.0000000000200210
- Travagin, F., Vladiskovic, C., Giovenzana, G. B., Mantegazza, S., & Razzetti, G. (2024). Improving Zonisamide Manufacturing: Insights into Stereochemistry and Mechanisms for Continuous Optimization. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 27 (41). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202400686
- Malik, S., Ahuja, P., Sahu, K., Khan, S. A. (2014). Design and synthesis of new of 3-(benzo[d]isoxazol-3-yl)-1-substituted pyrrolidine-2, 5-dione derivatives as anticonvulsants. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 84, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.07.016
- Aratikatla, E. K., Bhattacharya, A. K. (2019). A Short Review of Synthetic Routes for the Antiepileptic Drug (R)-Lacosamide. Organic Process Research & Development, 24 (1), 17–24. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00373
- Salomé, C., Salomé-Grosjean, E., Park, K. D., Morieux, P., Swendiman, R., DeMarco, E. et al. (2009). Synthesis and Anticonvulsant Activities of (R)-N-(4′-Substituted)benzyl 2-Acetamido-3-methoxypropionamides. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 53 (3), 1288–1305. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm901563p
- Morieux, P., Salomé, C., Park, K. D., Stables, J. P., Kohn, H. (2010). The Structure-Activity Relationship of the 3-Oxy Site in the Anticonvulsant (R)-N-Benzyl 2-Acetamido-3-methoxypropionamide. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 53 (15), 5716–5726. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm100508m
- Morieux, P. P. (2010). A chemical biology approach to discover the biological targets of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide. [Doctoral dissertation, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill]. https://doi.org/10.17615/h062-c988
- Zhan, K., Liu, Y., Chen, Q., Zhuang, C., Zheng, R. (2024). Advances in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid derivatives. Sheng wu gong cheng xue bao = Chinese journal of biotechnology, 40 (9), 2831–2845. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.240032
- Papagiouvannis, G., Theodosis-Nobelos, P., Tziona, P., Gavalas, A., Kourounakis, P. N., Rekka, E. A. (2022). Gabapentin antioxidant derivatives with anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective potency. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 19 (7), 579–590. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570180818666211210161922
- Shi, W., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Zhong, B., Yang, H. (2005). Design, Synthesis, and Preliminary Evaluation of Gabapentin‐Pregabalin Mutual Prodrugs in Relieving Neuropathic Pain. Archiv Der Pharmazie, 338 (8), 358–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.200400958
- Barenie, R., Darrow, J., Avorn, J., Kesselheim, A. S. (2021). Discovery and Development of Pregabalin (Lyrica). Neurology, 97 (17). https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000012730
- Kavoussi, R. (2006). Pregabalin: From molecule to medicine. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 16, S128–S133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2006.04.005
- Bryans, J. S., Wustrow, D. J. (1999). 3-Substituted GABA analogs with central nervous system activity: A review. Medicinal Research Reviews, 19 (2), 149–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1128(199903)19:2<149::aid-med3>3.0.co;2-b
- Belliotti, T. R., Capiris, T., Ekhato, I. V., Kinsora, J. J., Field, M. J., Heffner, T. G. et al. (2005). Structure-Activity Relationships of Pregabalin and Analogues That Target the α2-δ Protein. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 48 (7), 2294–2307. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049762l
- Fijałkowski, Ł., Sałat, K., Podkowa, A., Zaręba, P., Nowaczyk, A. (2017). Potential role of selected antiepileptics used in neuropathic pain as human GABA transporter isoform 1 (GAT1) inhibitors – Molecular docking and pharmacodynamic studies. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 96, 362–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2016.10.004
- Yuen, P. W. (2007). α2δ Ligands: Neurontin®(Gabapentin) and Lyrica®(Pregabalin). The Art of Drug Synthesis, 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470134979.ch16
- Taylor, C. P., Angelotti, T., Fauman, E. (2007). Pharmacology and mechanism of action of pregabalin: The calcium channel α2–δ (alpha2–delta) subunit as a target for antiepileptic drug discovery. Epilepsy Research, 73 (2), 137–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.09.008
- Howard, P., Remi, J., Remi, C., Charlesworth, S., Whalley, H., Bhatia, R. et al. (2018). Levetiracetam. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 56 (4), 645–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.07.012
- Klitgaard, H., Verdru, P. (2007). Levetiracetam: the first SV2A ligand for the treatment of epilepsy. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2 (11), 1537–1545. https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.2.11.1537
- Kenda, B. M., Matagne, A. C., Talaga, P. E., Pasau, P. M., Differding, E., Lallemand, B. I. et al. (2003). Discovery of 4-Substituted Pyrrolidone Butanamides as New Agents with Significant Antiepileptic Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 47 (3), 530–549. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm030913e
- Contreras-García, I. J., Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N., Romo-Mancillas, A., Bandala, C., Zamudio, S. R., Gómez-Manzo, S. et al. (2022). Levetiracetam Mechanisms of Action: From Molecules to Systems. Pharmaceuticals, 15 (4), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040475
- Matagne, A., Margineanu, D., Kenda, B., Michel, P., Klitgaard, H. (2008). Anti‐convulsive and anti‐epileptic properties of brivaracetam (ucb 34714), a high‐affinity ligand for the synaptic vesicle protein, SV2A. British Journal of Pharmacology, 154 (8), 1662–1671. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.198
- Sills, G. J., Rogawski, M. A. (2020). Mechanisms of action of currently used antiseizure drugs. Neuropharmacology, 168, 107966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.107966
- Makki, M., Bakhotmah, D. A., Abdel-Rahman, R. M., Aqlan, F. M. (2018). New Route to Synthesize Fluorine Substituted Lamotrigine Drug Analogues as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent. Current Organic Synthesis, 15 (1), 116–125. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570179414666170509151123
- Alkorta, I., Elguero, J., Font, A., Galcera, J., Mata, I., Molins, E., Virgili, A. (2014). An experimental and theoretical study of the structure of Lamotrigine in its neutral and protonated forms: evidence of Lamotrigine enantiomers. Tetrahedron, 70 (17), 2784–2795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2014.02.075
- Saralaya, S. S., Hiriyalau, S. S. (2024). An overview of prior art disclosures about the synthesis of lamotrigine and a glimpse of its closely related compounds. Indian Journal of Pharmacy & Drug Studies, 3 (1), 8–15. Available at: https://mansapublishers.com/index.php/ijpds/article/view/4503
- Pearl, N. Z., Babin, C. P., Catalano, N. T., Blake, J. C., Ahmadzadeh, S., Shekoohi, S., Kaye, A. D. (2023). Narrative Review of Topiramate: Clinical Uses and Pharmacological Considerations. Advances in Therapy, 40 (9), 3626–3638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-023-02586-y
- Casini, A., Antel, J., Abbate, F., Scozzafava, A., David, S., Waldeck, H., Schäfer, S., Supuran, C. T. (2003). Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: SAR and X-ray crystallographic study for the interaction of sugar sulfamates/sulfamides with isozymes I, II and IV. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 13 (5), 841–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-894x(03)00029-5
- Maryanoff, B. (2009). Sugar Sulfamates for Seizure Control: Discovery and Development of Topiramate, a Structurally Unique Antiepileptic Drug. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 9 (11), 1049–1062. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802609789630938
- Maryanoff, B. E., McComsey, D. F., Costanzo, M. J., Hochman, C., Smith-Swintosky, V., Shank, R. P. (2004). Comparison of Sulfamate and Sulfamide Groups for the Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase-II by Using Topiramate as a Structural Platform. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 48 (6), 1941–1947. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm040124c
- Moore, G. (2017). The design and synthesis of novel APIs based upon topiramate. [Doctoral Dissertation: Newcastle University]. Available at: https://theses.ncl.ac.uk/jspui/handle/10443/3828
- Ghiasi, M., Kamalinahad, S., Arabieh, M., Zahedi, M. (2012). Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A quantum mechanical study of interaction between some antiepileptic drugs with active center of carbonic anhydrase enzyme. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 992, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2012.05.005
- Saeidian, H., Abdoli, M. (2015). The first general protocol forN-monoalkylation of sulfamate esters: benign synthesis ofN-alkyl Topiramate (anticonvulsant drug) derivatives. Journal of Sulfur Chemistry, 36 (5), 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415993.2015.1069294
- El Kayal, W., Severina, H., Tsyvunin, V., Zalevskyi, S., Shtrygol’, S., Vlasov, S. et al. (2022). Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity evaluation of n-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-2-(2,4-dioxo-1h-quinazolin-3-yl)acetamide novel 1-benzylsubstituted derivatives. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (35), 58–69. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.253554
- Kushniruk, V. M., Kovalevska, I. V., Ruban, O. A., Harna, N. V., Georgiyants, V. A. (2016). (2016). Technology scaling for obtaining N,N –dibenzyl amide of malonic acid – a potential anticonvulsant – in industrial environments. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (4), 30–35. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2016.87441
- Kavraiskyi, D. P., Shtrygol, S. Yu., Georgiyants, V. A., Severina, H. I. (2016). Experimental study of new pyrazolo[3,4-D]pyrimidine-4-one derivatives for anticonvulsant activity spectrum. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (1), 10–17. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2016.70528
- Davydov, E., Hoidyk, M., Shtrygol’, S., Karkhut, A., Polovkovych, S., Klyuchivska, O. et al. (2024). Evaluation of thiopyrano[2,3‐d]thiazole derivatives as potential anticonvulsant agents. Archiv Der Pharmazie, 357 (10). https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.202400357
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maryna Stasevych, Mykhailo Hoidyk, Olexandra Roman, Roksolana Konechna, Andriy Karkhut, Andrii Lozynskyi, Sviatoslav Polovkovych, Roman Lesyk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






