Вивчення впливу складових на біофармацевтичні фактори та фармакологічну активність лікарського засобу з екстрактом моркви посівної та рутином
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.277562Ключові слова:
густий екстракт коренеплодів моркви, рутин, технологія, аналіз, проктологічні захворюванняАнотація
Мета. Метою роботи стало вивчення впливу складових м’якого ректального лікарського засобу з екстрактом коренеплодів моркви посівної та рутину на біофармацевтичні показники та його фармакологічну активність.
Матеріали і методи. Об'єктами дослідження були зразки м’якої лікарської форми, виготовлені на різних основах. При дослідженні використовувалися фармакологічні, біофармацевтичні, фізико-хімічні та фармакотехнологічні методи дослідження.
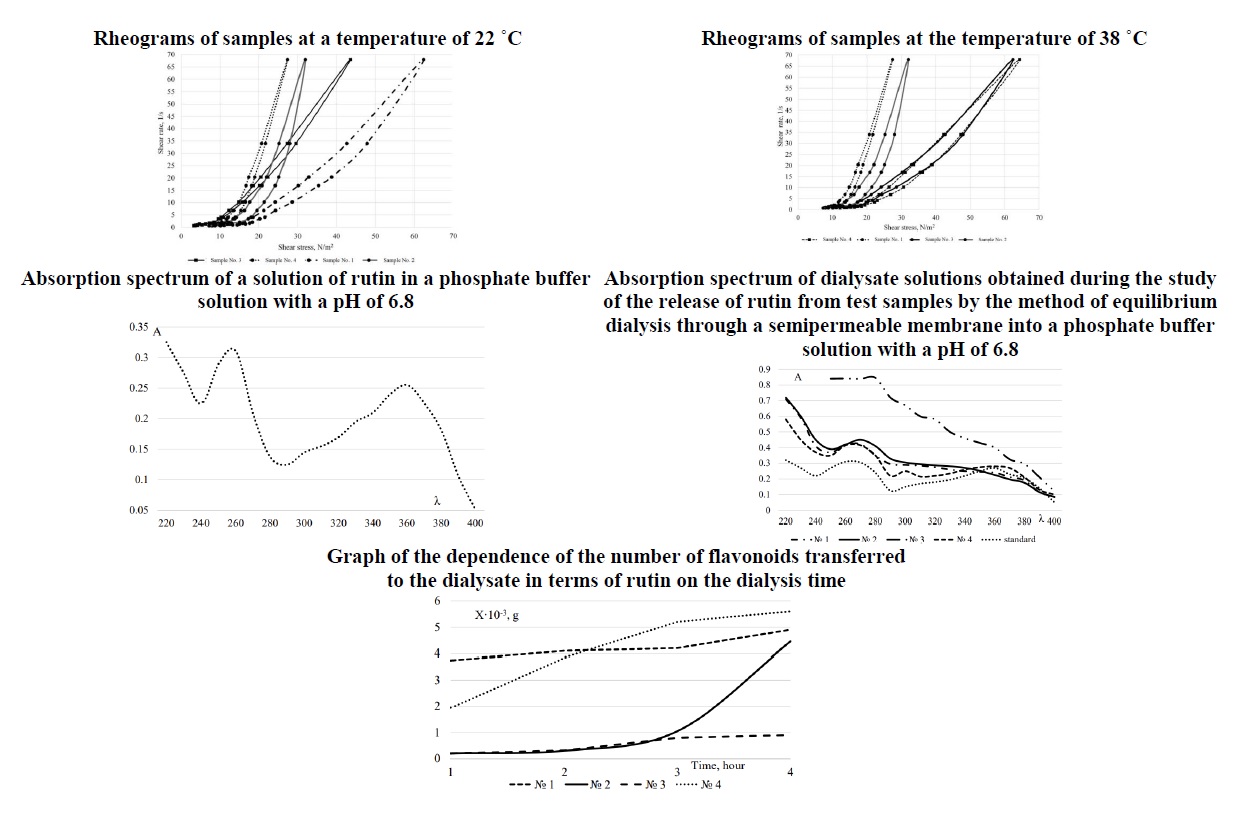
Результати. За даними органолептичних досліджень, визначення колоїдної стабільності, визначення рН було встановлено, що досліджувані зразки були стабільні протягом всього терміну спостереження. За даними реологічних досліджень було встановлено, що всі системи є тиксотропними, але час відновлення системи є різним, що пов’язано з фізико-хімічними властивостями допоміжних речовин, що входять до складу зразків. Проведений спектральний аналіз розчинів діалізатів експериментальних зразків м’якого лікарського засобу свідчить про можливість кількісного визначення вмісту суми флавоноїдів у діалізатах у перерахунку на рутин. Компоненти основи зразків та густого екстракту коренеплодів моркви не заважають визначенню рутину в діалізатах з рН 6,8 методом абсорбційної спектрофотометрії при довжині хвилі 352 нм. Аналіз отриманих результатів дослідження вивільнення рутину із зразків у фосфатний буферний розчин шляхом діалізу крізь напівпроникну мембрану показує, що найбільш повне вивільнення забезпечують допоміжні речовини, використані при виготовленні зразку № 4, що являє собою емульсію першого роду. Отримані дані фармакологічних досліджень щодо динаміки планіметричних показників на моделі трафаретних ран у щурів продемонстрували наявність ранозагоювальної дії в усіх досліджуваних зразків та референтному засобі-супозиторіях «Гемороль». Однак, застосування зразку №4 при лікуванні трафаретної рани сприяє більш швидкому перебігу загоєння, що при клінічному застосуванні може сприяти зменшенню ризику інфікування, розповсюдженню інфекції та скороченню площі ранового дефекту.
Висновки. За результатами комплексу досліджень встановлено помірні переваги зразку № 4 перед препаратом порівняння та іншими зразками, що обумовлює перспективу його подальших досліджень
Посилання
- Indrayan, A., Malhotra, K. R. (2018). Medical biostatistics. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 685.
- Tol, R. R., Kleijnen, J., Watson, A. J. M., Jongen, J., Altomare, D. F., Qvist, N., Higuero, T., Muris, J. W. M., Breukink, S. O., Henquet, C. J. M. (2020). European Society of ColoProctology: guideline for haemorrhoidal disease. Colorectal Disease, 22 (6), 650–662. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.14975
- Lohsiriwat, V. (2015). Treatment of hemorrhoids: A coloproctologist’s view. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 21 (31), 9245–9252. doi: https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9245
- Zaychenko, V. S., Ruban, О. А., Khanin, V. A., Kyslychenko, V. S., Masliy, Ju. S. (2018). Development of meloxicam and indole-3-carbinol quantification method in rectal suppositories for prevention and treatment of benign diseases of the prostate gland. International Journal of Green Pharmacy, 12 (2), 129–135.
- Velia, M., Ruban, O., Khalavka, M., Hohlova, L. (2021). Research of the choice of the basis of a semi-solid medicine with a semi-solid extract of Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium). ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (29), 51–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2021.225764
- Borko, Y., Inna, K., Grudko, V., Kononenko, N., Velya, M. (2022). Comprehensive study for the development of rectal suppositories with diosmin and hesperidin. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (35), 14–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.253518
- Pata, F., Gallo, G., Pellino, G., Vigorita, V., Podda, M., Di Saverio, S. et al. (2021). Evolution of Surgical Management of Hemorrhoidal Disease: An Historical Overview. Frontiers in Surgery, 8. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2021.727059
- Sheikh, P., Lohsiriwat, V., Shelygin, Y. (2020). Micronized Purified Flavonoid Fraction in Hemorrhoid Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Advances in Therapy, 37 (6), 2792–2812. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01353-7
- Ahmadi, Z., Mohammadinejad, R., Roomiani, S., Afshar, E. G., Ashrafizadeh, M. (2021). Biological and Therapeutic Effects of Troxerutin: Molecular Signaling Pathways Come into View. Journal of Pharmacopuncture, 24 (1), 1–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.3831/kpi.2021.24.1.1
- Godeberge, P., Sheikh, P., Lohsiriwat, V., Jalife, A., Shelygin, Y. (2021). Micronized purified flavonoid fraction in the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research, 10 (10), 801–813. doi: https://doi.org/10.2217/cer-2021-0038
- Ju, L., Ke, F., Yadav, P. (2012). Herbal medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology, 18 (1), 3–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-3767.91726
- Falzon, C. C., Balabanova, A. (2017). Phytotherapy: An Introduction to Herbal Medicine. Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice, 44 (2), 217–227. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2017.02.001
- Stadnytska, N. Ye., Pavliuk, I. V., Dumych, I. I., Blonskyi, O. V. (2014). Doslidzhennia perspektyvnosti vykorystannia plodiv morkvy dykoi yak dzherela novykh kompleksiv biolohichno aktyvnykh rechovyn. Visnyk Natsionalnoho universytetu "Lvivska politekhnika". Khimiia, tekhnolohiia rechovyn ta yikh zastosuvannia, 787, 243–248.
- Pazyuk, D.-M. V., Zhuravel, I. A., Kyslychenko, A. A., Burda, N. Ye., Korniyenko, S. I., Mogilnaya, E. N. (2017). HPLC determination of phenolic acids in the underground part of carrots of “Nantska Kharkivska” and “Yaskrava” varieties. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 8 (2), 1833–1836.
- Ayeni, E. A., Abubakar, A., Ibrahim, G., Atinga, V., Muhammad, Z. (2018). Phytochemical, nutraceutical and antioxidant studies of the aerial parts of Daucus carota L.(Apiaceae). Journal of Herbmed Pharmacology, 7 (2), 68–73. doi: https://doi.org/10.15171/jhp.2018.12
- Sheila, J., Priyadarshini, S., Sarah, J. M., Arumugam, P. (2017). Phytochemical profile and thin layer chromatographic studies of Daucus carota peel extracts. International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition, 2 (1), 23–26.
- Shebaby, W. N., Daher, C. F., El-Sibai, M., Bodman-Smith, K., Mansour, A., Karam, M. C., Mroueh, M. (2015). Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of the oil fractions from wild carrot (Daucus carotassp.carota). Pharmaceutical Biology, 53 (9), 1285–1294. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.976349
- Yarnykh, T. G., Ivaniuk, O. I., Kovalevska, I. V., Kukhtenko, H. P., Kutsenko, S. A. (2018). Rheology-based substantiation of a gel-former choice for vaginal gel. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Researc, 1 (11), 2825–2828.
- State Pharmacopoeia of Ukraine. Vol. 1 (2015). Kharkiv: RIREG, State Enterprise "Scientific Expert Pharmacopoeia Center", 1135.
- Maslii, Y., Ruban, O., Kasparaviciene, G., Kalveniene, Z., Materiienko, A., Ivanauskas, L. et al. (2020). The Influence of pH Values on the Rheological, Textural and Release Properties of Carbomer Polacril® 40P-Based Dental Gel Formulation with Plant-Derived and Synthetic Active Components. Molecules, 25 (21), 5018. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215018
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes (2010). OJEU, L276, 33–79.
- Kovalenka, V. M. (Ed.) (2019). Compendium 2019 – medicinal products. Kyiv: MORION, 2480.
- Kyslychenko O. A., Protska V. V., Zhuravel I. O., Hutsol V. V. (2018). The study of Daucus carota subsp. sativus fruits fatty acid composition of «Olenka», «Kharkivska Nantska» and «Yaskrava» varieties. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 9 (6), 307–312.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Olena Ruban, Mohammad Al Sayasneh, Inna Kovalevska , Volodymir Grudko , Dmytro Lytkin, Oksana Dunaіevska

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Наше видання використовує положення про авторські права Creative Commons CC BY для журналів відкритого доступу.







