Synthesis and evaluation of zinc–quercetin complex: in vitro anti-glycation and DNA methylation analysis with molecular docking studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2025.333614Keywords:
zinc-quercetin complex, type 2 diabetes, glycation, DNA methylationAbstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a growing global health concern, associated with complications driven by molecular alterations such as excessive protein glycation and abnormal DNA methylation. These processes contribute to the progression of metabolic and epigenetic dysfunctions characteristic of T2DM.
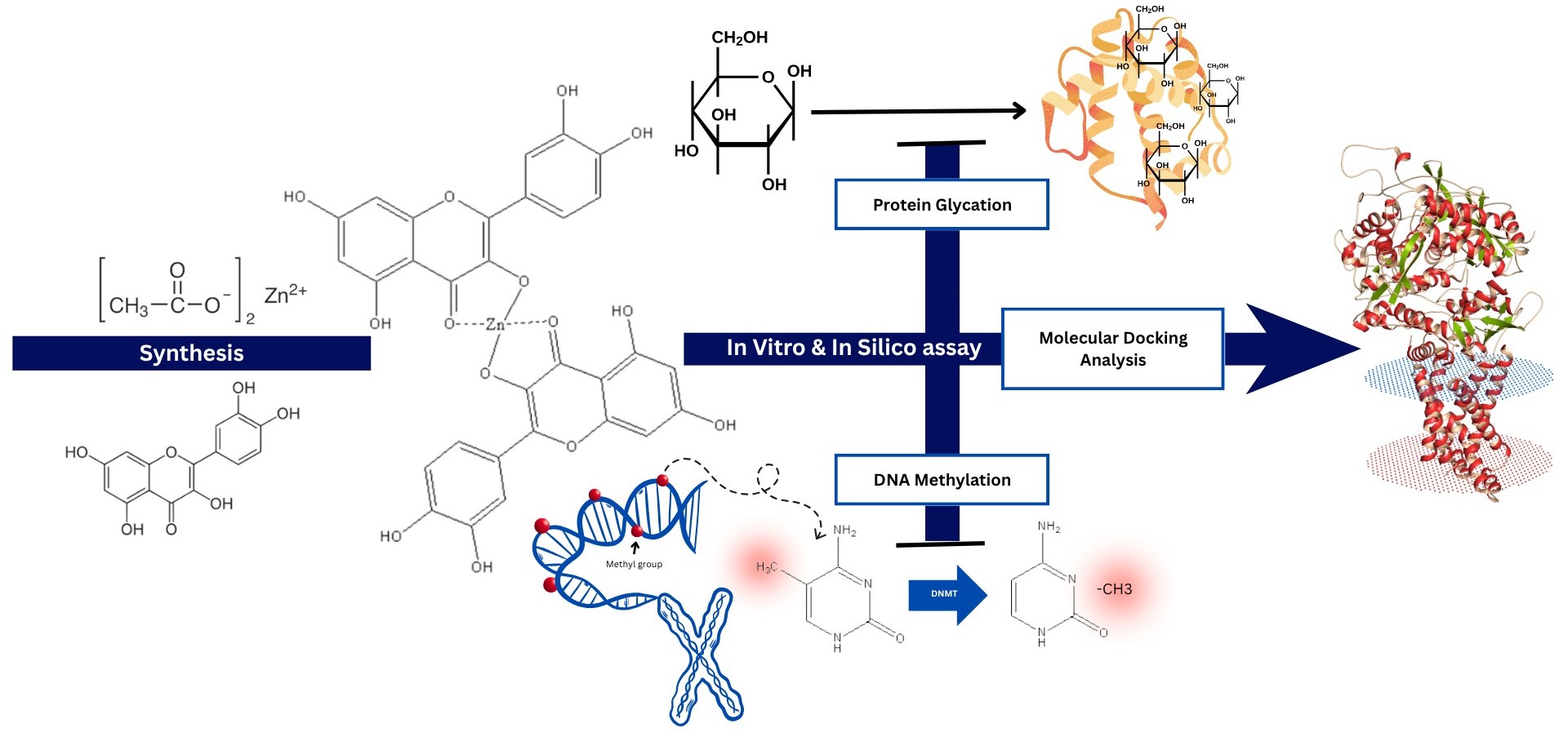
The aim. This study aimed to synthesize a zinc–quercetin complex (ZQC) and evaluate its in vitro biological activities, particularly its potential to inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and modulate DNA methylation levels.
Materials and methods. ZQC was synthesized and tested for antiglycation activity using BSA–methylglyoxal and BSA–glucose model systems. DNA methylation levels were assessed via cell imaging in HEK293T and C2C12 cells using an oxazole yellow-based fluorescent probe. Molecular docking was performed to assess the interaction of ZQC with DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1).
Results. ZQC exhibited dose-dependent antiglycation effects, with significantly reduced fluorescence intensity compared to untreated and quercetin-treated groups, suggesting potent inhibition of AGE formation. In DNA methylation assays, ZQC more effectively reduced methylation levels than free quercetin. Molecular docking showed a stronger binding affinity of ZQC (–11 kcal/mol) to DNMT1 compared to quercetin alone (–8.1 kcal/mol), indicating the potential for enhanced inhibitory activity.
Conclusion. The zinc–quercetin complex demonstrated superior antiglycation and epigenetic-modulating effects relative to free quercetin. These findings support the potential of ZQC as a candidate for therapeutic intervention in glycation-associated and epigenetically driven complications of T2DM
Supporting Agency
- This study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DOST)-Science Education Institute (SEI) Accelerated Science and Technology Human Resource Development Program (DOST-ASTHRDP).
References
- Tomic, D., Shaw, J. E., Magliano, D. J. (2022). The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 18 (9), 525–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-022-00690-7
- Kuzan, A. (2021). Toxicity of advanced glycation end products (Review). Biomedical Reports, 14 (5). https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2021.1422
- Natarajan, R. (2021). Epigenetic Mechanisms in Diabetic Vascular Complications and Metabolic Memory: The 2020 Edwin Bierman Award Lecture. Diabetes, 70 (2), 328–337. https://doi.org/10.2337/dbi20-0030
- Raciti, G. A., Desiderio, A., Longo, M., Leone, A., Zatterale, F., Prevenzano, I. et al. (2021). DNA Methylation and Type 2 Diabetes: Novel Biomarkers for Risk Assessment? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (21), 11652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111652
- Khalid, M., Petroianu, G., Adem, A. (2022). Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules, 12 (4), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040542
- Kuo, F.-C., Chao, C.-T., Lin, S.-H. (2022). The Dynamics and Plasticity of Epigenetics in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Therapeutic Applications Vis-à-Vis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (2), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020843
- Carrillo-Martinez, E. J., Flores-Hernández, F. Y., Salazar-Montes, A. M., Nario-Chaidez, H. F., Hernández-Ortega, L. D. (2024). Quercetin, a Flavonoid with Great Pharmacological Capacity. Molecules, 29 (5), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29051000
- Matías-Pérez, D., Antonio-Estrada, C., Guerra-Martínez, A., García-Melo, K. S., Hernández-Bautista, E., García-Montalvo, I. A. (2024). Relationship of quercetin intake and oxidative stress in persistent COVID. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2023.1278039
- Aghababaei, F., Hadidi, M. (2023). Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals, 16 (7), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020
- Pavun, L., Janošević-Ležaić, A., Tanasković, S., Ušjak, D., Milenković, M., Uskokovic-Markovic, S. (2021). Antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial effects of zinc complexes of flavonoids – Does synergism exist? Macedonian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 40 (2), 231–239. https://doi.org/10.20450/mjcce.2021.2401
- Elumalai, S., Soundararajan, S., Kanagaraj, P., Sadhasivam, D. R. (2022). In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Quercetin isolated from Indigofera aspalathoides and Quercetin-Zinc metal complex. International Journal of Health Sciences, 4314–4326. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6ns3.6859
- da Silva, W. M. B., de Oliveira Pinheiro, S., Alves, D. R., de Menezes, J. E. S. A., Magalhães, F. E. A., Silva, F. C. O. et al. (2019). Synthesis of Quercetin-Metal Complexes, In Vitro and In Silico Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Evaluation, and In Vivo Toxicological and Anxiolitic Activities. Neurotoxicity Research, 37 (4), 893–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00142-7
- Wangsawangrung, N., Choipang, C., Chaiarwut, S., Ekabutr, P., Suwantong, O., Chuysinuan, P. et al. (2022). Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Gels, 8 (9), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8090573
- Hori, Y., Otomura, N., Nishida, A., Nishiura, M., Umeno, M., Suetake, I., Kikuchi, K. (2018). Synthetic-Molecule/Protein Hybrid Probe with Fluorogenic Switch for Live-Cell Imaging of DNA Methylation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140 (5), 1686–1690. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b09713
- Zhang, M., Lu, A., Wang, H., Yang, J. (2023). Quercetin downregulates the expression of IL15 in cancer cells through DNA methylation. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 27 (6), 2580–2590. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202303_31795
- Baksi, R., Rana, R., Nivsarkar, M. (2021). Chemopreventive potential of plant-derived epigenetic inhibitors silibinin and quercetin: an involvement of apoptotic signaling cascade modulation. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00214-6
- Prestianni, L., Espinal, E. R., Hathcock, S. F., Vollmuth, N., Wang, P., Holler, R. A. et al. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Quercetin–Iron Complex Nanoparticles for Overcoming Drug Resistance. Pharmaceutics, 15 (4), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041041
- Chen, Z., Świsłocka, R., Choińska, R., Marszałek, K., Dąbrowska, A., Lewandowski, W., Lewandowska, H. (2024). Exploring the Correlation Between the Molecular Structure and Biological Activities of Metal–Phenolic Compound Complexes: Research and Description of the Role of Metal Ions in Improving the Antioxidant Activities of Phenolic Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25 (21), 11775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111775
- Primikyri, A., Mazzone, G., Lekka, C., Tzakos, A. G., Russo, N., & Gerothanassis, I. P. (2014). Understanding Zinc(II) Chelation with Quercetin and Luteolin: A Combined NMR and Theoretical Study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 119 (1), 83–95. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp509752s
- Kalinowska, M., Lewandowska, H., Pruszyński, M., Świderski, G., Gołębiewska, E., Gryko, K. et al. (2021). Co(II) Complex of Quercetin–Spectral, Anti-/Pro-Oxidant and Cytotoxic Activity in HaCaT Cell Lines. Applied Sciences, 11 (19), 9244. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199244
- Muhammad, D. S., Aziz, D. M., Aziz, S. B. (2024). Zinc metal complexes synthesized by a green method as a new approach to alter the structural and optical characteristics of PVA: new field for polymer composite fabrication with controlled optical band gap. RSC Advances, 14 (36), 26362–26387. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra04228j
- Oso, B. J., Olaoye, I., Oso, O. T. (2023). Experimental and hypothetical appraisal on inhibition of glucose-induced glycation of bovine serum albumin by quercetin. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 21 (1), 123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-023-00588-5
- Ronsisvalle, S., Panarello, F., Longhitano, G., Siciliano, E. A., Montenegro, L., Panico, A. (2020). Natural Flavones and Flavonols: Relationships among Antioxidant Activity, Glycation, and Metalloproteinase Inhibition. Cosmetics, 7 (3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7030071
- Lund, M. N., Ray, C. A. (2017). Control of Maillard Reactions in Foods: Strategies and Chemical Mechanisms. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65 (23), 4537–4552. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00882
- Jan, Z., Ahmed, W. S., Biswas, K. H., Jithesh, P. V. (2023). Identification of a potential DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitor. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 42 (9), 4730–4744. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2023.2233637
- Kritsi, E., Christodoulou, P., Tsiaka, T., Georgiadis, P., Zervou, M. (2024). A Computational Approach for the Discovery of Novel DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46 (4), 3394–3407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46040213
- Horton, J. R., Pathuri, S., Wong, K., Ren, R., Rueda, L., Fosbenner, D. T. et al. (2022). Structural characterization of dicyanopyridine containing DNMT1-selective, non-nucleoside inhibitors. Structure, 30 (6), 793-802.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2022.03.009
- Miletić, V., Odorčić, I., Nikolić, P., Svedružić, Ž. M. (2017). In silico design of the first DNA-independent mechanism-based inhibitor of mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1. PLOS ONE, 12 (4), e0174410. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174410
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Orlie B. Basalo, Godzelle O. Bulahan, Charlie A. Lavilla Jr, Aaron L. Degamon, James V. Lavilla, Richemae Grace R. Lebosada, Hajime Iwamoto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






