Intensity of endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and apoptosis in the cerebral cortex of rats with chronic ethanol consumption under the influence of the complex compound of germanium with nicotinic acid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.295491Keywords:
apoptosis, autophagy, chronic alcohol consumption, coordination compound of germaniumAbstract
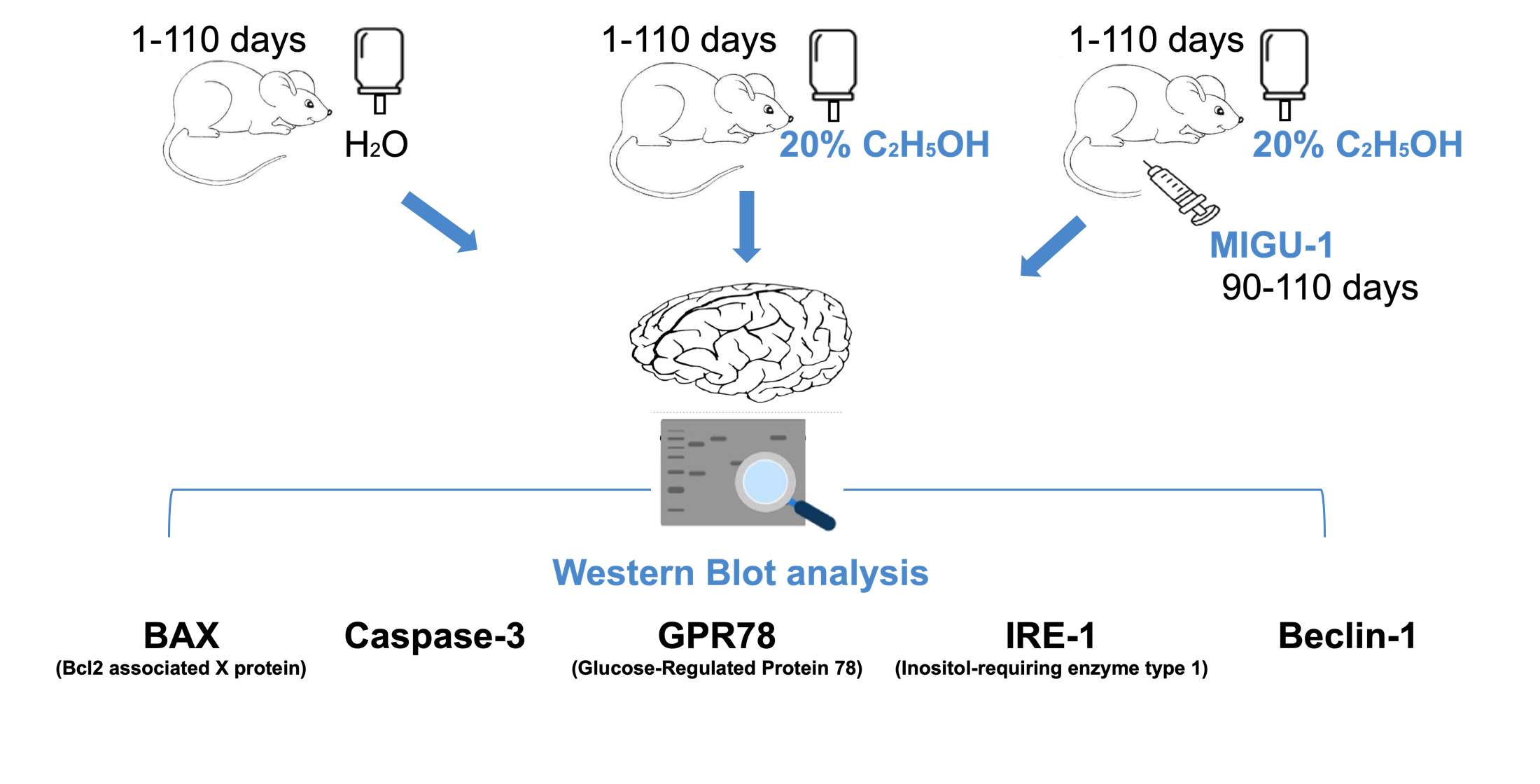
The aim of the research – to determine the level of BAX, caspase-3, GRP78, IRE1 and Beclin-1 in the cerebral cortex of rats with chronic ethanol consumption and under conditions of exposure to the germanium complex with nicotinic acid (MIGU-1).
Materials and methods. Female rats had free access to 20 % C2H5OH as the only source of fluid for 110 days. Starting from the 90th day, the animals were injected with MIGU-1 (10 mg/kg/day, IP). The expression level of BAX, caspase-3, GRP78, IRE1 and Beclin-1 in the tissue was determined by Western blot analysis.
Results. In rats with chronic ethanol consumption, the level of BAX-dimer increased by 2.06 times (p˂0.001). The introduction of MIGU-1 caused a decrease in the level of BAX-dimer by 1.42 times (p˂0.05). In rats with chronic ethanol consumption, the level of caspase-3 increased by 2.12 times (p˂0.05), cleaved caspase-3 increased by 6.37 times (p˂0.05). When MIGU-1 was administered, the level of caspase-3 decreased by 1.73 times (p˂0.05). Under the conditions of MIGU-1 administration, protein bands of cleaved caspase-3 were reduced to an undetectable level. In rats with chronic ethanol consumption, the level of GRP78 increased by 1.72 times (p˂0.05). After administration of MIGU-1, no changes in the level of GRP78 were recorded. Long-term ethanol consumption increased the levels of IRE1 by 1.74 times (p˂0.05) and p-IRE1 by 2.7 times (p˂0.001). In the presence of MIGU-1, the levels of IRE1 and p-IRE1 did not change. Under the conditions of chronic ethanol consumption, an increase in the levels of Beclin-1 by 2.33 times (p˂0.001) and p-Beclin-1 by 4.69 times (p˂0.001) was observed. Administration of MIGU-1 did not affect the level of Beclin-1, while the level of p-Beclin-1 decreased by 3.09 times (p˂0.001).
Conclusions. Long-term ethanol consumption triggers metabolic changes in the cerebral cortex, resulting in ER stress, UPR activation, autophagy, and apoptosis. Administration of MIGU-1 alleviates ER stress by selectively inhibiting specific branches of apoptosis through effects on Beclin-1 levels, suggesting an effect of MIGU-1 on neuronal survival under chronic ethanol consumption
References
- Nutt, D., Hayes, A., Fonville, L., Zafar, R., Palmer, E. O. C., Paterson, L., Lingford-Hughes, A. (2021). Alcohol and the Brain. Nutrients, 13 (11), 3938. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113938
- Galandra, C., Basso, G., Cappa, S., Canessa, N. (2017). The alcoholic brain: neural bases of impaired reward-based decision-making in alcohol use disorders. Neurological Sciences, 39 (3), 423–435. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-3205-1
- Waddell, J., McKenna, C. M., Tibor, K. (2023). Brain ethanol metabolism and mitochondria. Current Topics in Biochemical Research, 23, 1–13
- Cannady, R., Rinker, J. A., Nimitvilai, S., Woodward, J. J., Mulholland, P. J. (2018). Chronic Alcohol, Intrinsic Excitability, and Potassium Channels: Neuroadaptations and Drinking Behavior. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 311–343. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2017_90
- Hoyt, L. R., Randall, M. J., Ather, J. L., DePuccio, D. P., Landry, C. C., Qian, X. et al. (2017). Mitochondrial ROS induced by chronic ethanol exposure promote hyper-activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Redox Biology, 12, 883–896. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.020
- Xu, H., Liu, D., Chen, J., Li, H., Xu, M., Wen, W. et al. (2019). Effects of Chronic Voluntary Alcohol Drinking on Thiamine Concentrations, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Oxidative Stress in the Brain of Crossed High Alcohol Preferring Mice. Neurotoxicity Research, 36 (4), 777–787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00032-y
- Senft, D., Ronai, Z. A. (2015). UPR, autophagy, and mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 40 (3), 141–148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2015.01.002
- Hetz, C., Zhang, K., Kaufman, R. J. (2020). Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 21 (8), 421–438. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0250-z
- Shemonaieva, F. K., Kresiun, Y. V., Seifullina, I. Y. (2019). Comparative parameters of pharmacokinetics scheme distribution of coordination germanium compounds. Odeskyi medychnyi zhurnal, 4/5 (174/175), 10–14.
- Bukhtiarova, T. A., Bobkova, L. S., Lukianchuk, V. D., Seifullina, I. Y., Martsynk, O. E. (2019). Pharmacokinetic analysis of the distribution of a potential cerebroprotector «Cerebrogerm» from the central chamber to the peripheral on the model of craniocerebral trauma in rats. Farmakolohiia ta likarska toksykolohiia, 13 (3), 175–186.
- Nizhenkovska, I. V., Narokha, V. P., Kuznetsova, O. V., Briuzghina, T. S., Seifullina, I. Y., Martsynko, O. E., Chebanenko, O. A. (2015). Effects of nicotinic acid and complex of germanium with nicotinic acid (MIGU-1) on lipid fatty acid composition of cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes in rats with experimental chronic heart failure. Farmakolohiia ta likarska toksykolohiia, 1, 68–75.
- Narokha, V. P. (2016). The effect of the germanium complex with nicotinic acid on oxidative modification of cardiac and hepatic proteins in the experimental chronic intoxication with doxorubicin in rats. Klinicna Farmacia, 20 (4), 35–38. doi: https://doi.org/10.24959/cphj.16.1381
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes: EUR-Lex (2010). EU. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02010L0063-20190626
- Cunningham, C. L., Pina, M. M. (2015). Alcohol Preference Tests. Stolerman Price. Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 79–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-36172-2_32
- Narokha, V. (2016). The effect of different doses of coordination compounds of germanium with nicotinic acid on lipid peroxidation and comparative influence of coordination compounds of germanium with different bioligands on fatty acid spectrum of lipids of cardiomyocytes in. Ukrainian Scientific Medical Youth Journal, 2 (95), 86–91.
- Pillai-Kastoori, L., Schutz-Geschwender, A. R., Harford, J. A. (2020). A systematic approach to quantitative Western blot analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 593, 113608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113608
- Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227 (5259), 680–685. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
- Obeng, E. (2021). Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals – A review. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 81 (4), 1133–1143. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.228437
- Ibrahim, I. M., Abdelmalek, D. H., Elfiky, A. A. (2019). GRP78: A cell’s response to stress. Life Sciences, 226, 156–163. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022
- Lee, K.-W., Hong, H.-R., Lim, J.-S., Ko, K.-P., Lee, M.-G., Chi, S.-G. (2022). XAF1 drives apoptotic switch of endoplasmic reticulum stress response through destabilization of GRP78 and CHIP. Cell Death & Disease, 13 (7). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05112-0
- Adams, C. J., Kopp, M. C., Larburu, N., Nowak, P. R., Ali, M. M. U. (2019). Structure and Molecular Mechanism of ER Stress Signaling by the Unfolded Protein Response Signal Activator IRE1. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 6. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00011
- Siwecka, N., Rozpędek-Kamińska, W., Wawrzynkiewicz, A., Pytel, D., Diehl, J. A., Majsterek, I. (2021). The Structure, Activation and Signaling of IRE1 and Its Role in Determining Cell Fate. Biomedicines, 9 (2), 156. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020156
- Read, A., Schröder, M. (2021). The Unfolded Protein Response: An Overview. Biology, 10 (5), 384. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050384
- Fleming, A., Bourdenx, M., Fujimaki, M., Karabiyik, C., Krause, G. J., Lopez, A. et al. (2022). The different autophagy degradation pathways and neurodegeneration. Neuron, 110 (6), 935–966. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.017
- Li, C., Li, J., Xu, G., Sun, H. (2020). Influence of Chronic Ethanol Consumption on Apoptosis and Autophagy Following Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Male Mice. Scientific Reports, 10 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63213-2
- Nizhenkovska, I., Kuznetsova, O., Narokha, V. (2023). Scientific practice: modern and classical research methods. Effect of coordination compound of germanium with nicotinic acid on the expression of markers of nervous tissue damage in rats under conditions of chronic ethanol consumption. Boston: Collection of scientific papers «ΛΌГOΣ», 366–368.
- Kwon, H. S., Koh, S.-H. (2020). Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Translational Neurodegeneration, 9 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-020-00221-2
- Narokha, V., Nizhenkovskaya, I., Kuznetsova, O. (2014). Antioxidant effect of nicotinic acid on experimental doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure. Current Topics in Pharmacology, 18 (1-2), 105–111.
- Nizhenkovskaya, I., Narokha, V., Kuznetsova, O. (2018). Effects of nicotinic acid on protein oxidative modifications in experimental chronic heart failure. Farmacia, 66 (6), 959–962. doi: https://doi.org/10.31925/farmacia.2018.6.5
- Nizhenkovskaya, I., Narokha, V. (2016). Influence of coordination compound of germanium and nicotinic acid on the energy homeostasis of the heart and liver of rats in conditions of chronic intoxication with doxorubicin. Recipe, 19 (2), 174–181.
- Narokha, V., Nizhenkovska, I., Kuznetsova, O. (2021). Potential of germanium-based compounds in coronavirus infection. Acta Pharmaceutica, 72 (2), 245–258. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/acph-2022-0016
- Hetz, C., Saxena, S. (2017). ER stress and the unfolded protein response in neurodegeneration. Nature Reviews Neurology, 13 (8), 477–491. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.99
- Ghemrawi, R., Khair, M. (2020). Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21 (17), 6127. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176127
- Chung, Y., Lee, J., Jung, S., Lee, Y., Cho, J. W., Oh, Y. J. (2018). Dysregulated autophagy contributes to caspase-dependent neuronal apoptosis. Cell Death & Disease, 9 (12). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1229-y
- Merighi, A., Lossi, L. (2022). Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling and Neuronal Cell Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (23), 15186. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315186
- Ploumi, C., Papandreou, M.-E., Tavernarakis, N. (2022). The complex interplay between autophagy and cell death pathways. Biochemical Journal, 479 (1), 75–90. doi: https://doi.org/10.1042/bcj20210450
- Sorice, M. (2022). Crosstalk of Autophagy and Apoptosis. Cells, 11 (9), 1479. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091479
- Kaur, S., Changotra, H. (2020). The beclin 1 interactome: Modification and roles in the pathology of autophagy-related disorders. Biochimie, 175, 34–49. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2020.04.025
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Iryna Nizhenkovska, Olena Kuznetsova, Violetta Narokha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






