Оцінка протипсориазного ефекту метанольного екстракту Scrophularia deserti на мишах
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.299266Ключові слова:
протипсоріазний, Scrophularia deserti, метанол, екстракт, антиоксидант, феноли, флавоноїди, цитокін, іміквімод, мишача модельАнотація
Псоріаз є недооціненим хронічним та аутоімунним захворюванням шкіри. Місцеві хімічні препарати застосовуються для контролю та лікування псоріазу, незважаючи на їх низьку ефективність або безуспішність. В якості альтернативи для його лікування також можна використовувати фітотерапію.
Метою даного дослідження було оцінити антипсоріазний ефект Scrophularia deserti на мишах.
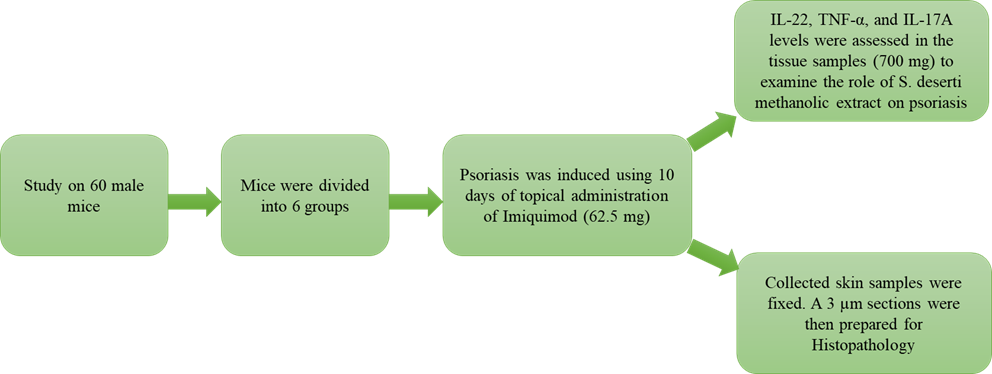
Матеріали та методи: S. deserti був придбаний і використаний для метанольної екстракції. Вивчали активність екстракту DPPH, що поглинає радикали, вміст поліфенолів і флавоноїдів. Було придбано 60 мишей-самців, і псоріаз був індукований за допомогою 10 днів місцевого застосування іміквімоду (62,5 мг). Мишей поділили на 6 груп: контрольна група без псоріазу (отримували лише дистильовану воду), контрольна група псоріазу (тільки місцевий іміквімод), дві групи, що отримували лікування S. deserti (місцеве 300 і 500 мг/кг), місцевий бетаметазон і місцевий α-пінен 9 %. Також визначали розподіл цитокінів і гістопатологічні властивості.
Результати: значення, при якому метанольний екстракт S. deserti поглинає 50 % вільних радикалів (IC50), становило 602,71±15,33 мкг/мл. Загальний вміст флавоноїдів і поліфенолів метанольного екстракту S. deserti становив 16,85±1,12 мг QE/г і 58,47±3,25 мг GAE/г відповідно. Концентрації IL-22, TNF-α та IL-17A були збільшені після індукції псоріазу порівняно з контрольною групою (P <0,05). Миші, які отримували бетаметазон, мали найнижчі концентрації IL-22, TNF-α та IL-17A (P <0,05).
Висновки: Миші, які отримували метанольний екстракт S. deserti (500 мг/кг), також містили значно нижчий рівень IL-22, TNF-α та IL-17A (P <0,05). порівняно з α-піненом і метанольним екстрактом S. deserti (300 мг/кг). Миші з контрольної групи псоріазу показали значний гіперкератоз епідермісу, акантоз і кірку з великою кількістю запальних клітин. У той час як миші, які отримували метанольний екстракт S. deserti (500 мг/кг), показали значне відновлення тканини з нормальним епідермісом шкіри та дерми, сальних залоз і волосяних фолікулів, окрім найнижчого рівня запальних реакцій. Результати показали, що метанольний екстракт S. deserti (500 мг/кг) можна ефективно використовувати як практичну заміну для лікування псоріазу. Однак слід провести деякі додаткові дослідження
Посилання
- Schön, M. P., Wilsmann‐Theis, D. (2023). Current developments and perspectives in psoriasis. JDDG: Journal Der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft, 21 (4), 363–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.15033
- Potestio, L., Ruggiero, A., Fabbrocini, G., Martora, F., Megna, M. (2023). Effectiveness and Safety of Deucravacitinib for the Management of Psoriasis: A Review of the Current Literature. Psoriasis: Targets and Therapy, Volume 13, 19–26. https://doi.org/10.2147/ptt.s407647
- Man, A.-M., Orăsan, M. S., Hoteiuc, O.-A., Olănescu-Vaida-Voevod, M.-C., Mocan, T. (2023). Inflammation and Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24 (22), 16095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216095
- Nicolescu, A. C., Ionescu, M.-A., Constantin, M. M., Ancuta, I., Ionescu, S., Niculet, E. et al. (2022). Psoriasis Management Challenges Regarding Difficult-to-Treat Areas: Therapeutic Decision and Effectiveness. Life, 12 (12), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122050
- Greb, J. E., Goldminz, A. M., Elder, J. T., Lebwohl, M. G., Gladman, D. D., Wu, J. J. et al. (2016). Psoriasis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.82
- Lee, H.-J., Kim, M. (2023). Challenges and Future Trends in the Treatment of Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24 (17), 13313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713313
- Khaleel, R. A., Shareef, S. M., Hameed, Z. E., Alsaraf, K. M., Nassar, M. F. (2021). The effect of fluoxetine and imipramine on the improvement of depressive-like behaviors and HPA axis (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex) activity – an animal model. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 5 (33), 79–88. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2021.243526
- Mardani, M., Rezapour, S., Eftekhari, Z., Asadi-Samani, M., Rashidipour, M., Afsordeh, O. et al. Chemical composition of Elamit scrophularia deserti. International Journal of PharmTech Research, 9 (6), 285–290.
- Zarshenas, M. M., Mousavi, S. S., Haghighi, T. M. (2022). A critical overview of Scrophularia striata Boiss.: Phytochemical and pharmacological investigations. Pharmacological Research – Modern Chinese Medicine, 5, 100182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prmcm.2022.100182
- Mahmoud, B., Hadavi, M., Abbasi, N. (2020). Study of extraction and chemical compounds of Scrophularia striata Boiss. and Scrophularia deserti Delile using HS-SPME and GC-MS. Plant Biotechnology Persa, 2 (1), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.29252/pbp.2.1.8
- Singleton, V. L., Orthofer, R., Lamuela-Raventós, R. M. (1999). Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods in Enzymology, 299, 152–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(99)99017-1
- Shareef, S. M., Khaleel, R. A., Hameed, Z. E., Alsaraf, K. M. (2021). The protective effect of Zingiber officinale L. extract on kidney tissues and blood factors of kidney functions after the damage caused by Azathioprine. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4(32), 78–86. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2021.239434
- Pang, X., Zhang, K., Huang, J., Wang, H., Gao, L., Wang, T. et al. (2018). Decryption of Active Constituents and Action Mechanism of the Traditional Uighur Prescription (BXXTR) Alleviating IMQ-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in BALB/c Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19 (7), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071822
- Pirowska, M., Podolec, K., Lipko-Godlewska, S., Sułowicz, J., Brzewski, P., Obtułowicz, A. et al. (2019). Level of inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor, interleukins 12, 23 and 17 in patients with psoriasis in the context of metabolic syndrome. Advances in Dermatology and Allergology, 36 (1), 70–75. https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2018.73136
- Elkhawaga, O. Y., Ellety, M. M., Mofty, S. O., Ghanem, M. S., & Mohamed, A. O. (2023). Review of natural compounds for potential psoriasis treatment. Inflammopharmacology, 31 (3), 1183–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01178-0
- Bezuglaya, E., Stolper, Y., Lyapunov, N., Zinchenko, I., Liapunov, O. (2023). Study of factors affecting some properties of hydrophilic suppository base. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 5 (45), 4–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.286315
- Aghmiuni, A. I., Khiavi, A. A. (2017). Medicinal Plants to Calm and Treat Psoriasis Disease. Aromatic and Medicinal Plants – Back to Nature, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.5772/67062
- Nowak-Perlak, M., Szpadel, K., Jabłońska, I., Pizon, M., Woźniak, M. (2022). Promising Strategies in Plant-Derived Treatments of Psoriasis-Update of In Vitro, In Vivo, and Clinical Trials Studies. Molecules, 27 (3), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030591
- Pasdaran, A., Hamedi, A. (2017). The genus Scrophularia: a source of iridoids and terpenoids with a diverse biological activity. Pharmaceutical Biology, 55 (1), 2211–2233. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1397178
- Borodina, N., Maloshtan, L., Artemova, K., Kukhtenko, O. (2023). Study of pharmacological activity of dry extract of sakhalin willow shoots against the background of experimental thrombophlebitis. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (44), 97–103. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.286723
- Tanideh, N, Haddadi, M. H., Rokni Hosseini, M. H., Hossienzadeh, M., Mehrabani, D., Sayehmiri, K., Koohi-Hossienabadi, O. (2015). The healing effect of Scrophularia striata on experimental burn wounds infected to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rat. World Journal of Plastic Surgery, 4, 16–23.
- Jafary, A., Latifi, A., Shohrati, M., Haji Hosseini, R., Salesi, M. (2013). The effect of Scrophularia striata extracts on wound healing of mice. Armaghane Danesh, 18, 194–209
- Haddadi, R., Tamri, P., Javani Jooni, F. (2019). In vitro wound healing activity of Scrophularia striata hydroalcoholic extract. South African Journal of Botany, 121, 505–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.01.002
- Dı́az, A. M., Abad, M. J., Fernández, L., Silván, A. M., De Santos, J., Bermejo, P. (2004). Phenylpropanoid glycosides from Scrophularia scorodonia: In vitro anti-inflammatory activity. Life Sciences, 74 (20), 2515–2526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2003.10.008
- Ghashghaii, A., Hashemnia, M., Nikousefat, Z., Zangeneh, M. M., Zangeneh, A. (2017). Wound Healing Potential of Methanolic Extract of Scrophularia striata in Rats. Pharmaceutical Sciences, 23 (4), 256–263. https://doi.org/10.15171/ps.2017.38
- Sabahi, M. R., Taghipour, M., Nouredini, M., Javadi, S. M. (2020). Evaluation of wound healing effects of Scrophularia striata seed extract in rat. International Journal of Medical Investigation, 9 (1), 20–28.
- Zengin, G., Stefanucci, A., Rodrigues, M. J., Mollica, A., Custodio, L., Aumeeruddy, M. Z., Mahomoodally, M. F. (2019). Scrophularia lucida L. as a valuable source of bioactive compounds for pharmaceutical applications: In vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, enzyme inhibitory properties, in silico studies, and HPLC profiles. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 162, 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.09.035
- Xu, Y., Shi, Y., Huang, J., Gu, H., Li, C., Zhang, L., Liu, G., Zhou, W., Du, Z. (2022). The Essential Oil Derived from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Attenuates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin Lesions in BALB/c Mice. Molecules, 27 (9), 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092996
- Lee, J. H., Lee, M.-Y. (2023). In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Psoriasis Activity of Ficus carica Fruit Extracts via JAK-STAT Modulation. Life, 13 (8), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081671
- Khaledi, M., Sharif Makhmal Zadeh, B., Rezaie, A., Nazemi, M., Safdarian, M., Nabavi, M. B. (2020). Chemical profiling and anti-psoriatic activity of marine sponge (Dysidea avara) in induced imiquimod-psoriasis-skin model. PLOS ONE, 15 (11), e0241582. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241582
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Raghad Abdulsalam Khaleel, Saja Majeed Shareef, Tayf Mohammed Maryoosh

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Наше видання використовує положення про авторські права Creative Commons CC BY для журналів відкритого доступу.







