The usage of salts of chaotropic anions for the development of HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of cisplatin and carboplatin in model mixture
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2025.341476Keywords:
platinum-based drugs, high-performance liquid chromatography, assay, validation, greennessAbstract
The aim of the work was to develop an RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of extremely polar and non-UV-absorbing chromophore molecules of cisplatin and carboplatin in a model mixture using salts of chaotropic anions, which can be used for single-analyte determination too.
Material and methods: HPLC analysis was performed using Agilent 1260 and Shimadzu LC-2050C with diode array detector (DAD). Cisplatin and carboplation (purity ≥99% (HPLC)) were supplied from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Used dosage forms: cisplatin «Ebeve» (0.5 mg/ml, Austria) and carboplatin «Ebeve» (10 mg/ml, Austria). All used reagents were HPLC gradient chromatography quality and purchased from Merck Darmstadt, Germany.
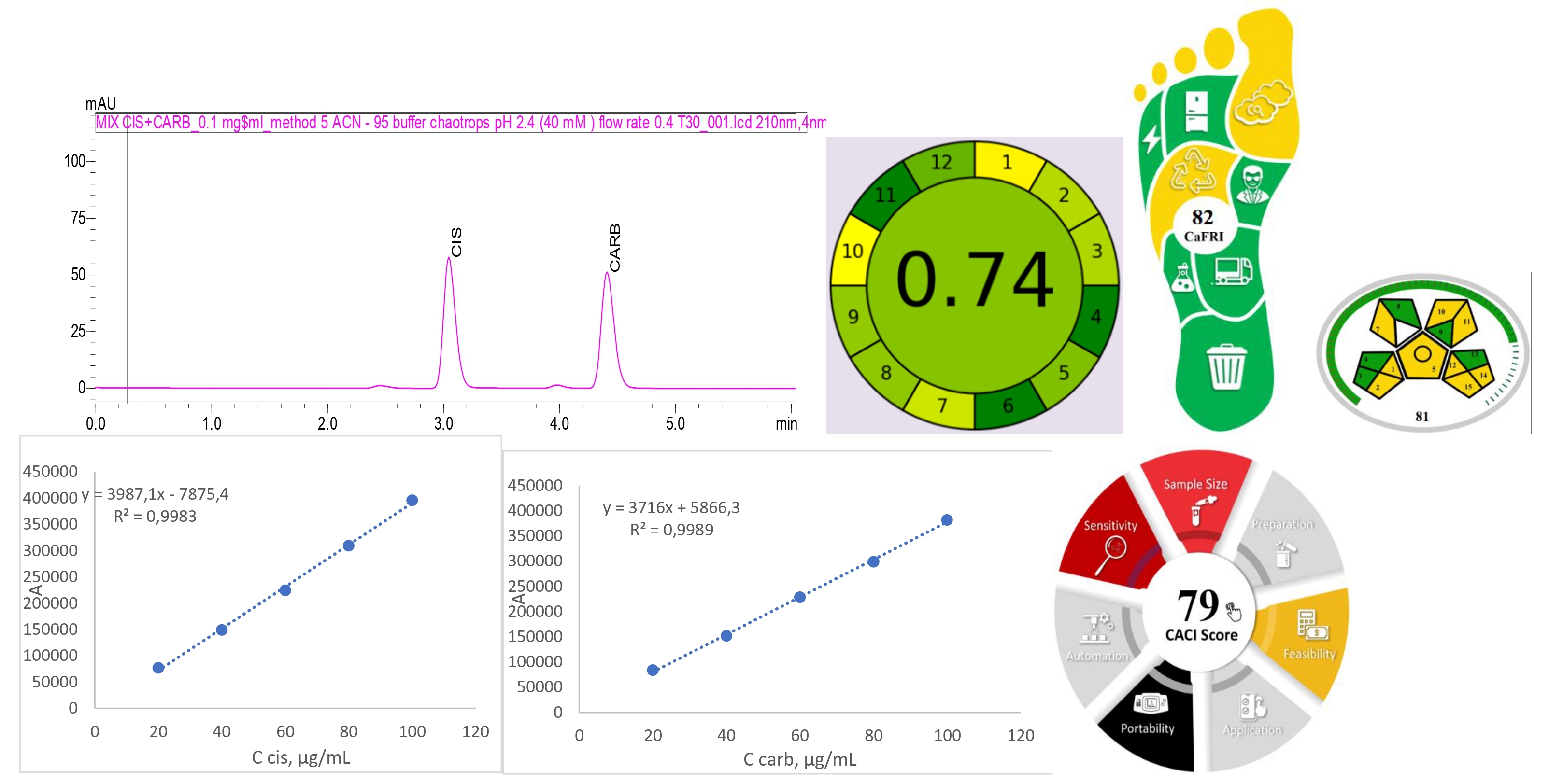
Results and discussion: Chaotropic agents enhance retention of basic molecules in acidic mobile phases on reversed-phase chromatographic columns and improve peak shape and symmetry. The chaotropic anions that increase interaction between the basic N-containing analyte and the alkyl chains of reversed-phase ligands, such as C-8 and C-18, are frequently employed to enhance and improve the performance of HPLC methods. The chromatographic analysis of cisplatin and carboplatin presented a unique challenge due to their inorganic structure. The experimentally established optimal chromatographic conditions are: mobile phase - 40 mM KPF6 buffer solution (pH 2.4) and ACN (95:5), chromatographic column - Luna C18 (100 x 4.6 mm 3 µm), column temperature - 30 °C, flow rate - 0.4 ml/min, detection wavelength - 210 nm. Linearity was assessed using five levels of each of the investigated drugs, where concentration varied in the range of 20–100 μg/mL. The proposed HPLC method is green, as confirmed by the most modern metrics for studying greenness (AGREE, MoGAPI, complex MoGAPI, AGSA, CaFRI and CACI).
Conclusions. In this work, thorough scientific research was carried out with the presentation of HPLC method development for the simultaneous determination of extremely highly polar molecules cisplatin and carboplatin in a model mixture using salts of chaotropic anions. In addition, two studied drugs were quantified using rapid, simple, cost-effective HPLC method approaches
References
- Zhang, C., Xu, C., Gao, X., Yao, Q. (2022). Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics, 12(5), 2115–2132. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.69424
- PubChem – National Library of Medicine. Available at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ Last accessed: 31.05.2025
- European Pharmacopoeia. 11 ed. (2022). European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare. Available at: https://www.edqm.eu/en/european-pharmacopoeia-ph.-eur.-11th-edition Last accessed: 22.03.2025
- The National Formulary (2021). Rockville: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Available at: https://www.uspnf.com Last accessed: 22.03.2025
- British Pharmacopoeia Commission. British Pharmacopoeia (2025). London: TSO.
- Zhao, Z., Tepperman, K., Dorsey, J. G., Elder, R. C. (1993). Determination of cisplatin and some possible metabolites by ion-pairing chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric detection. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 615 (1), 83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(93)80293-d
- Kaushik, K. H., Sripuram, V. K., Bedada, S., Reddy, N. Y., Priyadarshini, G. I., Devarakonda, K. R. (2010). A simple and sensitive validated HPLC method for quantitative determination of cisplatin in human plasma. Clinical Research and Regulatory Affairs, 27 (1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/10601330903490462
- Ramos, Y., Hernández, C., Fernandez, L. A., Bataller, M., Veliz, E., Small, R. (2011). Optimization of a HPLC procedure for simultaneous determination of cisplatin and the complex cis,cis,trans-diamminedichlorodihydroxoplatinum(IV) in aqueous solutions. Química Nova, 34 (8), 1450–1454. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422011000800026
- Toro-Córdova, A., Ledezma-Gallegos, F., Mondragon-Fuentes, L., Jurado, R., Medina, L. A., Pérez-Rojas, J. M., Garcia-Lopez, P. (2016). Determination of Liposomal Cisplatin by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application in Pharmacokinetic Studies. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 54 (6), 1016–1021. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmw039
- Mittal, A., Chitkara, D., Kumar, N. (2007). HPLC method for the determination of carboplatin and paclitaxel with cremophorEL in an amphiphilic polymer matrix. Journal of Chromatography B, 855 (2), 211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.05.005
- Kazakevich, Y. V., Lobrutto, R. (2006). HPLC for pharmaceutical scientists. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470087951
- Horyn, M., Piponski, M., Zaremba, T., Kucher, T., Krstevska Balkanov, S., Bakovska Stoimenova, T. et al. (2023). Application of salts of chaotropic anions in the development of hplc methods for the determination of meldonium in dosage forms. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (41), 14–22. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.274469
- Munawar Hayat, M., Sohail, M., Ashraf, M. (2019). Spectrophotometric determination of cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin in pure and injectable dosage forms. Biomedical Research, 30 (4), 557–562. https://doi.org/10.35841/biomedicalresearch.30-19-244
- Validation of Analytical Procedures, Q2 (R2) (2023). ICH. Available at: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q2%28R2%29_Guideline_2023_1130.pdf Last accessed: 24.06.2025
- Pena-Pereira, F., Wojnowski, W., Tobiszewski, M. (2020). AGREE – Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Analytical Chemistry, 92 (14), 10076–10082. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01887
- Mansour, F. R., Płotka-Wasylka, J., Locatelli, M. (2024). Modified GAPI (MoGAPI) Tool and Software for the Assessment of Method Greenness: Case Studies and Applications. Analytica, 5 (3), 451–457. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica5030030
- Mansour, F. R., Omer, K. M., Płotka-Wasylka, J. (2024). A total scoring system and software for complex modified GAPI (ComplexMoGAPI) application in the assessment of method greenness. Green Analytical Chemistry, 10, 100126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.greeac.2024.100126
- Mansour, F. R., Bedair, A., Belal, F., Magdy, G., Locatelli, M. (2025). Analytical Green Star Area (AGSA) as a new tool to assess greenness of analytical methods. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 46, 102051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2025.102051
- Mansour, F. R., Nowak, P. M. (2025). Introducing the carbon footprint reduction index (CaFRI) as a software-supported tool for greener laboratories in chemical analysis. BMC Chemistry, 19 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-025-01486-2
- Mansour, F. R., Bedair, A., Locatelli, M. (2025). Click Analytical Chemistry Index as a novel concept and framework, supported with open source software to assess analytical methods. Advances in Sample Preparation, 14, 100164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sampre.2025.100164
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mariana Druchok, Marjan Piponski, Mariana Horyn, Nadiya Zarivna, Liliya Logoyda

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






