Biopharmaceutical justification of the creation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems with simvastatin
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.277351Keywords:
self-emulsifying drug delivery systems, accelerated release, increased solubility, simvastatin capsulesAbstract
The aim of the research – to conduct biopharmaceutical tests of capsules with a self-emulsifying delivery system of simvastatin to confirm the effectiveness and feasibility of introducing into the composition of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems active pharmaceutical ingredients that are difficult to dissolve in the gastric juice environment.
Material and methods. Substances, excipients, reagents and materials used during research were simvastatin (India, p. DK40-2005021, 99.09 %), castor oil (Ukraine), polyethylene glycol 40 hydrogenated castor oil (India), Tween 80 (Ukraine), glycerol monostearate (Gustav Heess GmbH, Germany), polyethylene glycol 100 stearate (ERCA, Italy), hard gelatin capsules No. 3 white (China), 0.1 M hydrochloric acid solution (made from concentrated hydrochloric acid), ethanol 96 % (Ukraine), filter paper 90 mm white tape (Ukraine). The reference drug is "Simvastatin-Sandoz" (Salyutas Pharma, Germany, series LX5161).
An Evolution 60S spectrophotometer (USA) was used to carry out studies by absorption spectrophotometry.
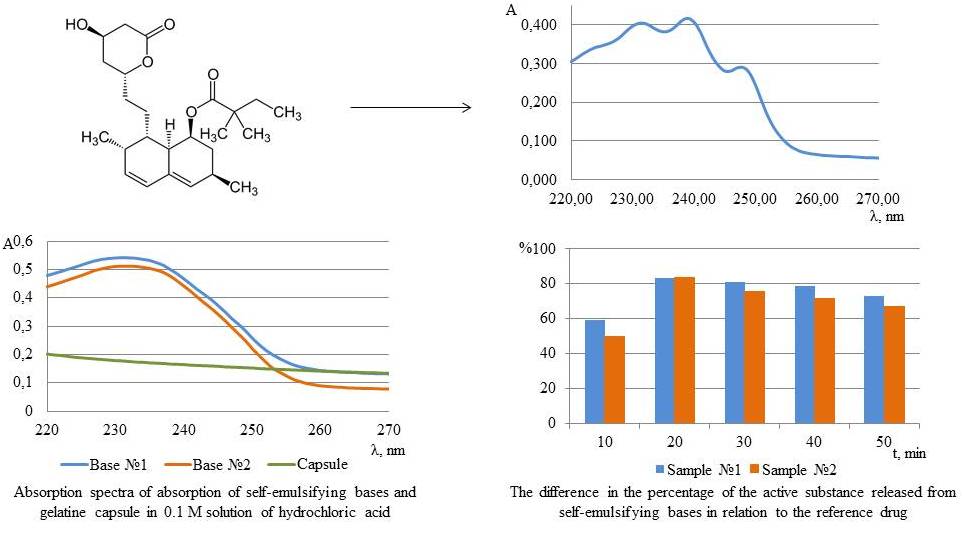
Results. Preliminary study of the absorption spectra of absorption of the substance, bases, gelatin capsules, developed self-emulsifying systems and the reference drug made it possible to predict and optimize the conduct of biopharmaceutical research. The study of the release of simvastatin from the developed delivery systems and the reference drug, which was carried out at a temperature of 37 ℃ in an environment of 0.1M hydrochloric acid, showed that the introduction of simvastatin into the composition of the investigated self-emulsifying compositions allows to increase its solubility in this solvent by five times, compared to the reference drug.
Conclusions. The obtained results indicate the effectiveness of the introduction of simvastatin into the composition of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems and the feasibility of using such systems to improve the solubility and accelerate the release of a poorly water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredient into the gastric juice environment
References
- Salawi, A. (2022). Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: a novel approach to deliver drugs. Drug Delivery, 29 (1), 1811–1823. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2083724
- Pehlivanov, I. (2020). Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS): Excipient Selection, Formulation and Characterization. Journal of IMAB, 26 (3), 3226–3233. doi: https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2020263.3226
- Pehlivanov, I. (2020). Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (sedds): excipient selection, formulation and characterization. Journal of IMAB – Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers), 26 (3), 3226–3233. doi: https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2020263.3226
- Derzhavna farmakopeia Ukrainy. Vol. 2 (2014). Kharkiv: DP «Ukrainskyi naukovyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 723.
- Chen, Zh. Q., Liu, Y., Zhao, J. H., Wang, L., Feng, N. P. (2012). Improved Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Indirubin by a Supersaturatable Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 7, 1115–1125. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s28761
- Kazi, M., Al amri, R., Alanazi, F. K., Hussain, M. D. (2018). In vitro Methods for In vitro-In vivo Correlation (IVIVC) for Poorly Water Soluble Drugs: Lipid Based Formulation Perspective. Current Drug Delivery, 15 (7), 918–929. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201815666180116090910
- Mahmood, A., Haneef, R., Al Meslamani, A. Z., Bostanudin, M. F., Sohail, M., Sarfraz, M., Arafat, M. (2022). Papain-Decorated Mucopenetrating SEDDS: A Tentative Approach to Combat Absorption Issues of Acyclovir via the Oral Route. Pharmaceutics, 14 (8), 1584. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081584
- Zupančič, O., Rohrer, J., Thanh Lam, H., Grießinger, J. A., Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2017). Development and in vitro characterization of self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for oral opioid peptide delivery. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 43 (10), 1694–1702. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2017.1338722
- Leichner, C., Baus, R. A., Jelkmann, M., Plautz, M., Barthelmes, J., Dünnhaupt, S., Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2019). In vitro evaluation of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for nasal administration of dimenhydrinate. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 9 (5), 945–955. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-019-00634-1
- Abou Assi, R., M. Abdulbaqi, I., Seok Ming, T., Siok Yee, C., A. Wahab, H., Asif, S. M., Darwis, Y. (2020). Liquid and Solid Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDs) as Carriers for the Oral Delivery of Azithromycin: Optimization, In Vitro Characterization and Stability Assessment. Pharmaceutics, 12 (11), 1052. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111052
- Singh, M. K., Singh, M. P., Jain, A. P., Lokesh, K. R. (2021). Formulation And Evaluation Of Self Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SEDDS) Of Commiphora Wightti Extract. Journal of Advanced Scientific Research, 12 (1), 140–149. doi: https://doi.org/10.55218/jasr.202112118
- Singh, B., Beg, S., Khurana, R. K., Sandhu, P. S., Kaur, R., Katare, O. P. (2014). Recent Advances in Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS). Critical Reviews in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 31 (2), 121–185. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.2014008502
- Jiang, F., Choi, J.-Y., Lee, J.-H., Ryu, S., Park, Z.-W., Lee, J.-G. et al. (2017). The influences of SLCO1B1 and ABCB1 genotypes on the pharmacokinetics of simvastatin, in relation to CYP3A4 inhibition. Pharmacogenomics, 18 (5), 459–469. doi: https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs-2016-0199
- Giddam, R. K., Hepsiba, S., Mukeri, I. H. (2022). Formulation of Self Emulsifying Drug Delivery System of Dolutegravir sodium. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition, 18 (12), 195–209.
- European Department for the Quality of Medicines (2013). European Pharmacopoeia. Strasbourg, 3655.
- The MHLW Ministerial Notification No. 220 (2021). The Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Tokyo, 2587.
- Derzhavna farmakopeia Ukrainy. Vol. 1. (2015) Kharkiv: DP «Ukrainskyi naukovyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 1126.
- Bodnar, L. A., Polovko, N. P. (2023). The study on the development of self-emulsifying compositions with simvastatin. News of Pharmacy, 105 (1), 32–37. doi: https://doi.org/10.24959/nphj.23.104
- Vinit, Ch., Kavya, R., Kashmira, A. (2014). Development of uv spectrophotometric methods and validation for estimation of simvastatin in bulk and tablet dosage form by absorbance maxima and area under the curve method. Journal of Applied Pharmacy, 6 (1), 55–64. doi: https://doi.org/10.21065/19204159.6.55
- Erk, N. (2002). Rapid spectrophotometric method for quantitative determination of simvastatin and fluvastatin in human serum and pharmaceutical formulations. Pharmazie, 57 (12), 817–819.
- Lee, Y. Z., Seow, E. K., Lim, S. C., Yuen, K. H., Abdul Karim Khan, N. (2021). Formulation and In Vivo Evaluation of a Solid Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System Using Oily Liquid Tocotrienols as Model Active Substance. Pharmaceutics, 13 (11), 1777. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111777
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Любов Анатоліївна Боднар, Наталя Петрівна Половко, Наталія Юріївна Бевз, Володимир Олексійович Грудько, Олеся Орестівна Перепелиця

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






