Polymer solid dispersion system of nimesulide: in vitro dissolution assessment, thermodynamic and physicochemical characteristics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2025.322985Keywords:
nimesulide, phase solubility, thermodynamic characteristics, polyvinylpyrrolidone, solid dispersed system, increase in solubilityAbstract
Nimesulide is a well-known non-steroidal anti-inflammatory active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), but it is poorly soluble in water, which makes its bioavailability relatively low.
The aim of the work was to investigate the effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) of different molecular weights on the phase solubility of nimesulide and to evaluate the thermodynamic parameters of the obtained complexes in order to determine the optimal polymer for further development of a solid dispersed system (SDS) of nimesulide and to study its physicochemical properties, which lead to an improvement in the solubility of API in the composition of the obtained composite material.
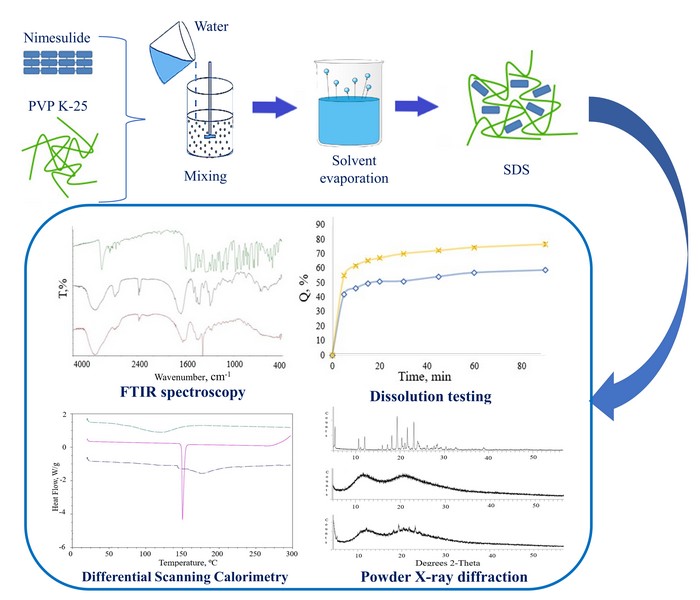
Materials and methods. The dependence of the nimesulide dissolution profile in water on the concentration of PVP of different molecular weights was studied by the Higuchi and Connors method. SDS was prepared by the «green» method of solvent evaporation and were characterised by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and were evaluated for dissolution profiles.
Research results. The influence of PVP of different molecular weights on the phase solubility of nimesulide was studied, and it was found that the best increase in solubility in water was observed in the system with PVP K-25 – 5.27 times. Thermodynamic parameters of this composition were also investigated. The FTIR results indicate that the formation of complexes between the API and the polymer is predominantly due to hydrogen bonds. DSC and PXRD showed that nimesulide is present in SDS in an amorphous form. The results of the in vitro release kinetics study showed that the release rate of nimesulide from the formed SDS was higher than the dissolution rate of the comparison drug.
Conclusions. A solid dispersed system prepared by the «green» method of solvent evaporation using PVP K-25 as a carrier can be used as a good strategy for formulating effective anti-inflammatory drugs of nimesulide with increased bioavailability
Supporting Agency
- Volodymyr Bessarabov was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine [0122U000139]
References
- Sohail, R., Mathew, M., Patel, K. K., Reddy, S. A., Haider, Z., Naria, M. et al. (2023). Effects of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Gastroprotective NSAIDs on the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Narrative Review. Cureus, 15 (4). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.37080
- Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Bian, Y., Zhang, Y., Du, R., Li, M. et al. (2023). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the environment: Recent updates on the occurrence, fate, hazards and removal technologies. Science of The Total Environment, 904, 166897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166897
- Bindu, S., Mazumder, S., Bandyopadhyay, U. (2020). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochemical Pharmacology, 180, 114147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114147
- Ozleyen, A., Yilmaz, Y. B., Donmez, S., Atalay, H. N., Antika, G., Tumer, T. B. (2022). Looking at NSAIDs from a historical perspective and their current status in drug repurposing for cancer treatment and prevention. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 149 (5), 2095–2113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04187-8
- Kress, H. G., Baltov, A., Basiński, A., Berghea, F., Castellsague, J., Codreanu, C. et al. (2015). Acute pain: a multifaceted challenge – the role of nimesulide. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 32 (1), 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1185/03007995.2015.1100986
- Güngör, T., Ozleyen, A., Yılmaz, Y. B., Siyah, P., Ay, M., Durdağı, S., Tumer, T. B. (2021). New nimesulide derivatives with amide/sulfonamide moieties: Selective COX-2 inhibition and antitumor effects. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 221, 113566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113566
- Bessone, F., Hernandez, N., Mendizabal, M., Ridruejo, E., Gualano, G., Fassio, E. et al. (2021). Serious liver injury induced by Nimesulide: an international collaborative study. Archives of Toxicology, 95 (4), 1475–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03000-8
- Kwon, J., Kim, S., Yoo, H., Lee, E. (2019). Nimesulide-induced hepatotoxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE, 14 (1), e0209264. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209264
- Ferreira, R. G., Narvaez, L. E. M., Espíndola, K. M. M., Rosario, A. C. R. S., Lima, W. G. N., Monteiro, M. C. (2021). Can Nimesulide Nanoparticles Be a Therapeutic Strategy for the Inhibition of the KRAS/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer? Frontiers in Oncology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.594917
- Rainsford, K. D. (2006). Nimesulide – a multifactorial approach to inflammation and pain: scientific and clinical consensus. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 22 (6), 1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1185/030079906x104849
- Caiazzo, E., Ialenti, A., Cicala, C. (2019). The relatively selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor nimesulide: What’s going on? European Journal of Pharmacology, 848, 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.044
- Luo, W., Luo, Y., Yang, J. (2020). Proteomics-based screening of the target proteins associated with antidepressant-like effect and mechanism of nimesulide. Scientific Reports, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66420-z
- Khanduja, K. L., Sohi, K. K., Pathak, C. M., Kaushik, G. (2006). Nimesulide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of superoxide anions and nitric oxide and iNOS expression in alveolar macrophages. Life Sciences, 78 (15), 1662–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.07.033
- Manicourt, D.-H., Bevilacqua, M., Righini, V., Famaey, J.-P., Devogelaer, J.-P. (2005). Comparative Effect of Nimesulide and??Ibuprofen on the Urinary Levels of??Collagen Type II C-Telopeptide Degradation Products and on the Serum Levels of Hyaluronan and Matrix Metalloproteinases-3 and -13 in??Patients with Flare-Up of Osteoarthritis. Drugs in R & D, 6 (5), 261–271. https://doi.org/10.2165/00126839-200506050-00002
- Rasheed, S., Sánchez, S. S., Yousuf, S., Honoré, S. M., Choudhary, M. I. (2018). Drug repurposing: In-vitro anti-glycation properties of 18 common drugs. PLOS ONE, 13 (1), e0190509. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190509
- Afzal, M., Bhardwaj, D. P., Khan, R., Kazmi, I., Saleem, S., Al-Abbasi, F. A., Anwar, F. (2018). Antineoplastic influence of nimesulide in chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibition of DNA synthesis. Inflammopharmacology, 27 (1), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0481-1
- Trindade, J. D. S., Freire-de-Lima, C. G., Côrte-Real, S., Decote-Ricardo, D., Freire de Lima, M. E. (2021). Drug repurposing for Chagas disease: In vitro assessment of nimesulide against Trypanosoma cruzi and insights on its mechanisms of action. PLOS ONE, 16 (10), e0258292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0258292
- Wang, M., Liu, S., Jia, L., Zhang, J., Du, S., Gong, J. (2020). Exploring the physical stability of three nimesulide–indomethacin co-amorphous systems from the perspective of molecular aggregates. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 147, 105294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105294
- Antunes Rocha, H. V., Augusto, R. de S., Prado, L. D., De Carvalho, E. M. (2019). Characterization of nimesulide and development of immediate release tablets. Eclética Química Journal, 44 (3), 20–35. https://doi.org/10.26850/1678-4618eqj.v44.3.2019.p20-35
- Wei, W., Evseenko, V. I., Khvostov, M. V., Borisov, S. A., Tolstikova, T. G., Polyakov, N. E. et al. (2021). Solubility, Permeability, Anti-Inflammatory Action and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Properties of Several Mechanochemically Obtained Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions of Nimesulide. Molecules, 26 (6), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061513
- Seedher, N., Bhatia, S. (2003). Solubility enhancement of cox-2 inhibitors using various solvent systems. AAPS PharmSciTech, 4 (3), 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1208/pt040333
- Ismail, S., El-Mahdy, M., Al-Kubati, S. (2009). Enhancement of solubility and dissolution of nimesulide using solubilization, solid dispersion and complexation techniques. Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Assiut, 32 (2), 321–338. https://doi.org/10.21608/bfsa.2009.63509
- Franco, P., De Marco, I. (2021). Preparation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by supercritical antisolvent process. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 44, 101397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2020.101397
- Grekhneva, E. V., Barteneva, E. S., & Efanov, K. S. (2022). Peculiarities of Obtaining and Modeling the Structure of Nimesulide Clathrate Complexes with β- and γ-Cyclodextrins. The 26th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, 12 (1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-26-13707
- Semalty, A., Tanwar, Y. S. (2013). Nimesulide-phosphatidylcholine Complex for Improvement of Solubility and Dissolution. American Journal of Drug Discovery and Development, 3 (4), 225–234. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajdd.2013.225.234
- Al-Edresi, S. S., Razzaq, I. F. A., Alshaibani, A. J. (2020). Enhancing the Solubility of Nimesulide by Loading to a Nanoemulsion. Latin American Journal of Pharmacy, 39 (11), 2299–2308.
- Ranendra, S., Sajeev, C., Priya, K., Sreekhar, C., Shashikanth, G. (2002). Solubility enhancement of nimesulide and ibuprofen by solid dispersion technique. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 64, 529–534.
- Zhao, Y.-M., Zhao, H.-Y., Ma, C. (2013). Preparation of nimesulide solid dispersion by hot melt extrusion technology. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences, 48 (3), 185–190. https://doi.org/10.11669/cpj.2013.03.007
- Liu, G., Gong, L., Zhang, J., Wu, Z., Deng, H., Deng, S. (2020). Development of nimesulide amorphous solid dispersions via supercritical anti-solvent process for dissolution enhancement. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 152, 105457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105457
- Tekade, A. R., Yadav, J. N. (2020). A Review on Solid Dispersion and Carriers Used Therein for Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs. Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 10 (3), 359–369. https://doi.org/10.34172/apb.2020.044
- Kumar, R., Singh, A., Salwan, R., Bhanot, R., Rahar, S., Dhawan, R. K. (2023). An informative review on solid dispersion. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 23 (1), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2023.22.1.0498
- Kaushik, R., Budhwar, V., Kaushik, D. (2020). An Overview on Recent Patents and Technologies on Solid Dispersion. Recent Patents on Drug Delivery & Formulation, 14 (1), 63–74. https://doi.org/10.2174/1872211314666200117094406
- Malkawi, R., Malkawi, W. I., Al-Mahmoud, Y., Tawalbeh, J. (2022). Current Trends on Solid Dispersions: Past, Present, and Future. Advances in Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2022, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5916013
- Zhang, X., Xing, H., Zhao, Y., Ma, Z. (2018). Pharmaceutical Dispersion Techniques for Dissolution and Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics, 10 (3), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030074
- Bhujbal, S. V., Mitra, B., Jain, U., Gong, Y., Agrawal, A., Karki, S. et al. (2021). Pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersion: A review of manufacturing strategies. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 11 (8), 2505–2536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.014
- Singh, G., Kaur, L., Gupta, G. D., Sharma, S. (2017). Enhancement of the Solubility of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs through Solid Dispersion: A Comprehensive Review. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 79 (5). https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000279
- Franco, P., De Marco, I. (2020). The Use of Poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) in the Delivery of Drugs: A Review. Polymers, 12 (5), 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051114
- Higuchi, T., Connors, K. A. (1965). Phase solubility techniques. Advanced Analytical Chemistry of Instrumentation, 4, 117–212.
- Kostiuk, V. G., Bessarabov, V. I. (2024). Validation of the spectrophotometric method for the quantitative determination of nimesulide in solid dispersions systems obtained by centrifugal fiber formation. Farmatsevtychnyi Zhurnal, 4, 39–51. https://doi.org/10.32352/0367-3057.4.24.04
- Kicuntod, J., Sangpheak, K., Mueller, M., Wolschann, P., Viernstein, H., Yanaka, S. et al. (2018). Theoretical and Experimental Studies on Inclusion Complexes of Pinostrobin and β-Cyclodextrins. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 86 (1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86010005
- Sembo-Backonly, B. S., Estour, F., Gouhier, G. (2021). Cyclodextrins: promising scaffolds for MRI contrast agents. RSC Advances, 11 (47), 29762–29785. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra04084g
- Iyer, R., Petrovska Jovanovska, V., Berginc, K., Jaklič, M., Fabiani, F., Harlacher, C. et al. (2021). Amorphous Solid Dispersions (ASDs): The Influence of Material Properties, Manufacturing Processes and Analytical Technologies in Drug Product Development. Pharmaceutics, 13 (10), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101682
- Pandi, P., Bulusu, R., Kommineni, N., Khan, W., Singh, M. (2020). Amorphous solid dispersions: An update for preparation, characterization, mechanism on bioavailability, stability, regulatory considerations and marketed products. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 586, 119560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119560
- Corciova, A., Ivanescu, B. (2014). Study on the hesperidin–cyclodextrins interactions by thin layer chromatography. European Chemical Bulletin, 3 (6), 548–551.
- Lima, E. C., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., Moreno-Piraján, J. C., Anastopoulos, I. (2019). A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 273, 425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
- Schönbeck, C., Holm, R. (2019). Exploring the Origins of Enthalpy–Entropy Compensation by Calorimetric Studies of Cyclodextrin Complexes. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 123 (31), 6686–6693. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b03393
- 9.3. Dissolution test for solid dosage forms (2023). European Pharmacopoeia. Strasbourg: European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines, 1, 348–355.
- Pereira, A. M., Kaya, A., Alves, D., Ansari-Fard, N., Tolaymat, I., Arafat, B., Najlah, M. (2022). Preparation and Characterization of Disulfiram and Beta Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Potential Application in the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 via Nebulization. Molecules, 27 (17), 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175600
- dos Santos Ferreira, C. I., Gonzales, A. P., Mazzobre, M. F., Ulrih, N. P., Buera, M. del P. (2022). Solubility, sorption isotherms and thermodynamic parameters of β-cyclodextrin complexes with poplar propolis components: Practical implicances. LWT, 167, 113811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113811
- Rybczyńska, M., Sikorski, A. (2023). The synthesis, thermal behaviour, spectral and structural characterization, and in silico prediction of pharmacokinetic parameters of tetraalkylammonium salts of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug nimesulide. Scientific Reports, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-44557-x
- Georgescu, M., Meltzer, V., Stănculescu, I., Pincu, E. (2021). Thermal Behavior of the Nimesulide-Salicylic Acid Eutectic Mixtures Prepared by Mechanosynthesis and Recrystallization. Materials, 14 (24), 7715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247715
- Irfan, M., Irfan, M., Shah, S. M., Baig, N., Saleh, T. A., Ahmed, M. et al. (2019). Hemodialysis performance and anticoagulant activities of PVP-k25 and carboxylic-multiwall nanotube composite blended Polyethersulfone membrane. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 103, 109769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109769
- Farmoudeh, A., Rezaeiroshan, A., Abbaspour, M., Nokhodchi, A., Ebrahimnejad, P. (2020). Solid Dispersion Pellets: An Efficient Pharmaceutical Approach to Enrich the Solubility and Dissolution Rate of Deferasirox. BioMed Research International, 2020 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8583540
- Ayenew, Z., Paudel, A., Van den Mooter, G. (2012). Can compression induce demixing in amorphous solid dispersions? A case study of naproxen–PVP K25. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 81 (1), 207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.01.007
- Svoboda, R., Macháčková, J., Nevyhoštěná, M., Komersová, A. (2024). Thermal stability of amorphous nimesulide: from glass formation to crystal growth and thermal degradation. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 26 (2), 856–872. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3cp02260a
- Fouad, S. A., Malaak, F. A., El-Nabarawi, M. A., Abu Zeid, K., Ghoneim, A. M. (2021). Preparation of solid dispersion systems for enhanced dissolution of poorly water soluble diacerein: In-vitro evaluation, optimization and physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. PLOS ONE, 16 (1), e0245482. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245482
- Zhu, Y., Yu, J., Zhou, G., Gu, Z., Adu-Frimpong, M., Deng, W., Yu, J., Xu, X. (2020). Piperine fast disintegrating tablets comprising sustained-release matrix pellets with enhanced bioavailability: formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 25 (5), 617–624. https://doi.org/10.1080/10837450.2020.1725892
- Knopp, M. M., Nguyen, J. H., Becker, C., Francke, N. M., Jørgensen, E. B., Holm, P. et al. (2016). Influence of polymer molecular weight on in vitro dissolution behavior and in vivo performance of celecoxib:PVP amorphous solid dispersions. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 101, 145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.02.007
- Sui, X., Chu, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Wang, H., Liu, T., Han, C. (2020). The Effect of PVP Molecular Weight on Dissolution Behavior and Physicochemical Characterization of Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersions. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2020, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8859658
- Patel, R., Purohit, N. (2009). Physico-Chemical Characterization and In Vitro Dissolution Assessment of Clonazepam – Cyclodextrins Inclusion Compounds. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10 (4), 1301–1312. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9321-3
- Hurley, D., Potter, C. B., Walker, G. M., Higginbotham, C. L. (2018). Investigation of Ethylene Oxide-co-propylene Oxide for Dissolution Enhancement of Hot-Melt Extruded Solid Dispersions. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 107 (5), 1372–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.01.016
- Kahali, N., Khanam, J., Ghosh, N. (2021). An attempt to enhance solubility of metoclopramide base by Solid dispersion strategy and its application on development of Transdermal device. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 57. https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902020000418910
- Mohamed Ameen, H., Kunsági-Máté, S., Bognár, B., Szente, L., Poór, M., Lemli, B. (2019). Thermodynamic Characterization of the Interaction between the Antimicrobial Drug Sulfamethazine and Two Selected Cyclodextrins. Molecules, 24 (24), 4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244565
- Hamed, R., Mohamed, E. M., Sediri, K., Khan, M. A., Rahman, Z. (2021). Development of stable amorphous solid dispersion and quantification of crystalline fraction of lopinavir by spectroscopic-chemometric methods. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 602, 120657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120657
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Volodymyr Bessarabov, Viktor Kostiuk, Viktoriia Lyzhniuk, Vadym Lisovyi, Tetiana Derkach, Galina Kuzmina, Andriy Goy, Liubov Vakhitova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






