Design of the inverter in high accuracy and development of work therein by using compound ligation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.270314Keywords:
Compound ligation (CL), three-phase dynamic load, VSI, FPGA, PPI 8255A, Ultrasonic PWM, Oscillator circuitAbstract
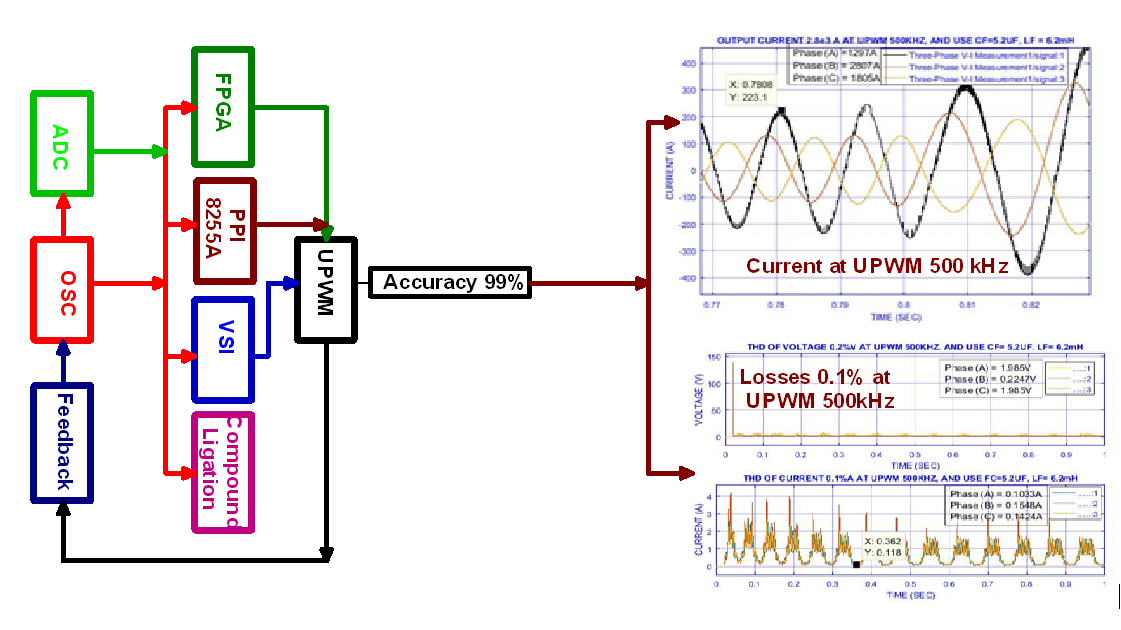
A ligation (CL) system with a very high frequency in an inverter was used, it is a novelty in this study. We also employed a three-phase dynamic load (positive sequence voltage) to correct the power factor and account for active and reactive power in the output system this work is a novelty. The technique through compound ligation (CL) can improve inverter output waveform by reducing losses caused by ingrained agents in voltage source inverters (VSI), such as dead time caused by overload or voltage drop in an inverter's output, or abnormal load current conditions such as a short circuit current occur in the output stage of the inverter, and so on. The invention relates to the conversion of D.C. to A.C. power inverters, it is preferable to use compound ligation to achieve high efficiency, the device is lightweight, and has low losses and good precision. In addition, the present invention relates to improving an inverter load request sensation circuit, smoothing operational current, inverter response, and inverter spontaneous power factor improvement, as well as correction of the reactive power of passive components. In addition, an inverter with high active power (P) equal to (2.6×106 Watt), reactive power (Q) (5.4×107 VAR), was designed, and used positive sequence voltage (1.6×108 Watt ), as well as the switching period (10µs), The system's total harmonic distortion (THD) in voltage and current was 0.11 percent, while the system's accuracy was 99 percent. This is developed by using FPGA and oscillator circuit and programmable peripheral interface 8255 A as well as, ultrasonic PWM with a high-frequency range of (20–500 kHz) as demonstrated evidenced by the results obtained
Supporting Agency
- The authors would like to thank the president of the university and Vice-Chancellor of affairs of academics, prof. DR. ISMI ARIF BIN ISMAIL in Universiti Putra Malaysia for their assistance in overcoming difficulties
References
- Cheng, T.-C., Hsu, C.-W. C., Wang, H.-C., Tsai, T.-H. (2016). A low-power oscillator-based readout interface for medical ultrasonic sensors. 2016 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test (VLSI-DAT). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/vlsi-dat.2016.7482523
- Meng, X., Zhou, L., Lin, F., Heng, C.-H. (2019). A Low-Noise Digital-to-Frequency Converter Based on Injection-Locked Ring Oscillator and Rotated Phase Selection for Fractional- N Frequency Synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 27 (6), 1378–1389. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tvlsi.2019.2898258
- Xu, H., Xu, L., Wang, K., Zheng, Z., Li, Y. (2019). Switching Losses Reduction of Grid-tied Inverters With Variable Switching Frequency Discontinuous PWM. 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ecce.2019.8913206
- Mohammadi, M., Moghani, J. S., Milimonfared, J. (2018). A Novel Dual Switching Frequency Modulation for Z-Source and Quasi-Z-Source Inverters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65 (6), 5167–5176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2017.2784346
- Attia, H., Al Zarooni, M., Cazan, A. (2019). Ultrasonic Frequency Inverter for Piezoelectric Transducer Driving: The Negative Effects on Grid and the Intelligent Solution. 2019 International Conference on Electrical and Computing Technologies and Applications (ICECTA). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icecta48151.2019.8959609
- Rymarski, Bernacki, Dyga, Davari (2019). Passivity-Based Control Design Methodology for UPS Systems. Energies, 12 (22), 4301. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224301
- Yue, X., Boroyevich, D., Lee, F. C., Chen, F., Burgos, R., Zhuo, F. (2018). Beat Frequency Oscillation Analysis for Power Electronic Converters in DC Nanogrid Based on Crossed Frequency Output Impedance Matrix Model. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 33 (4), 3052–3064. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tpel.2017.2710101
- Chen, Y., Liu, Y.-H., Zong, Z., Dijkhuis, J., Dolmans, G., Staszewski, R. B., Babaie, M. (2019). A Supply Pushing Reduction Technique for LC Oscillators Based on Ripple Replication and Cancellation. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 54 (1), 240–252. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jssc.2018.2871195
- You, J., Vilathgamuwa, D. M., Ghasemi, N., Malan, W. L. (2019). An Active Power Decoupling Method for Single Phase DC/AC DAB Converters. IEEE Access, 7, 12964–12972. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2893286
- Qian, W., Zhang, X., Jin, F., Bai, H., Lu, D., Cheng, B. (2018). Using High-Control-Bandwidth FPGA and SiC Inverters to Enhance High-Frequency Injection Sensorless Control in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Access, 6, 42454–42466. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2858199
- Ueta, H., Yokoyama, T. (2018). 1MHz multisampling deadbeat control with disturbance compensation method for three phase PWM inverter. 2018 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Niigata 2018 -ECCE Asia). doi: https://doi.org/10.23919/ipec.2018.8507418
- He, N., Chen, M., Wu, J., Zhu, N., Xu, D. (2019). 20-kW Zero-Voltage-Switching SiC-mosfet Grid Inverter With 300 kHz Switching Frequency. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 34 (6), 5175–5190. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tpel.2018.2866824
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Muhammed Hussein Baqir, Nor Mohd Haziq, Noor Izzri Abdul Wahab

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








