Organization of online learning using the intelligent metasystem of open semantic technology for intelligent systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.272952Keywords:
online learning, online course, data visualization method, machine learning methodAbstract
Distance learning today allows you to create a system of mass continuous self-learning, universal exchange of information, regardless of the presence of time and space zones. For more effective online learning, it is necessary to introduce artificial intelligence technologies and methods for implementing learning systems.
In this paper, the objects of research were:
1) the capabilities of the OSTIS open semantic technology, the capabilities of the IMS.OSTIS metasystem for organizing online learning;
2) machine learning method – classification.
Results of the study:
1) an online course was organized using the IMS.OSTIS metasystem of the OSTIS open semantic technology;
2) for the analysis and visualization of training data, a machine learning method is implemented – classification.
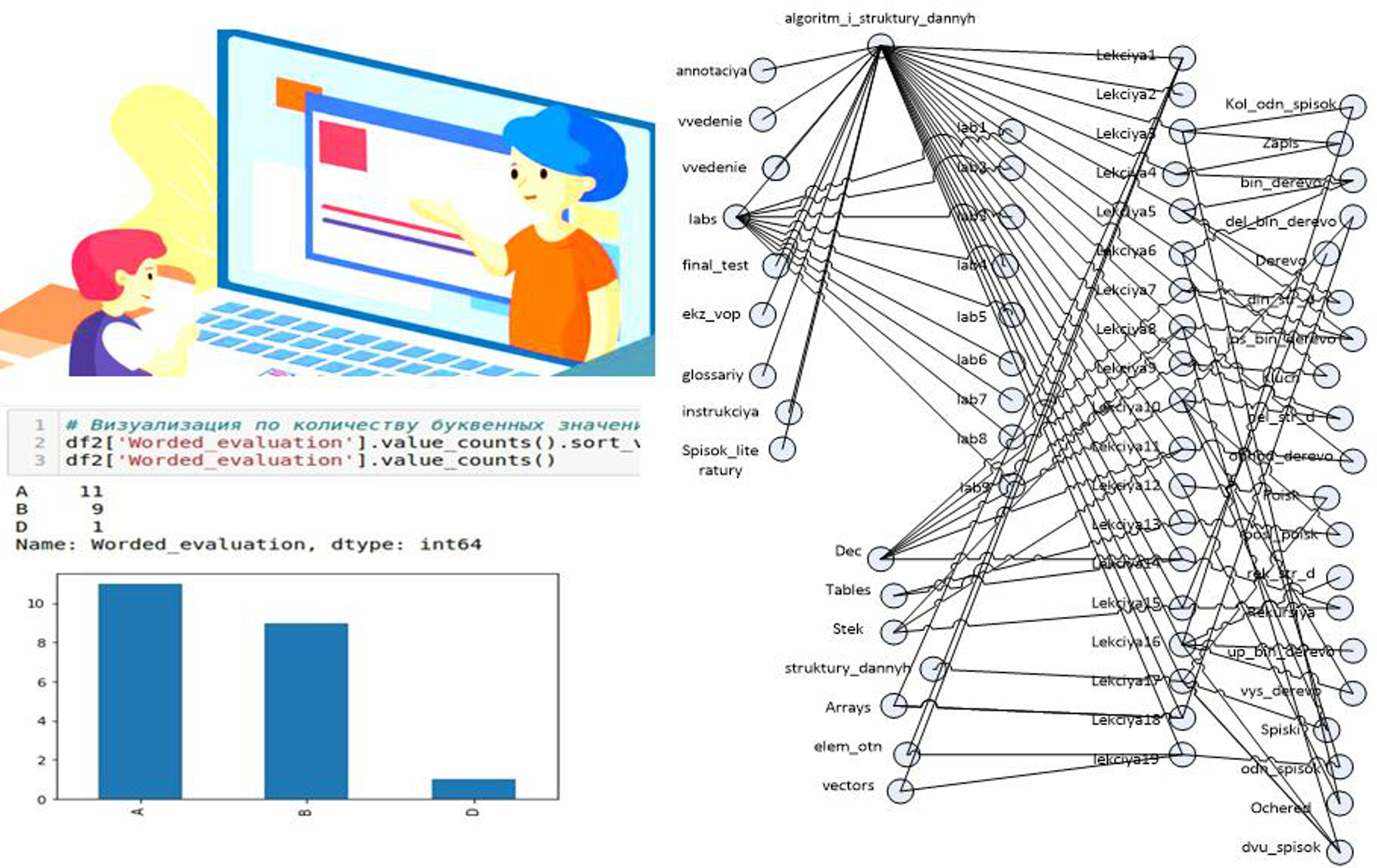
The results of the implementation of the online course were obtained using the semantic technology for designing an intelligent learning system: the IMS.OSTIS metasystem using the graphical semantic code SCg. The OSTIS kernel requires a machine with the Ubuntu operating system installed, which is a GNU/Linux distribution based on Debian GNU/Linux, an operating system based on the Linux kernel.
The paper also shows an example of using the machine learning method – classification. This method allows you to classify data. Intelligent processing and visualization of data were carried out based on the results of testing students in order to classify them into letter categories A, B, C, D according to a set of features: scores and points of the average score. The high-level Python library Pandas was used, this is a library for data analysis. To visualize the results of data processing, the Matplotlib library in Python was used
References
- Khor, E. T., Looi, C. K. (2022). A Learning Analytics Approach to Model and Predict Learners’ Success in Digital Learning. ASCILITE Publications, 476–480. doi: https://doi.org/10.14742/apubs.2019.315
- Obaid, T., Eneizan, B., Abumandil, M. S. S., Mahmoud, A. Y., Abu-Naser, S. S., Ali, A. A. A. (2022). Factors Affecting Students’ Adoption of E-Learning Systems During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 227–242. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16865-9_19
- Huang, A. Y. Q., Lu, O. H. T., Yang, S. J. H. (2018). Applying Learning Analytics for the Early Prediction of Students' Academic Performance in Blended Learning. Educational Technology & Society, 21 (2), 220–232. Available at: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1175301
- Barthakur, A., Joksimovic, S., Kovanovic, V., Richey, M., Pardo, A. (2022). Aligning objectives with assessment in online courses: Integrating learning analytics and measurement theory. Computers & Education, 190, 104603. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104603
- Sukirman, D., Setiawan, B., Riyana, C. (2022). Development of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) Content to Improve Indonesian Teachers’ Pedagogical Competence: MOOC Technology Instructional Process. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 11 (6), 255. doi: https://doi.org/10.36941/ajis-2022-0166
- Abbitt, J. T. (2011). An Investigation of the Relationship between Self-Efficacy Beliefs about Technology Integration and Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK) among Preservice Teachers. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 27 (4), 134–143. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2011.10784670
- Paaßen, B., McBroom, J., Jeffries, B., Yacef, K., Koprinska, I. (2021). Mapping Python Programs to Vectors using Recursive Neural Encodings. Journal of Educational Data Mining, 13 (3), 1–35. Available at: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1320641
- Kintonova, A. Zh., Nurmukanova, Zh. (2016). Using OSTIS technology to create a knowledge base of an intelligent electronic publication. V International Scientific and Practical Conference "Informatization of Society". Kazakhstan, 226–228.
- Kintonova, A., Povkhan, I. F., Sabitov, A., Tokkuliyeva, A., Demidchik, N. (2022). Online Learning Technologies. 2022 IEEE 7th International Energy Conference (ENERGYCON). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/energycon53164.2022.9830387
- Golenkov, V. V., Gulyakina, N. A. (2015). Semantic technology of component design of knowledge-driven systems. OSTIS-2015.
- Raymond, E. (1999). The Cathedral & the Bazaar. O’Reilly Media.
- Ghandour, A., Kintonova, A., Demidchik, N., Sverdlikova, E. (2021). Solving Tourism Management Challenges by Means of Mobile Augmented Reality Applications. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies, 16 (6), 1–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/ijwltt.293280
- Gulyakina, N. A., Pivovarchik, O. V. (2011). Integrated methodology for designing and teaching the design of intelligent reference systems. OSTIS-2011.
- Shunkevich, D. V. (2013). Models and tools for component design of knowledge processing machines based on semantic networks. OSTIS-2013.
- Caiko, J., Kintonova, A., Mussina, G., Kurmanbayeva, A., Nazarmatova, B. (2022). Modern Models Of Learning At The University. 2022 IEEE 7th International Energy Conference (ENERGYCON). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/energycon53164.2022.9830331
- Brooker, A., Corrin, L., De Barba, P., Lodge, J., Kennedy, G. (2018). A tale of two MOOCs: How student motivation and participation predict learning outcomes in different MOOCs. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 34 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.3237
- Adomavicius, G., Tuzhilin, A. (2005). Toward the next generation of recommender systems: a survey of the state-of-the-art and possible extensions. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 17 (6), 734–749. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2005.99
- Fincham, E., Gasevic, D., Jovanovic, J., Pardo, A. (2019). From Study Tactics to Learning Strategies: An Analytical Method for Extracting Interpretable Representations. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 12 (1), 59–72. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tlt.2018.2823317
- George, G., Lal, A. M. (2019). Review of ontology-based recommender systems in e-learning. Computers & Education, 142, 103642. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103642
- Henrie, C. R., Halverson, L. R., Graham, C. R. (2015). Measuring student engagement in technology-mediated learning: A review. Computers & Education, 90, 36–53. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.09.005
- Hsiao, C. C., Huang, J. C. H., Huang, A. Y. Q., Lu, O. H. T., Yin, C. J., Yang, S. J. H. (2018). Exploring the effects of online learning behaviors on short-term and long-term learning outcomes in flipped classrooms. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (8), 1160–1177. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1522651
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Aliya Kintonova, Amanbek Sabitov, Igor Povkhan, Dinara Khaimulina, Galymzhan Gabdreshov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








