Construction of a simulation model for the transportation of perishable goods along variable routes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.277948Keywords:
perishable goods, minimum batch, small shipments, simulation modeling, discrete-event modeling, agent-based modelingAbstract
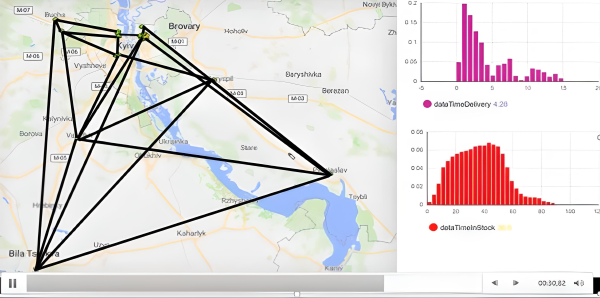
The object of research is the system of organization of transportation of perishable goods. The study subject is the technological process of transportation of perishable goods by small shipments. The problem solved was a multicriteria optimization of the technological process of delivery of perishable goods by small shipments. The results are the built simulation model for the distribution of small consignments of perishable goods and the optimization according to the criterion of minimizing delivery time while limiting the rational use of available vehicles. To construct a simulation model, discrete-event and agent-based principles were used.
The model built combines the solution to the transport problem and the traveling salesman problem simultaneously with taking into account the stochastic duration of technological operations. When forming the distribution route, the model algorithm takes into account the minimum allowable batch size to the i-th destination, which allows each time to build a new unique route of the vehicle.
Unlike existing ones, the model constructed allows taking into account the peculiarities of the distribution network, the minimum consignment of cargo, and dynamically changing the route in accordance with the available cargo. Each time the cargo mass arrives at the logistics terminal, the condition of a sufficient quantity of goods intended for delivery to points of sale is checked. If the quantity of cargo sufficient for shipment is equal to the capacity of the car body, a new information message is generated on the availability of goods ready for shipment.
Scope and conditions of practical use of the obtained results include transport companies, retail chains, distribution logistics
References
- Moskvichenko, I., Stadnik, V., Krysyuk, L. (2022). On determining the optimal schemes for importing frozen fish to Ukraine. Economy and Society, 37. doi: https://doi.org/10.32782/2524-0072/2022-37-31
- Mazaraki, A., Matsiuk, V., Ilchenko, N., Kavun-Moshkovska, O., Grygorenko, T. (2020). Development of a multimodal (railroad-water) chain of grain supply by the agent-based simulation method. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (3 (108)), 14–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.220214
- Matsiuk, V., Galan, O., Prokhorchenko, A., Tverdomed, V. (2021). An Agent-Based Simulation for Optimizing the Parameters of a Railway Transport System. ICTERI. Kherson, 121–128.
- Matsiuk, V., Ilchenko, N., Pryimuk, O., Kochubei, D., Prokhorchenko, A. (2022). Risk assessment of transport processes by agent-based simulation. AIP Conference Proceedings. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0105913
- Katsman, M. D., Myronenko, V. K., Matsiuk, V. I., Lapin, P. V. (2021). Approach to determining the parameters of physical security units for a critical infrastructure facility. Reliability: Theory & Applications, 16 (1), 71–80. doi: https://doi.org/10.24412/1932-2321-2021-161-71-80
- Panchenko, S., Prokhorchenko, A., Dekarchuk, O., Gurin, D., Mkrtychian, D., Matsiuk, V. (2020). Development of a method for studying the impact of the time reserve value on the reliability of the train schedule based on the epidemiological SIR model. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1002 (1), 012016. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1002/1/012016
- Abbas, H., Zhao, L., Gong, X., Faiz, N. (2023). The perishable products case to achieve sustainable food quality and safety goals implementing on-field sustainable supply chain model. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 101562. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2023.101562
- Alvarez, A., Cordeau, J.-F., Jans, R., Munari, P., Morabito, R. (2020). Formulations, branch-and-cut and a hybrid heuristic algorithm for an inventory routing problem with perishable products. European Journal of Operational Research, 283 (2), 511–529. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2019.11.015
- Deng, X., Yang, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Lu, Z. (2019). Risk propagation mechanisms and risk management strategies for a sustainable perishable products supply chain. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 135, 1175–1187. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.01.014
- Koszorek, M., Huk, K. (2020). Selected logistics processes in the flow of perishable products. Acta Logistica, 7 (3), 209–215. doi: https://doi.org/10.22306/al.v7i3.181
- Lejarza, F., Baldea, M. (2020). Closed-loop real-time supply chain management for perishable products. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53 (2), 11458–11463. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.584
- Liu, A., Zhu, Q., Xu, L., Lu, Q., Fan, Y. (2021). Sustainable supply chain management for perishable products in emerging markets: An integrated location-inventory-routing model. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 150, 102319. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2021.102319
- Mousavi, R., Bashiri, M., Nikzad, E. (2022). Stochastic production routing problem for perishable products: Modeling and a solution algorithm. Computers & Operations Research, 142, 105725. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2022.105725
- Melkonyan, A., Gruchmann, T., Lohmar, F., Kamath, V., Spinler, S. (2020). Sustainability assessment of last-mile logistics and distribution strategies: The case of local food networks. International Journal of Production Economics, 228, 107746. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107746
- Vieira, A. A. C., Dias, L. M. S., Santos, M. Y., Pereira, G. A. B., Oliveira, J. A. (2019). Supply chain hybrid simulation: From Big Data to distributions and approaches comparison. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 97, 101956. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2019.101956
- Orozonova, A., Gapurbaeva, S., Kydykov, A., Prokopenko, O., Prause, G., Lytvynenko, S. (2022). Application of smart logistics technologies in the organization of multimodal cargo delivery. Transportation Research Procedia, 63, 1192–1198. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2022.06.124
- Shramenko, N., Muzylyov, D., Shramenko, V. (2020). Methodology of costs assessment for customer transportation service of small perishable cargoes. International Journal of Business Performance Management, 21 (1/2), 132. doi: https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbpm.2020.106113
- Shramenko, V., Muzylyov, D., Shramenko, N. (2020). Integrated business-criterion to choose a rational supply chain for perishable agricultural goods at automobile transportations. International Journal of Business Performance Management, 21 (1/2), 166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbpm.2020.10027634
- Saiensus, M. A. (2018). Analysis of cold logistics market in Ukraine: problem and prospects of development. Naukovyi visnyk Uzhhorodskoho natsionalnoho universytetu. Seriya: Mizhnarodni ekonomichni vidnosyny ta svitove hospodarstvo, 20 (3), 18–22. Available at: http://www.visnyk-econom.uzhnu.uz.ua/archive/20_3_2018ua/6.pdf
- Tiwari, K. V., Sharma, S. K. (2023). An optimization model for vehicle routing problem in last-mile delivery. Expert Systems with Applications, 222, 119789. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119789
- Naumenko, M., Valiavska, N., Saiensus, M., Ptashchenko, O., Nikitiuk, V., Saliuk, A. (2020). Optimization Model of the Enterprise Logistics System Using Information Technologies. International Journal of Management, 11 (5), 54–64. Available at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3628982
- Matskul, V., Kovalyov, A., Saiensus, M. (2021). Optimization of the cold supply chain logistics network with an environmental dimension. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 628 (1), 012018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/628/1/012018
- Ushakova, I. (2020). Application of computer agent modeling for optimization of the assembly process. Information Processing Systems, 1 (160), 18–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.30748/soi.2020.160.02
- Ptytsia, N. (2019). City Retail Network Influence on Transportation Expenses. SHS Web of Conferences, 67, 03011. doi: https://doi.org/10.1051/shsconf/20196703011
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tetyana Anufriyeva, Viacheslav Matsiuk, Natalya Shramenko, Nataliia Ilchenko, Olga Pryimuk, Viktoriia Lebid

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








