Метод оцінювання трендів продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів на основі модифікованого PageRank алгоритму
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.273929Ключові слова:
алгоритм PageRank, наукова робота, колективний науковий суб’єкт, наукометрія, наукова продуктивністьАнотація
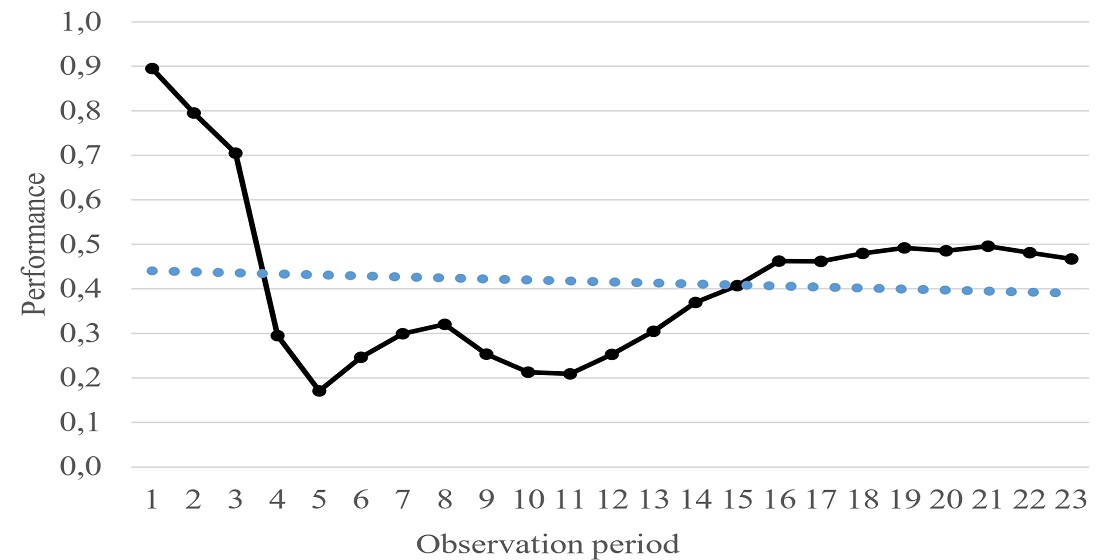
Задача розрахунку продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів є актуальною задачею наукометрії. В дослідження проведено формалізацію задачі оцінювання трендів продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів. Описано метод розрахунку продуктивності TWPR-CI на основі модифікованого PageRank алгоритму. Встановлено формули для розрахунку продуктивності, які дозволяють врахувати зміну продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів з часом. За основу було обрано показники базової середньої абсолютної зміни продуктивності та ланцюгової середньої відносної зміни продуктивності. Для відбору перспективних, з точки зору наукової роботи колективних суб’єктів, надають перевагу тим, у яких базова середня абсолютна зміна продуктивності додатна або ланцюгова середня відносна зміна продуктивності перевищує одиницю. Проведена верифікація методу оцінювання трендів продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів на основі модифікованого PageRank алгоритму з використанням публічного датасету Citation Network Dataset. Датасет включає більше 5 млн. наукових публікацій та 48 млн. цитувань. Було проаналізовано цитування наукових публікацій 27 500 колективних наукових суб’єктів за період з 2000 р. по 2022 р. Для цього періоду для 15 вибраних колективних наукових суб’єктів розраховано продуктивність за методом TWPR-CI, а також оцінки трендів продуктивності на основі їх середньої відносної зміни. Виділено три класи колективних наукових суб’єктів за трендами продуктивності. Отримані результати свідчать про релевантність запропонованого методу для кількісного оцінювання трендів продуктивності колективних наукових суб’єктів (закладів вищої освіти, наукових інститутів, лабораторій, інших установ, які займаються науковою діяльністю)
Посилання
- Biloshchytskyi, A., Kuchansky, A., Andrashko, Y., Omirbayev, S., Mukhatayev, A., Faizullin, A., Toxanov, S. (2021). Development of the set models and a method to form information spaces of scientific activity subjects for the steady development of higher education establishments. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (2 (111)), 6–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.233655
- Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102 (46), 16569–16572. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
- Brin, S., Page, L. (1998). The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual Web search engine. Computer Networks and ISDN Systems, 30 (1-7), 107–117. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7552(98)00110-x
- Leskovec, J., Rajaraman, A., Ullman, J. D. (2020). Mining of massive datasets. Cambridge University Press, 565. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108684163
- Lizunov, P., Biloshchytskyi, A., Kuchansky, A., Andrashko, Y., Biloshchytska, S. (2019). Improvement of the method for scientific publications clustering based on n-gram analysis and fuzzy method for selecting research partners. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (100)), 6–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.175139
- Bianchini, M., Gori, M., Scarselli, F. (2005). Inside PageRank. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 5 (1), 92–128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1052934.1052938
- Assessing universities and other research-focused institutions. Scimago Institutions Rankings. Available at: https://www.scimagoir.com/
- Bergstrom, C. (2007). Eigenfactor: Measuring the value and prestige of scholarly journals. College & Research Libraries News, 68 (5), 314–316. doi: https://doi.org/10.5860/crln.68.5.7804
- Zhang, F. (2017). Evaluating journal impact based on weighted citations. Scientometrics, 113 (2), 1155–1169. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2510-z
- Biloshchytskyi, A., Kuchansky, A., Andrashko, Y., Mukhatayev, A., Toxanov, S., Faizullin, A. (2020). Methods of Assessing the Scientific Activity of Scientists and Higher Education Institutions. 2020 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Advanced Trends in Information Theory (ATIT). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/atit50783.2020.9349348
- Zhang, J., Liu, X. (2022). Citation Oriented AuthorRank for Scientific Publication Ranking. Applied Sciences, 12 (9), 4345. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094345
- Lizunov, P., Biloshchytskyi, A., Kuchansky, A., Andrashko, Y., Biloshchytska, S. (2020). The use of probabilistic latent semantic analysis to identify scientific subject spaces and to evaluate the completeness of covering the results of dissertation studies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (106)), 21–28. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.209886
- Wang, Y., Zeng, A., Fan, Y., Di, Z. (2019). Ranking scientific publications considering the aging characteristics of citations. Scientometrics, 120 (1), 155–166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03117-9 9
- Xing, W., Ghorbani, A. (2004). Weighted PageRank algorithm. Proceedings. Second Annual Conference on Communication Networks and Services Research, 2004. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/dnsr.2004.1344743
- Manaskasemsak, B., Rungsawang, A., Yamana, H. (2010). Time-weighted web authoritative ranking. Information Retrieval, 14 (2), 133–157. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-010-9138-4
- Kuchansky, A., Biloshchytskyi, A., Andrashko, Y., Biloshchytska, S., Faizullin, A. (2022). The Scientific Productivity of Collective Subjects Based on the Time-Weighted PageRank Method with Citation Intensity. Publications, 10 (4), 40. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/publications10040040
- Citation Network Dataset: DBLP+Citation, ACM Citation network. Aminer. Available at: https://www.aminer.org/citation
- Tang, J., Zhang, J., Yao, L., Li, J., Zhang, L., Su, Z. (2008). ArnetMiner. Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1401890.1402008
- Microsoft Academic Graph. Microsoft. Available at: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/microsoft-academic-graph/
- DBLP Computer science bibliography. Available at: https://dblp.org/
- Association for Computing Machinery. Available at: https://www.acm.org/
- Xu, H., Kuchansky, A., Gladka, M. (2021). Devising an individually oriented method for selection of scientific activity subjects for implementing scientific projects based on scientometric analysis. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (3 (114)), 93–100. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.248040
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Yurii Andrashko, Oleksandr Kuchanskyi, Andrii Biloshchytskyi, Oleksandr Pohoriliak, Myroslava Gladka, Ganna Slyvka-Tylyshchak, Dmytro Khlaponin, Ivan Chychkan

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









