Determining the static characteristic of a measuring current transformer at a reduced load of the metering unit
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265068Keywords:
current transformer, static characteristic, current error, reduced load, regression lineAbstract
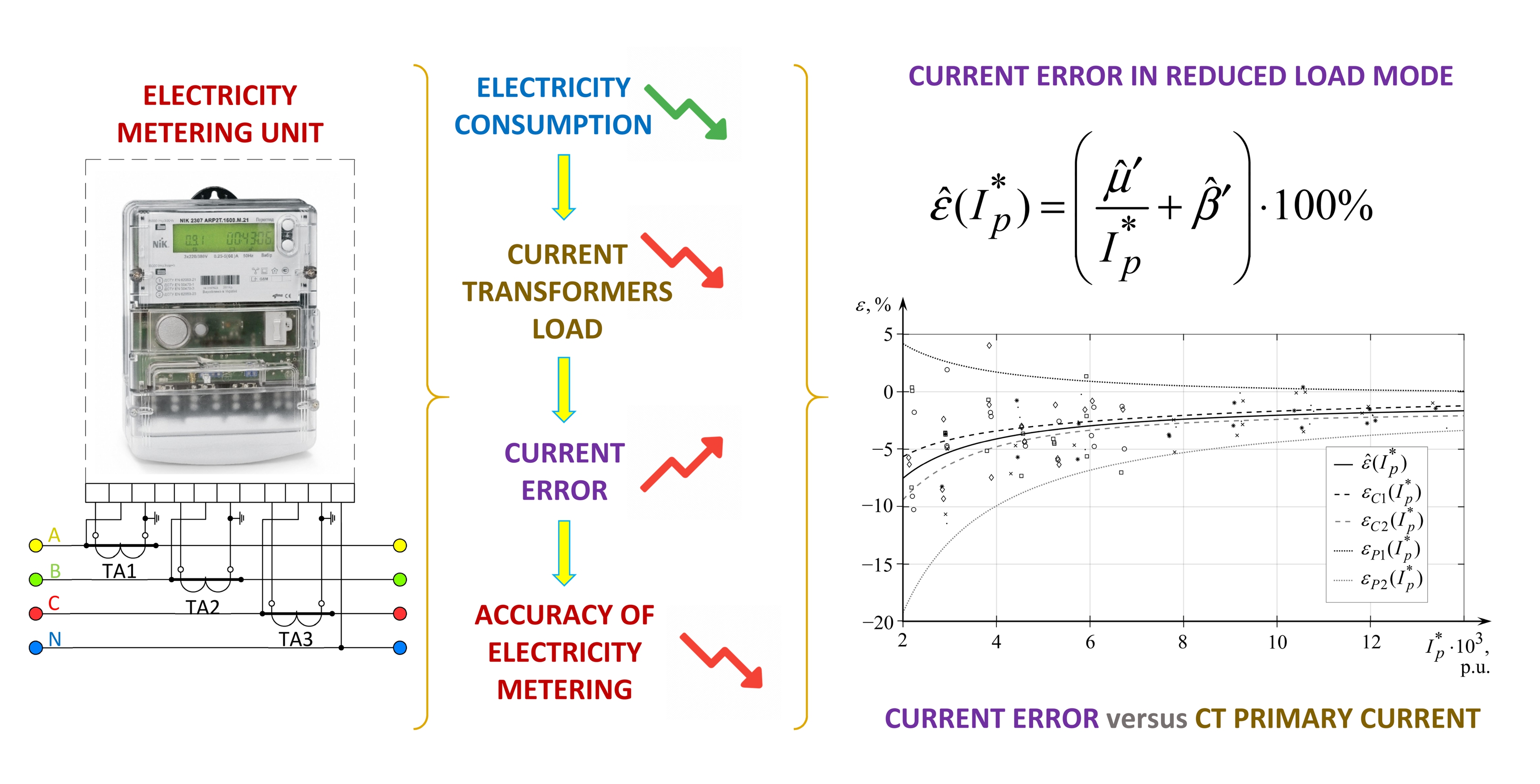
The object of the research is a measuring current transformer of the electromagnetic type, which is used as part of the electricity metering unit. The current transformers functioning in the mode of reduced primary current is accompanied by significant errors. The existence of such a regime for a long time due to downtime of production equipment leads to a significant underestimation of electricity. This leads to unjustified financial losses for energy supply companies as electricity in many countries has become more expensive. The static characteristic of the measuring current transformer at a reduced load of the metering unit is described by a linear statistical model. The parameters of the model are estimated on the basis of empirical data using methods of covariance analysis. The adequacy of the model is confirmed by analysis of regression residuals. The obtained statistical model of the static characteristic, unlike the known ones, is characterized by universality, as it describes current transformers with an arbitrary transformation ratio within the studied accuracy class of 0.5S. The uncertainty of the current error is estimated using the prediction intervals for the transformers secondary currents as a function of the primary currents, calculated on the basis of the obtained model. The prediction intervals for sample values of the current error were obtained through the application of the proposed approach for uncertainty estimation of such an error at a reduced load of the metering unit. It was found that the current error can reach −20 %. Taking into account the indicated intervals for measuring current transformers at a reduced load of the metering unit during billing will allow energy supply companies to increase the accuracy of commercial electricity metering.
References
- Global AC Current Transformers (CT) for Electrical Meters Market Research Report 2022 (2022). Market Reports World. Available at: https://www.marketreportsworld.com/global-ac-current-transformers-ct-for-electrical-meters-market-21024831
- IEC 61869-2:2012. Instrument transformers - Part 2: Additional requirements for current transformers. Available at: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/6050
- Instrument transformers. Application guide (2015). 1HSM 9543 40-00en. ABB. Available at: https://library.e.abb.com/public/94c2ba5a2f381077c1257df000504e0c/1HSM%209543%2040-00en%20IT%20Application%20Guide%20Ed4.pdf
- Quarterly report on European electricity markets (2022). Market Observatory for Energy, 15 (1). Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/energy_climate_change_environment/quarterly_report_on_european_electricity_markets_q1_2022.pdf
- Soinski, M., Pluta, W., Zurek, S., owski, A. K. (2014). Metrological attributes of current transformers in electrical energy meters. International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 44 (3-4), 279–284. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/jae-141790
- Kaczmarek, M. (2012). Method of current transformer metrological properties estimation for transformation of distorted currents. 2012 IEEE International Power Modulator and High Voltage Conference (IPMHVC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ipmhvc.2012.6518847
- Mingotti, A., Peretto, L., Bartolomei, L., Cavaliere, D., Tinarelli, R. (2020). Are Inductive Current Transformers Performance Really Affected by Actual Distorted Network Conditions? An Experimental Case Study. Sensors, 20 (3), 927. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030927
- Ghaderi, A., Mingotti, A., Peretto, L., Tinarelli, R. (2019). Inductive current transformer core parameters behaviour vs. temperature under different working conditions. 23rd IMEKO TC4 International Symposium Electrical & Electronic Measurements Promote Industry 4.0. Xi’an, 107–112. Available at: https://www.imeko.org/publications/tc4-2019/IMEKO-TC4-2019-024.pdf
- Puzovic, S., Koprivica, B., Milovanovic, A., Djekic, M. (2014). Analysis of measurement error in direct and transformer-operated measurement systems for electric energy and maximum power measurement. Facta Universitatis - Series: Electronics and Energetics, 27 (3), 389–398. doi: https://doi.org/10.2298/fuee1403389p
- Lesniewska, E., Rajchert, R. (2019). Behaviour of measuring current transformers with cores composed from different magnetic materials at non‐rated loads and overcurrents. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 13 (7), 944–948. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-smt.2018.5176
- Lee, S.-J., Jung, H.-K., Chung, T.-K., Lee, Y.-S., Ro, J.-S. (2019). Ratio Error Reduction of a Current Transformer Using Multiple Winding Technique. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 14 (2), 645–651. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-018-00040-6
- Vasylets, K., Kvasnikov, V., Vasylets, S. (2022). Refinement of the mathematical model of electrical energy measurement uncertainty in reduced load mode. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (8 (118)), 6–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.262260
- Ballal, M. S., Wath, M. G., Suryawanshi, H. M. (2020). Measurement Current Transformer Error Compensation by ANN Methodology. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 101 (3), 261–271. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-020-00454-9
- Ballal, M. S., Wath, M. G., Venkatesh, B. (2018). Current Transformer Accuracy Improvement by Digital Compensation Technique. 2018 20th National Power Systems Conference (NPSC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/npsc.2018.8771706
- Wath, M. G., Raut, P., Ballal, M. S. (2016). Error compensation method for current transformer. 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icpeices.2016.7853244
- C57.13-2016 - IEEE Standard Requirements for Instrument Transformers. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ieeestd.2016.7501435
- Montgomery, D. C. (2020). Design and analysis of experiments. John Wiley & Sons, 752. Available at: https://www.wiley.com/en-ie/Design+and+Analysis+of+Experiments,+9th+Edition,+EMEA+Edition-p-9781119638421
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Kateryna Vasylets, Volodymyr Kvasnikov, Sviatoslav Vasylets

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








