Building a model for planning rapid delivery of containers by rail under the conditions of intermodal transportation based on robust optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265668Keywords:
intermodal container transportation, modular container trains, robust optimization, double-circuit genetic algorithmAbstract
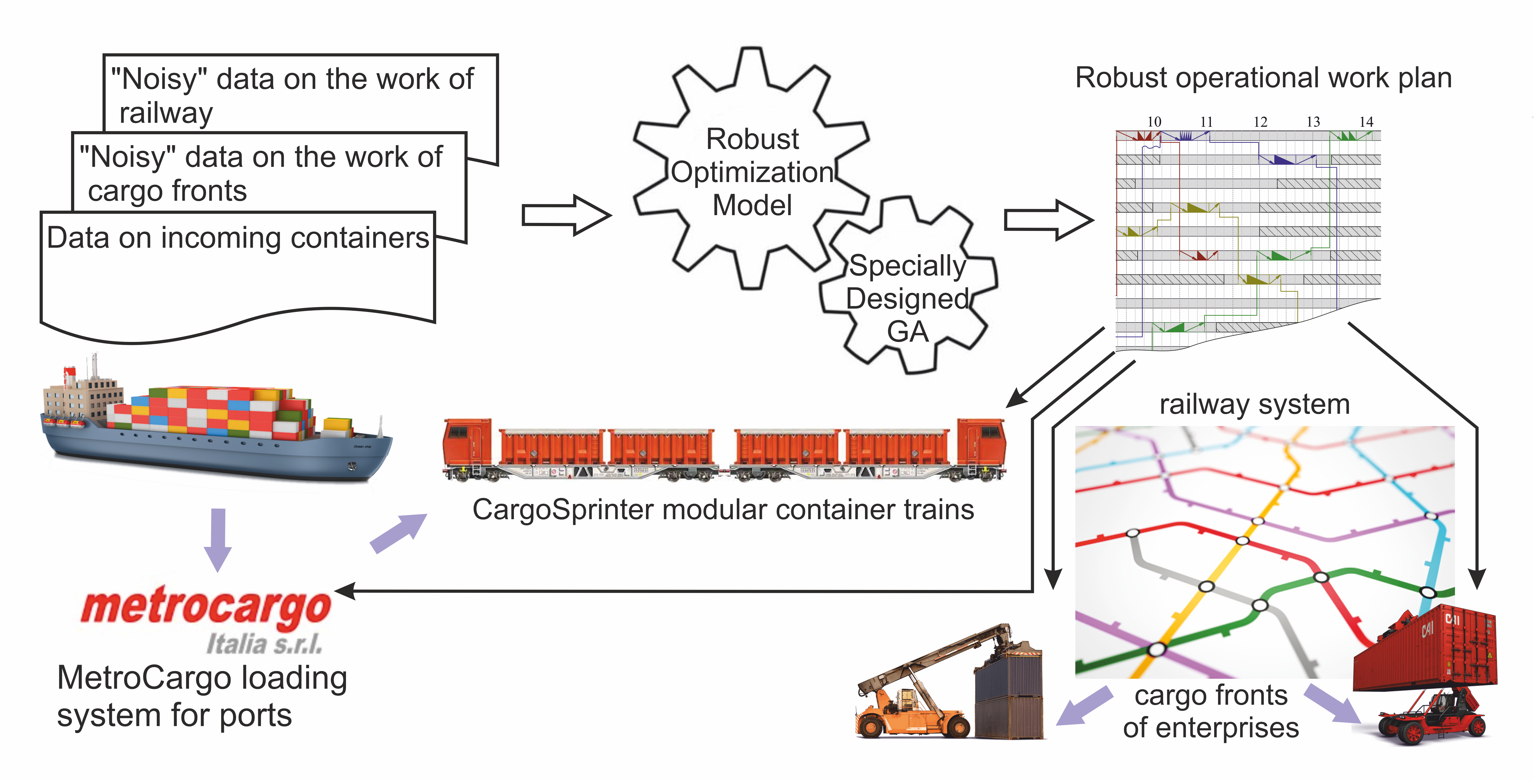
This paper considers the possibility of devising a technology of fast railroad communication for the transportation of containers between the port and customer enterprises in the course of intermodal transportation. The purpose of technology development is to reduce the share of the use of trucks on intermodal routes and thus solve a number of related environmental, transport, municipal, and economic problems. The devised technology is based on the principles of bringing the railroad as close as possible to the end points of the route, minimizing the number of intermediate modes of transport, and enabling the maximum speed of movement of containers by rail. For this purpose, the use of MetroCargo™ freight terminals and CargoSprinter modular trains is proposed. In the course of the study, the task to reliably plan the operation of the fleet of such trains for the delivery of containers between the port and enterprises under the conditions of "noisy" initial data was set and solved. To this end, the problem was formalized in the form of a model of mixed programming, based on the principles of robust optimization. To optimize the model taking into consideration the principles of robustness, a procedure was proposed that uses a two-circuit genetic algorithm. As a result of the simulation, it was found that the resulting plan was only 6.5 % inferior to the objective criterion of the plan, which was compiled without taking into consideration robustness. It was proved that the devised model makes it possible to build an operational plan for the delivery of containers by rail, which is close to optimal. At the same time, the plan is implemented even in the case of the most unfavorable set of circumstances in the form of delays, shifts in the time windows of the cargo fronts, etc., that is, under the actual conditions of the transport process
References
- Yan, B., Jin, J. G., Zhu, X., Lee, D.-H., Wang, L., Wang, H. (2020). Integrated planning of train schedule template and container transshipment operation in seaport railway terminals. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 142, 102061. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2020.102061
- Liu, D., Yang, H. (2012). Dynamic Pricing Model of Container Sea-Rail Intermodal Transport on Single OD Line. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 12 (4), 122–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1570-6672(11)60216-x
- Liu, D., Yang, H. (2013). Optimal Slot Control Model of Container Sea-Rail Intermodal Transport based on Revenue Management. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 96, 1250–1259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.08.142
- Fan, Q., Jin, Y., Wang, W., Yan, X. (2019). A performance-driven multi-algorithm selection strategy for energy consumption optimization of sea-rail intermodal transportation. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 44, 1–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.11.007
- Muravev, D., Hu, H., Rakhmangulov, A., Mishkurov, P. (2021). Multi-agent optimization of the intermodal terminal main parameters by using AnyLogic simulation platform: Case study on the Ningbo-Zhoushan Port. International Journal of Information Management, 57, 102133. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102133
- Ambrosino, D., Asta, V., Crainic, T. G. (2021). Optimization challenges and literature overview in the intermodal rail-sea terminal. Transportation Research Procedia, 52, 163–170. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2021.01.089
- Yan, B., Zhu, X., Lee, D.-H., Jin, J. G., Wang, L. (2020). Transshipment operations optimization of sea-rail intermodal container in seaport rail terminals. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 141, 106296. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106296
- Morganti, G., Crainic, T. G., Frejinger, E., Ricciardi, N. (2020). Block planning for intermodal rail: Methodology and case study. Transportation Research Procedia, 47, 19–26. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2020.03.068
- Nair, R., Miller-Hooks, E. D., Mahmassani, H. S., Arcot, V. C., Kuo, A., Zhang, K. et. al. (2008). Market Potential for International Rail-Based Intermodal Services in Europe. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2066 (1), 21–30. doi: https://doi.org/10.3141/2066-03
- Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A. (2002). Robust optimization – methodology and applications. Mathematical Programming, 92 (3), 453–480. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101070100286
- Kozan, E. (2000). Optimising container transfers at multimodal terminals. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 31 (10-12), 235–243. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-7177(00)00092-3
- Metrocargo and MetrocargoCity innovative solution for intermodal shipment. Available at: http://www.bestufs.net/download/Workshops/BESTUFS_II/Vilnius_Sep07/BESTUFS_Vilinius_Sep07_Ferraris_I-Log.pdf
- Parkhomenko, L. O., Kalashnikova, T. Yu., Prokhorov, V. M. (2021). Pidvyshchennia interoperabelnosti zaliznychnoi transportnoi systemy Ukrainy pry zdiysnenni intermodalnykh konteinernykh perevezen na osnovi tekhnolohiyi MetroCargo™. Innovations and prospects of world science – Proceedings of IV International Scientific and Practical Conference. Vancouver, 312–317.
- Prokopov, A., Prokhorov, V., Kalashnikova, T., Golovko, T., Bohomazova, H. (2021). Constructing a model for the automated operative planning of local operations at railroad technical stations. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (3 (111)), 32–41. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.233673
- Ben-Tal, A., Goryashko, A., Guslitzer, E., Nemirovski, A. (2004). Adjustable robust solutions of uncertain linear programs. Mathematical Programming, 99 (2), 351–376. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-003-0454-y
- Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A., Roos, C. (2003). Extended Matrix Cube Theorems with Applications to μ-Theory in Control. Mathematics of Operations Research, 28 (3), 497–523. doi: https://doi.org/10.1287/moor.28.3.497.16392
- Shor, N. Z. (1985). Minimization Methods for Non-Differentiable Functions. Springer, 164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-82118-9
- Yang, T., Kuo, Y., Cho, C. (2007). A genetic algorithms simulation approach for the multi-attribute combinatorial dispatching decision problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 176 (3), 1859–1873. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2005.10.048
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Larysa Parkhomenko, Tetiana Butko, Viktor Prokhorov, Tetiana Kalashnikova, Tetiana Golovko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








