Application of the principle of information objects description formalization for the design of information protection systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269030Keywords:
databases with incomplete information, automatic designer of information security systems, object of protection of the general structureAbstract
The development of information independence of the State requires the introduction of the latest technologies for analyzing, storing, processing, and transmitting information. The focus of this work is improving information security systems with limited access, in particular the development of new methods of designing such systems, which are characterized by minimal influence of the subject-designer on the design process. The object of the study is the methodology and means of designing systems for restricting and controlling physical access, as well as access to information at objects of information activity and information and telecommunication systems of Ukraine.
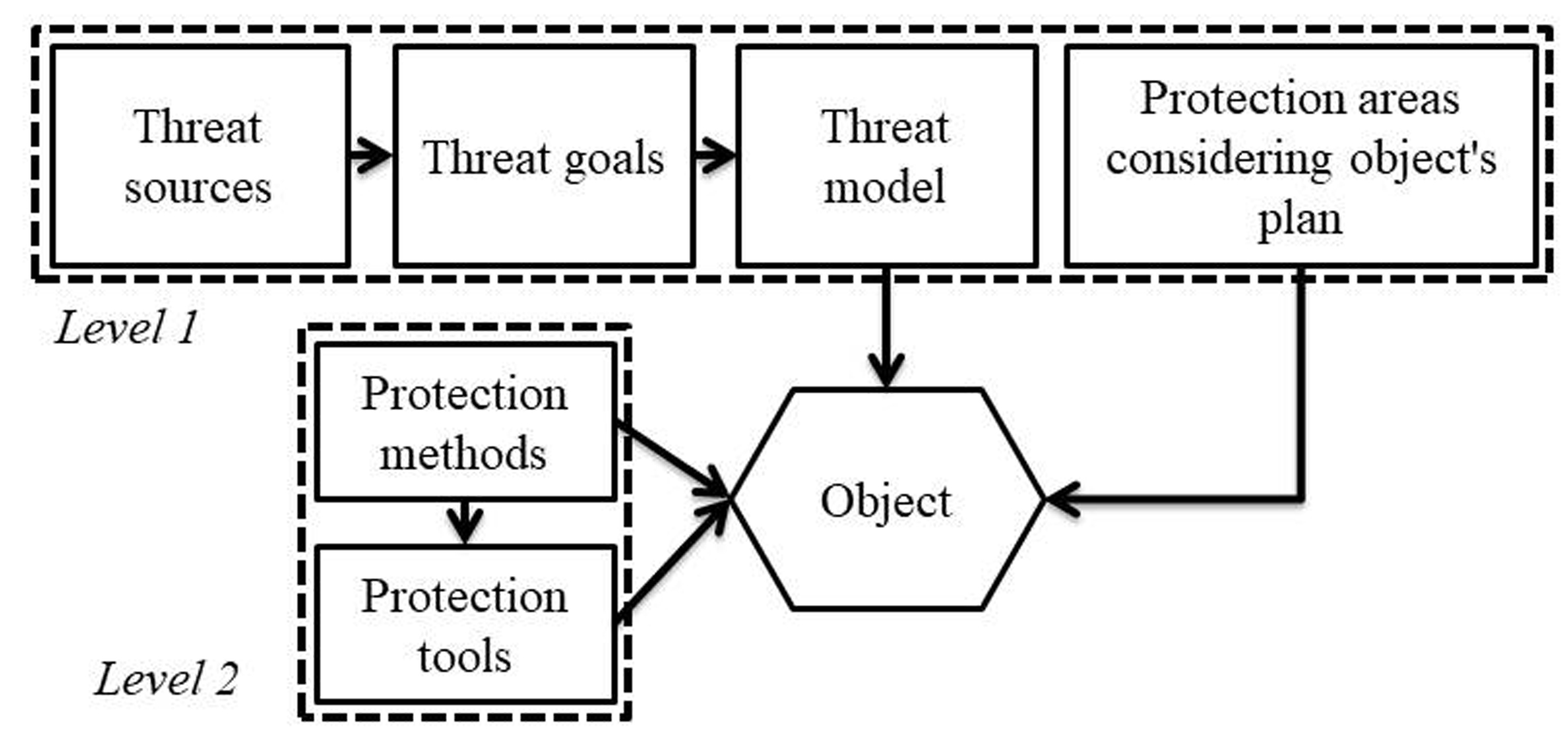
To exclude the influence of the subject of the designer, it is necessary to improve the design process itself. In this paper, the possibility of creating an automatic design system based on the representation of protection objects in the form of objects of a common structure has been mathematically proved. Such a structure combines both telecommunication objects and objects of information activity. Changes in the legislative, regulatory, and technical bases of information protection necessary for the implementation of the proposed system have been determined, in particular, granting the State Communications Committee of Ukraine new powers that ensure the balance of interests of the customer of protection systems and executors. The possibility of formalizing the representation of data on arbitrary objects of protection is shown. This representation makes it possible to create open library semantic databases with incomplete data on the object of protection.
A theoretical base has been built that makes it possible to determine the correspondence between the set of threats to the information security of the object and the unambiguous corresponding list of countermeasures. At the same time, information protection projects are distinguished by evolution and uniformity of choice of a set of means of protection to any threats to objects of arbitrary complexity
References
- Wu, T., Zhang, R., Dai, P., Liu, S. (2018). Research on information system architecture of standardized organization based on data repository. 2018 IEEE 4th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/itoec.2018.8740482
- Grishina, N. V. (2007). Organizaciya kompleksnoy sistemy zashchity informacii. Moscow: Gelios ARV, 256.
- Zakaria, K. N., Othman, S. H., Zainal, A. (2019). Review of Cybersecurity Audit Management and Execution Approaches. 2019 6th International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icriis48246.2019.9073641
- Karagiannis, S., Manso, M., Magkos, E., Ribeiro, L. L., Campos, L. (2021). Automated and On-Demand Cybersecurity Certification. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/csr51186.2021.9527958
- Turner, R. C. (2022). Process Mining for Asymmetric Cybersecurity Audit. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/csr54599.2022.9850298
- Progonov, D., Yarysh, M. (2022). Analyzing the accuracy of detecting steganograms formed by adaptive steganographic methods when using artificial neural networks. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (115)), 45–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251350
- Isazadeh, A., Karimpour, H. (2011). Formal Specification of Control Software Systems Using Behavioral Views. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 2 (1), 62–67. Available at: http://www.ijarcs.info/index.php/Ijarcs/article/view/246/236
- Mierlo, S. V., Vangheluwe, H. (2018). Introduction to statecharts modeling, simulation, testing, and deployment. 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/wsc.2018.8632384
- Hoffmann, J. L. C., Horstmann, L. P., Wagner, M., Vieira, F., de Lucena, M. M., Frohlich, A. A. (2022). Using Formal Methods to Specify Data-Driven Cyber-Physical Systems. 2022 IEEE 31st International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/isie51582.2022.9831686
- Eckhart, M., Ekelhart, A., Weippl, E. (2022). Automated Security Risk Identification Using AutomationML-Based Engineering Data. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 19 (3), 1655–1672. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tdsc.2020.3033150
- Cha, S.-C., Yeh, K.-H. (2018). An ISO/IEC 15408-2 Compliant Security Auditing System with Blockchain Technology. 2018 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS). https://doi.org/10.1109/cns.2018.8433185
- Buddy System. Available at: https://www.securitylab.ru/software/234275.php
- Budko, M., Vasylenko, V., Korolenko, M., Butochnov, O. (2002). Systema zakhystu informatsiyi vid NSD „RUBIZh”. Praktychni aspekty realizatsiyi kontseptsii tsentralizovanoho upravlinnia bezpekoiu korporatyvnoi systemy. Pravove, normatyvne ta metrolohichne zabezpechennia system zakhystu informatsiyi v Ukraini, 4, 154–161.
- Hodel, R. (2013). An Introduction to Mathematical Logic. Dover Publications, 512.
- Shoenfield, J. (2018). Mathematical Logic. A K Peters/CRC Press, 356. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203749456
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Vladimir Lutsenko, Dmytro Progonov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








