Development of a method for assessing the functioning of a grain product sub-complex using mathematical modeling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.276433Keywords:
assessment methodology, growth rate, integral indicator, mathematical modeling, agro-industrial complexAbstract
The object of the study is the process of functioning of enterprises of the grain product subcomplex. In the course of the study, the problem of the growth rate and the peculiarities of the functioning of enterprises of the grain product subcomplex were solved.
An assessment of the functioning of the grain product subcomplex was carried out Republic of Kazakhstan using mathematical modeling, for which a methodology has been developed that allows considering factors with a heterogeneous metric, which includes the following steps:
1) index analysis twenty-one indicators, divided into groups;
2) development of formulas for calculation and integral indicators characterizing their dynamics;
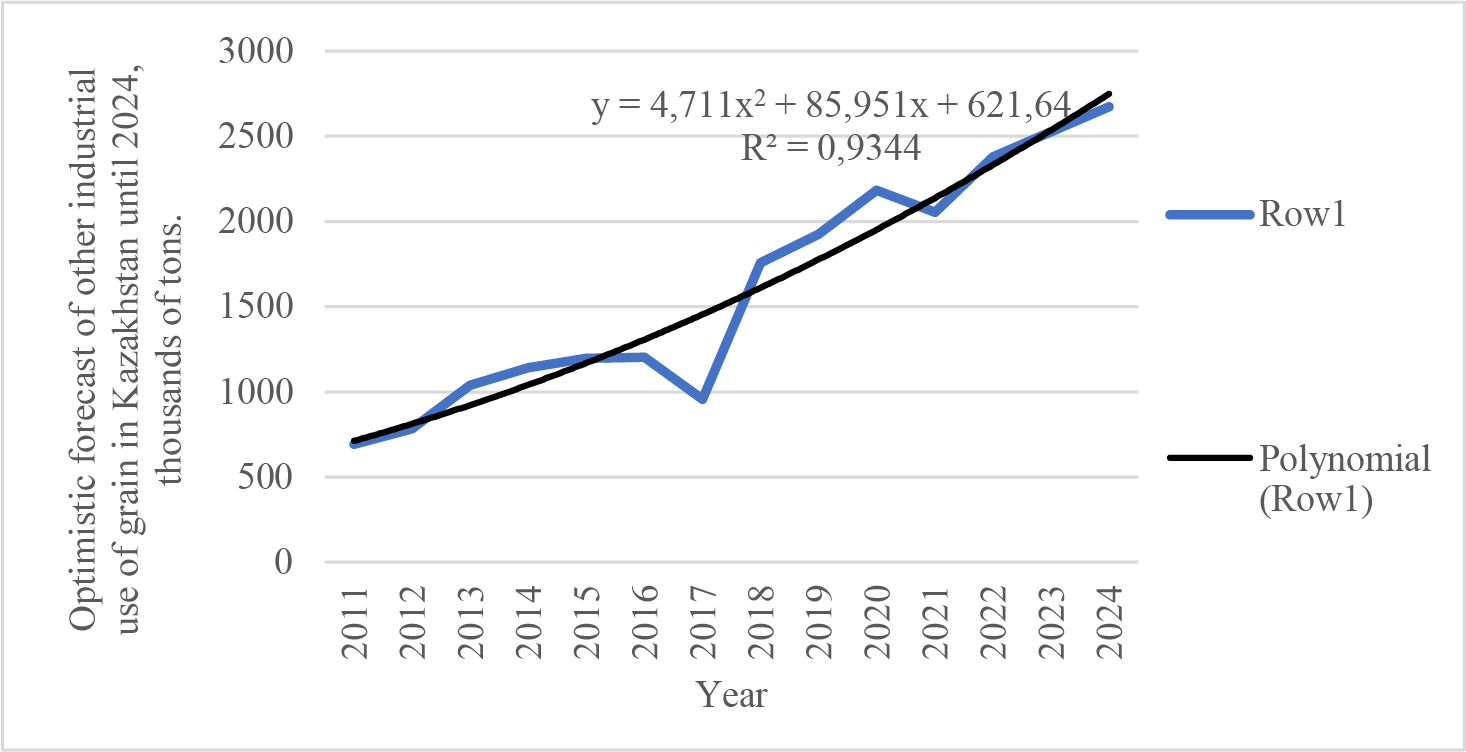
3) determining the pace of functioning of the grain product subcomplex for 2011–2021. Graphs were made and a forecast of the performance indicators of the subcomplex until 2024 is presented for one of each group with the maximum coefficient of determination R2. According to three scenarios: optimistic, probabilistic and pessimistic. R2 is an indicator of the quality of forecasts: than the closer its value is to one, the higher the probability of execution. For eleven charts, the coefficient of determination is in the range from 0.9003 (pessimistic forecast for other industrial use of grain) to 0.9838 (optimistic forecast for the number of granaries). For ten, from 0.8025 to 0.8702, and for nine, from 0.705 to 0.7932. This means that the reliability of the calculations for twenty-nine forecast options is in the range from 70 to 98 %. This indicates fairly objective predictive values of the subcomplex performance indicators until 2024. Based on the results of the studies, optimistic and pessimistic scenarios are more likely to be implemented.
References
- Verkhovtsev, A. A. (2019). Priority directions of strategic development of the market of grain. International Agricultural Journal, 1 (367). doi: https://doi.org/10.24411/2587-6740-2019-11015
- Beisekova, P. D., Bolatkyzy, S., Abutalipova, Zh. A. (2022). Features of grain product cluster: market reorientation. Problems of AgriMarket, 1, 120–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.46666/2022-1.2708-9991.14
- Albeaik, S., Kaltenberg, M., Alsaleh, M., Hidalgo, C. A. (2017). 729 new measures of economic complexity (Addendum to Improving the Economic Complexity Index). arXiv. doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1708.04107
- Iyer, K. C., Banerjee, P. S. (2016). Measuring and benchmarking managerial efficiency of project execution schedule performance. International Journal of Project Management, 34 (2), 219–236. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2015.10.008
- Chen, S., Huang, F., Zeng, W. (2017). Comments on systematic methodologies of action research in the new millennium: A review of publications 2000–2014. Action Research, 16 (4), 341–360. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1476750317691103
- Gungor, A., Akyuz, A. O., Şirin, C., Tuncer, A. D., Zaman, M., Gungor, C. (2019). Importance of mathematical modeling in innovation. Mathematical Modeling, 3 (1), 32–34. Available at: https://stumejournals.com/journals/mm/2019/1/32.full.pdf
- Hilty, L., Aebischer, B. (Eds.) (2015). ICT innovations for sustainability. Springer, 474. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09228-7
- Khanzadi, M., Nasirzadeh, F., Hassani, S. M. H., Nejad Mohtashemi, N. (2016). An integrated fuzzy multi-criteria group decision making approach for project delivery system selection. Scientia Iranica, 23 (3), 802–814. doi: https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2016.2160
- Konietschke, F., Schwab, K., Pauly, M. (2020). Small sample sizes: A big data problem in high-dimensional data analysis. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 30 (3), 687–701. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280220970228
- Copestake, J. (2014). Credible impact evaluation in complex contexts: Confirmatory and exploratory approaches. Evaluation, 20 (4), 412–427. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1356389014550559
- Orlov, V., Ivanova, T., Kadyshev, E., Chernyshova, T., Prokopiev, A., Ivanova, A. (2022). Mathematical Modeling in Forecasting Reproduction Processes in Agriculture. XIV International Scientific Conference “INTERAGROMASH 2021". Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Springer. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81619-3_37
- Mailybayeva, E., Imanbayev, A., Yessirkep, G., Mussayeva, S., Shingissov, A. (2022). Developing a procedure for controlling the rheological properties of dough during its kneading based on a parametric model. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (11 (117)), 31–38. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.257323
- Lee, S. J., Lee, E. H., Oh, D. S. (2017). Establishing the innovation platform for the sustainable regional development: Tech-valley project in sejong city, Korea, World Technopolis Review, 6 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.7165/wtr17b0904.16
- Lennert, J. (2018). Complex spatial modelling possibilities of the socio-economic changes of Hungary – potential approaches and methods. Mathematical Modeling, 2 (4), 160–162. Available at: https://stumejournals.com/journals/mm/2018/4/160.full.pdf
- Liu, J., Liu, P., Liu, S.-F., Zhou, X.-Z., Zhang, T. (2014). A study of decision process in MCDM problems with large number of criteria. International Transactions in Operational Research, 22 (2), 237–264. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12102
- Minina, N. N. (2018). Formation of equity capital of agricultural organizations of the Republic of Belarus. Achievements of science and technology of the agro-industrial complex, 32 (1), 50–56. doi: https://doi.org/10.24411/0235-2451-2018-10111
- Njøs, R., Jakobsen, S.-E. (2016). Cluster policy and regional development: scale, scope and renewal. Regional Studies, Regional Science, 3 (1), 146–169. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/21681376.2015.1138094
- Coryn, C. L. S., Noakes, L. A., Westine, C. D., Schröter, D. C. (2010). A Systematic Review of Theory-Driven Evaluation Practice From 1990 to 2009. American Journal of Evaluation, 32 (2), 199–226. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098214010389321
- Rezaei, J. (2015). Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega, 53, 49–57. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2014.11.009
- Shani, A. B. (Rami), Coghlan, D. (2019). Action research in business and management: A reflective review. Action Research, 19 (3), 518–541. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1476750319852147
- Polezhaev, V. D., Polezhaeva, L. N. (2018). Nonlinear paired regression models in the econometrics course. Sovremennye problemy nauki i obrazovaniya, 4. Available at: https://s.science-education.ru/pdf/2018/4/27855.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Perizat Beisekova, Assel Ilyas, Yelena Kaliyeva, Zhanar Kirbetova, Meruert Baimoldayeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









