Influence of the monomer form of orthosilicic acid on the stability of polyalumosilicon coagulants and their efficiency in the treatment of drinking water
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.282696Keywords:
aluminum hydroxychloride, composite coagulants, orthosilicic acid, aluminosilicic coagulants, water purificationAbstract
The object of the study was polymeric alumino-silicon coagulants modified with the monomeric form of orthosilicate acid. The methods and precursors for obtaining stable solutions of composite alumino-silicon coagulants, as well as the effectiveness of coagulation treatment of a surface source of drinking water, were considered. The samples were obtained in two ways:
1) partial hydrolysis of medium-basic aluminum polyhydroxychloride together with sodium silicate solution (PolyAKKg);
2) mixing highly basic aluminum polyhydroxychloride together with a ready solution of orthosilicic acid with a high (above 50 %) monomer content (PolyAKKz).
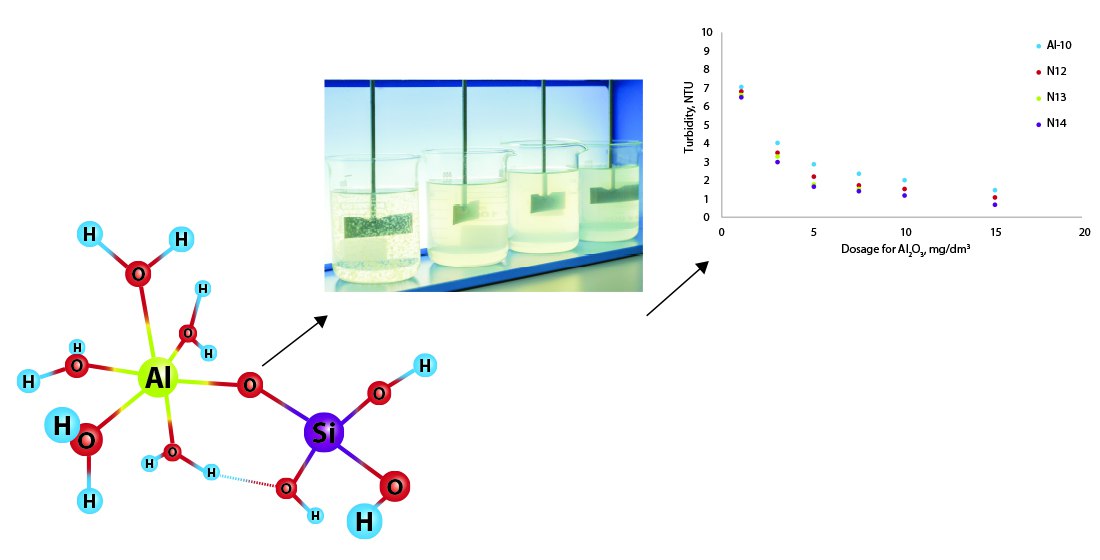
In the course of research, the problem of the short shelf life of composite alumino-silicon coagulants was solved, which had prevented their industrial implementation in drinking water preparation processes.
It was established that the resulting composite coagulants had the following parameters: Al2O3, 8.075–8.725 %; SiO2, 0.058–0.725 %; Al/Si ratio, 20–250; basicity, 41.4–80.7 %. The effectiveness of the obtained composite coagulant and commercial coagulant was tested under laboratory conditions at a surface source of drinking water by reducing turbidity and by the concentration of residual aluminum in the water after coagulation. The results showed that composite coagulants of the PolyAKKz type with the addition of orthosilicic acid with a high monomer content (above 50 %) obtained using methanesulfonic acid hydrolysis as a precursor have higher solution stability compared to other precursors or coagulants of the PolyAKKg type.
The study results could be used to design new composite coagulants for the preparation of drinking water from surface sources with high turbidity
References
- Zhang, Z., Jing, R., He, S., Qian, J., Zhang, K., Ma, G. et al. (2018). Coagulation of low temperature and low turbidity water: Adjusting basicity of polyaluminum chloride (PAC) and using chitosan as coagulant aid. Separation and Purification Technology, 206, 131–139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.051
- Mokienko, A. V., Petrenko, N. F., Gozhenko, A. I. (2011). Obezzarazhivaniya vody. Gigienicheskie i mediko-ekologicheskie aspekty. Vol. 1. Khlor i ego soedineniya. Odessa: TES, 484. Available at: https://www.onmedu.edu.ua/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/10876/Mokienko.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- Bigaj, I. M., Brzozowska, R., Łopata, M., Wiśniewski, G., Dunalska, J. A., Szymański, D., Zieliński, R. A. (2013). Comparison of coagulation behaviour and floc characteristics of polyaluminium chloride (PAX 18, PAX XL19H, ALCAT) with surface water treatment. Limnological Review, 13 (2), 73–78. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/limre-2013-0008
- Liu, Y., Wang, S., Hua, J. (2000). Synthesis of complex polymeric flocculant and its application in purifying water. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 76 (14), 2093–2097. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4628(20000628)76:14<2093::aid-app13>3.0.co;2-l
- Lin, Q.-W., He, F., Ma, J.-M., Zhang, Y., Liu, B.-Y., Min, F.-L. et al. (2017). Impacts of residual aluminum from aluminate flocculant on the morphological and physiological characteristics of Vallisneria natans and Hydrilla verticillata. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 145, 266–273. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.037
- Sarkar, A. K., Mandre, N. R., Panda, A. B., Pal, S. (2013). Amylopectin grafted with poly (acrylic acid): Development and application of a high performance flocculant. Carbohydrate Polymers, 95 (2), 753–759. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.025
- Pro zatverdzhennia Derzhavnykh sanitarnykh norm ta pravyl "Hihienichni vymohy do vody pytnoi, pryznachenoi dlia spozhyvannia liudynoiu" (DSanPiN 2.2.4-171-10). Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0452-10#Text
- Liu, X., Xu, Q., Wang, D., Wu, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, Y. et al. (2019). Unveiling the mechanisms of how cationic polyacrylamide affects short-chain fatty acids accumulation during long-term anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Research, 155, 142–151. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.036
- Igarashi, M., Matsumoto, T., Yagihashi, F., Yamashita, H., Ohhara, T., Hanashima, T. et al. (2017). Non-aqueous selective synthesis of orthosilicic acid and its oligomers. Nature Communications, 8 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00168-5
- Burenin, V. V., Sova, A. N., Marinko, A. N. (2014). Review of Oil-Bearing Effluent Cleaning Methods. Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, 49 (9-10), 690–695. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-014-9820-2
- Shablovski, V., Tuchkoskaya, A., Rukhlya, V., Pap, O. (2021). Coagulant-flocculant from secondary resources for treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Water and water purification technologies. SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL NEWS, 30 (2), 27–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.20535/2218-930022021240165
- Gao, B. Y., Hahn, H. H., Hoffmann, E. (2002). Evaluation of aluminum-silicate polymer composite as a coagulant for water treatment. Water Research, 36 (14), 3573–3581. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(02)00054-4
- Krewski, D., Yokel, R. A., Nieboer, E., Borchelt, D., Cohen, J., Harry, J. et al. (2007). Human Health Risk Assessment for Aluminium, Aluminium Oxide, and Aluminium Hydroxide. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, 10 (sup1), 1–269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400701597766
- Zhao, Y., Zheng, Y., Peng, Y., He, H., Sun, Z. (2021). Characteristics of poly-silicate aluminum sulfate prepared by sol method and its application in Congo red dye wastewater treatment. RSC Advances, 11 (60), 38208–38218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra06343j
- Pat. No. CN100369827C. Process for producing basic poly aluminium sulfate silicate by one step method (2005). No. CNB2005101009790A; declareted: 10.11.2005; published: 20.02.2008. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN100369827C/en
- Pasenko, O., Mandryka, A., Khrupchyk, Ye., Vereshchak, V. (2022). Stable solutions of orthosilicic acid. Voprosy Khimii i Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 4, 56–60. doi: https://doi.org/10.32434/0321-4095-2022-143-4-56-60
- Voda pytna. DSTU 7525:2014. Available at: http://iccwc.org.ua/docs/dstu_7525_2014.pdf
- Standards for Drinking Water Quality. GB 5749-2006. Available at: https://www.aqsiq.net/pdf/China_GB_5749-2006_Standards_for_Drinking_Water_Quality.pdf
- Mandryka, A., Pasenko, O., Vereschak, V., Osokin, Y. (2022). Quantum chemical modeling of orthosilicic acid clusters with some acids in aqueous solution. Journal of Chemistry and Technologies, 30 (2), 159–165. doi: https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v30i2.258938
- Mandryka, A. H., Pasenko, O. O., Vereschak, V. H., Osokin, Y. S. (2023). Modeling of complexes of low-basic aluminum oxychloride with orthosilicate acids in aqueous solution. Journal of Chemistry and Technologies, 31 (1), 44–50. doi: https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v31i1.271537
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Artem Mandryka, Oleksandr Pasenko, Viktor Vereschak, Yevhen Osokin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








