Improving the work process efficiency of a tillage module for pre-sowing tillage
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.284597Keywords:
soil environment, arable horizon, differentiated structure, pre-sowing treatment, simulation, modelingAbstract
The formation of a differentiated structure of the arable horizon during the pre-sowing processing of the grant is a relevant task that can be solved by designing appropriate soil-processing technical means.
A scientific hypothesis has been put forward, according to which increasing the efficiency of the process of forming a differentiated structure of the arable horizon can be achieved by improving the design and substantiating the structural and technological parameters of the tillage module for pre-sowing tillage. Numerical simulation was carried out in the Simcenter STAR-CCM+ software package using the Lagrangian multiphase model employing the discrete element method. Calculation of second-order regression equations and statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out in the Wolfram Cloud software package.
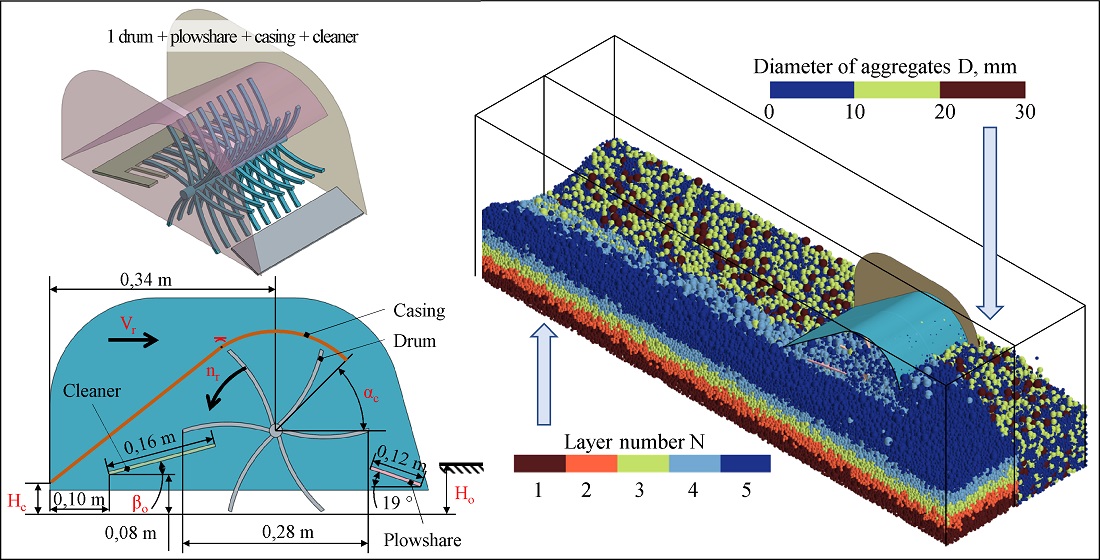
As a result of the simulation of the improved design of the tillage module, which includes one drum, plowshare, casing, and cleaner, it was found that it performs the operation of separation and redistribution of soil aggregates with almost the same efficiency as the basic design with 2 drums and plowshare.
As a result of the simulation of the work process of the improved tillage module, regression equations of the content of the 10–30 mm fraction in the 0–4 cm soil layer and the content of the 0–10 mm fraction in the 4–8 cm soil layer from the research factors were obtained. The chosen factors of influence were a casing outlet clearance, casing inlet clearance angle, cleaner inclination angle, drum rotation frequency, unit movement speed, and processing depth. Solving the problem of multi-criteria optimization, the rational structural and technological parameters of the tillage module for pre-sowing tillage were calculated
References
- Atkinson, B. S. (2008). Identification of optimum seedbed preparation for establishment using soil structural visualization. University of Nottingham. Available at: https://projectblue.blob.core.windows.net/media/Default/Research%20Papers/Cereals%20and%20Oilseed/3031_final_report_sr06.pdf
- Yankov, P., Drumeva, M. (2017). Effect of pre-sowing soil tillage for wheat on the crop structure and the yield components in Dobrudzha region. Agricultural Science and Technology, 9 (2), 124–128. doi: https://doi.org/10.15547/ast.2017.02.022
- Lemic, D., Pajač Živković, I., Posarić, M., Bažok, R. (2021). Influence of Pre-Sowing Operations on Soil-Dwelling Fauna in Soybean Cultivation. Agriculture, 11 (6), 474. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060474
- Sarkar, P., Upadhyay, G., Raheman, H. (2021). Active-passive and passive-passive configurations of combined tillage implements for improved tillage and tractive performance: A review. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 19 (4), e02R01. doi: https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2021194-18387
- Okolelova, A. A., Glinushkin, A. P., Sviridova, L. L., Podkovyrov, I. Y., Nefedieva, E. E., Egorova, G. S. et al. (2022). Biogeosystem Technique (BGT*) Methodology Will Provide Semiarid Landscape Sustainability (A Case of the South Russia Volgograd Region Soil Resources). Agronomy, 12 (11), 2765. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112765
- Hartemink, A. E., Zhang, Y., Bockheim, J. G., Curi, N., Silva, S. H. G., Grauer-Gray, J. et al. (2020). Soil horizon variation: A review. Advances in Agronomy, 125–185. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2019.10.003
- Bronick, C. J., Lal, R. (2005). Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma, 124 (1-2), 3–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.005
- Shevchenko, I. A. (2016). Keruvannia ahrofizychnym stanom gruntovoho seredovyshcha. Kyiv: Vydavnychyi dim «Vinichenko», 320.
- Pastukhov, V. I., Bielovol, S. A. (2014). Investigation of displacement of crushed soil in a vertical plane under the action of rotary tillage machines. Engineering of nature management, 2 (2), 80–83. Available at: https://repo.btu.kharkov.ua/bitstream/123456789/3582/1/16.pdf
- Sereda, L., Trukhanska, E., Shvets, L. (2019). Development and research of soil machine for strip-till technology with active milling working bodies. Vibrations in Engineering and Technology, 4 (95), 65–71. doi: https://doi.org/10.37128/2306-8744-2019-4-8
- Levchenko, P. (2014). Mashyny z aktyvnymy robochymy orhanamy v silhospvyrobnytstvi Ukrainy. Tekhniko-tekhnolohichni aspekty rozvytku ta vyprobuvannia novoi tekhniky i tekhnolohii dlia silskoho hospodarstva Ukrainy, 18 (1), 309–316. Available at: http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Ttar_2014_18%281%29__34
- Toscano, P., Brambilla, M., Cutini, M., Bisaglia, C. (2022). The Stony Soils Reclamation Systems in Agricultural Lands: A Review. Agricultural Sciences, 13 (04), 500–519. doi: https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2022.134034
- Kalinitchenko, V. P., Glinushkin, A. P., Sharshak, V. K., Ladan, E. P., Minkina, T. M., Sushkova, S. N. et al. (2021). Intra-Soil Milling for Stable Evolution and High Productivity of Kastanozem Soil. Processes, 9 (8), 1302. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081302
- Shinde, G. U., Kajale, S. R. (2012). Design Optimization in Rotary Tillage Tool System Components by Computer Aided EngineeringAnalysis. International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, 3 (3), 279–282. doi: https://doi.org/10.7763/ijesd.2012.v3.231
- Niu, Y., Zhang, J., Qi, J., Meng, H., Peng, H., Li, J. (2023). Design and Test of Soil–Fertilizer Collision Mixing and Mulching Device for Manure Deep Application Machine. Agriculture, 13 (3), 709. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030709
- Shevchenko, I. A., Kryzhachivskyi, R. M., Trachov, V. V. (2001). Pat. No. 41108 UA. Soil separator. No. 2001020958; declareted: 13.02.2001; published: 15.08.2001, Bul. No. 7. Available at: https://uapatents.com/4-41108-gruntovijj-separator.html
- Shevchenko, I. A., Koviazyn, O. S., Kryzhachivskyi, R. M. (2003). Pat. No. 64446 UA. Ploughshare and drum soil separator. No. 2003065074; declareted: 03.06.2003. published: 17.07.2006, Bul. No. 7. Available at: https://uapatents.com/2-64446-lemishno-barabannijj-separator-gruntu.html
- Shevchenko, I., Kryzhachkivskyi, R., Koviazin, O. (2006). Polovi doslidzhennia sektsiyi hruntovoho separatora dlia peredposivnoho obrobitku gruntu. Tekhnika APK, 12, 6–7.
- Koviazyn, O. S. (2005). Metodyka provedennia eksperymentalnykh doslidzhen lemishno-barabannoho separatora gruntu. Pratsi TDATA, 28, 152–157.
- Hutsol, O. P., Kovbasa, V. P. (2016). Obgruntuvannia parametriv i rezhymiv rukhu gruntoobrobnykh mashyn z dyskovymy robochymy orhanamy. Kyiv; Nizhyn: Lysenko M. M. [vyd.], 145.
- Kovbasa, V. P. (2016). Mekhanika vzaiemodii robochykh orhaniv iz gruntom. Kyiv; Nizhyn: Lysenko M. M. [vyd.], 297.
- Aliev, E. B., Yaropud, V. M., Dudin, V. Yr., Pryshliak, V. M., Pryshliak, N. V., Ivlev, V. V. (2018). Research on sunflower seeds separation by airflow. INMATEH – Agricultural Engineering, 56 (3), 119–128.
- Aliiev, E., Pavlenko, S., Golub, G., Bielka, O. (2022). Research of mechanized process of organic waste composting. Agraarteadus, Journal of Agricultural Science, 33 (1), 21–32. doi: https://doi.org/10.15159/jas.22.04
- Ucgul, M. (2023). Simulating Soil–Disc Plough Interaction Using Discrete Element Method–Multi-Body Dynamic Coupling. Agriculture, 13 (2), 305. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020305
- Okayasu, T., Morishita, K., Terao, H., Mitsuoka, M., Inoue, E., Fukami, K. (2012). Modeling and prediction of soil cutting behavior by a plow. International Conference of Agricultural Engineering CIGR-Ageng 2012 "Agriculture & Engineering for a Healthier Life". Valencia.
- Xu, T., Zhang, R., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., Feng, W., Wang, J. (2022). Simulation and Analysis of the Working Process of Soil Covering and Compacting of Precision Seeding Units Based on the Coupling Model of DEM with MBD. Processes, 10 (6), 1103. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061103
- Tagar, A. A., Changying, J., Adamowski, J., Malard, J., Qi, C. S., Qishuo, D., Abbasi, N. A. (2015). Finite element simulation of soil failure patterns under soil bin and field testing conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 145, 157–170. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.09.006
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Elchyn Aliiev, Hennadii Tesliuk, Olena Zolotovska, Andrii Puhach, Vladyslav Boiko, Oleksandr Kobets

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








