Determining the influence of higher harmonics of nonlinear technological load in dynamic action systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.285419Keywords:
dynamic system, technological load, continuous model, spectral characteristic, oscillation frequencyAbstract
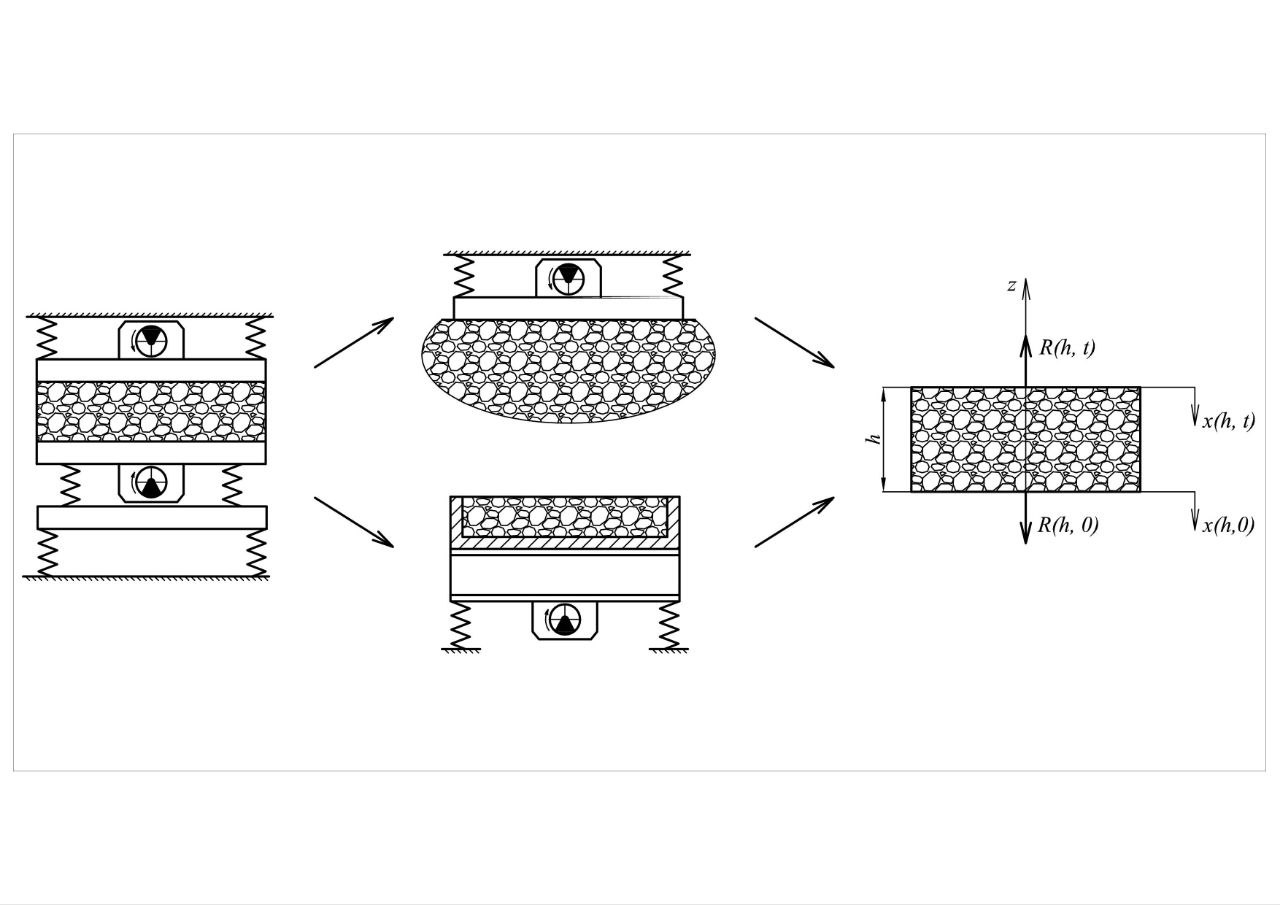
This paper considers the influence of higher harmonics in dynamic action systems due to their complex movement in the process of interaction with the technological load. The object of research is the process of propagation of oscillations in complex dynamic systems. One of the problems in the application of oscillatory processes is the consideration of higher harmonics in the overall movement of systems. To solve the problem, the idea of using a hybrid model that takes into account both discrete and distributed parameters was proposed. The resulting mathematical discrete model in the analytical equations of motion of the dynamic system preserves continuous properties in the form of wave coefficients. These coefficients in their analytical form take into account the contribution of higher harmonics of both the reactive (elastic-inertial) and active (dissipative) components of the resistance force. The studies were carried out on a model of a plant with a multimode spectrum of oscillations and a nonlinear dynamic system, which is a system with piecewise linear characteristics.A series of experimental studies with a wide variation of the change in the frequency of oscillations was carried out on the installation with a multimode spectrum of oscillations. Zones of manifestation of higher harmonics along the vertical axis of force action were revealed. The given spectrum at the exciter frequency of 35 Hz showed the manifestation of the spectrum component (around 70 Hz) along the X axis, which is an important result for practical application. For a system with piecewise linear characteristics, the manifestation of multimode, which manifests itself in the form of subharmonic and superharmonic oscillations, was determined. The contribution of each harmonic is determined by applying the obtained dependences. The results were used in the development of algorithms and calculation methods of a new class of dynamic action systems taking into account the contribution of higher harmonics
References
- Skurativskyi, S., Kendzera, O., Mykulyak, S., Semenova, Y., Skurativska, I. (2023). Seismic response assessment of a weakly nonlinear soil deposit. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 211, 104970. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2023.104970
- Connolly, D. P., Kouroussis, G., Giannopoulos, A., Verlinden, O., Woodward, P. K., Forde, M. C. (2014). Assessment of railway vibrations using an efficient scoping model. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 58, 37–47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.12.003
- Cleante, V. G., Brennan, M. J., Gatti, G., Thompson, D. J. (2017). On the spectrum of rail vibration generated by a passing train. Procedia Engineering, 199, 2657–2662. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.532
- Cacciola, P., Banjanac, N., Tombari, A. (2017). Vibration Control of an existing building through the Vibrating Barrier. Procedia Engineering, 199, 1598–1603. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.065
- Nazarenko, I., Mishchuk, Y., Kyzminec, M., Oryshchenko, S., Fedorenko, O., Tsepelev, S. (2021). Research of processes of producing materials by technical power loading systems. Dynamic processes in technological technical systems, 14–42. https://doi.org/10.15587/978-617-7319-49-7.ch2
- Luhovskyi, O., Bernyk, I., Gryshko, I., Abdulina, D., Zilinskyi, A. (2020). Mobile Equipment for Ultrasonic Cavitation Inactivation of Microorganisms in the Liquid Environment. Advances in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Drives and Control 2020, 272–281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59509-8_24
- Karamooz Mahdiabadi, M., Tiso, P., Brandt, A., Rixen, D. J. (2021). A non-intrusive model-order reduction of geometrically nonlinear structural dynamics using modal derivatives. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 147, 107126. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107126
- Nazarenko, I., Svidersky, A., Kostenyuk, A., Dedov, O., Kyzminec, N., Slipetskyi, V. (2020). Determination of the workflow of energy-saving vibration unit with polyphase spectrum of vibrations. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (7 (103)), 43–49. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.0.184632
- Nazarenko, I., Dedov, O., Delembovskyi, M., Mishchuk, Y., Nesterenko, M., Zalisko, I., Slipetskyi, V. (2021). Research of stress-strain state of elements of technological technical constructions. Dynamic processes in technological technical systems, 140–179. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/978-617-7319-49-7.ch8
- Jia, Y., Seshia, A. A. (2014). An auto-parametrically excited vibration energy harvester. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 220, 69–75. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2014.09.012
- Liang, H., Hao, G., Olszewski, O. Z., Pakrashi, V. (2022). Ultra-low wide bandwidth vibrational energy harvesting using a statically balanced compliant mechanism. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 219, 107130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107130
- Kavyanpoor, M., Shokrollahi, S. (2019). Dynamic behaviors of a fractional order nonlinear oscillator. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 31 (1), 14–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.03.006
- Rallu, A., Berthoz, N., Charlemagne, S., Branque, D. (2023). Vibrations induced by tunnel boring machine in urban areas: In situ measurements and methodology of analysis. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 15 (1), 130–145. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.02.014
- Giagopoulos, D., Arailopoulos, A., Dertimanis, V., Papadimitriou, C., Chatzi, E., Grompanopoulos, K. (2017). Computational Framework for Online Estimation of Fatigue Damage using Vibration Measurements from a Limited Number of Sensors. Procedia Engineering, 199, 1906–1911. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.424
- Yamamoto, G. K., da Costa, C., da Silva Sousa, J. S. (2016). A smart experimental setup for vibration measurement and imbalance fault detection in rotating machinery. Case Studies in Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 4, 8–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csmssp.2016.07.001
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ivan Nazarenko, Oleg Dedov, Iryna Bernyk, Andrii Bondarenko, Arthur Onyshchenko, Roman Lisnevskyi, Volodymyr Slyusar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








