Architecture of hybrid mechatronic dosing and packing module of packaging machine based on qualitative analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286615Keywords:
dose formation, hybrid mechatronic module, dosing and packaging operation, feedback, dosing accuracyAbstract
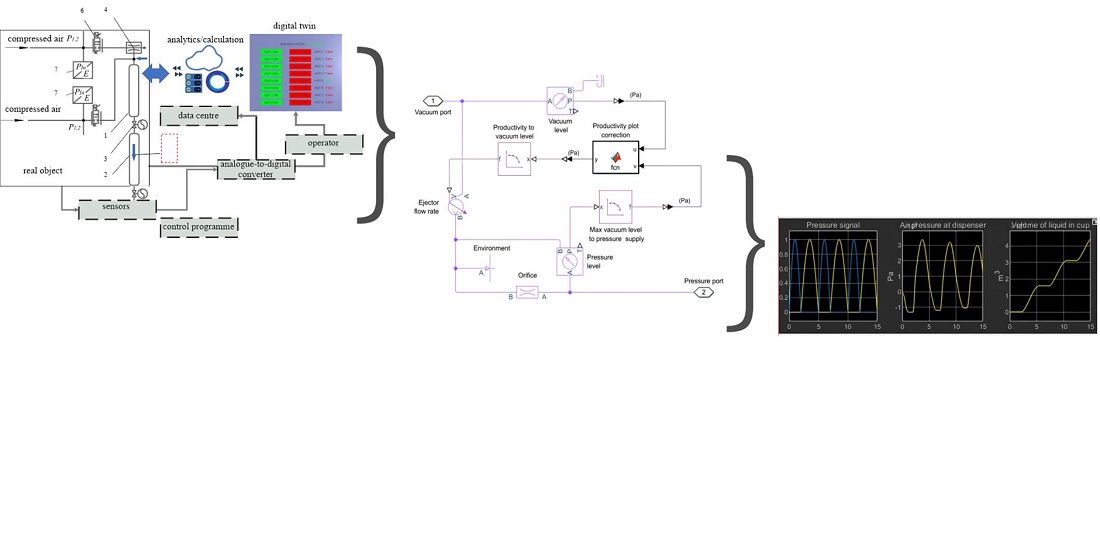
A qualitative analysis of the process of packaging liquid products (non-carbonated drinking water) using the example of a hybrid mechatronic dosing and packaging module was performed. The computer model of the mechatronic module is described by the basic operators of the Simulink program, taking into account the differential equations for changing the technological parameters of liquid dosing and the accepted initial and boundary conditions of the process. The modes of operation of the hybrid mechatronic dosing and packaging module are programmed using the driver. The boundary conditions of the process of formation and extrusion of the dose of the product are taken into account. The control system of the module is arranged on the principle of feedback and a sharp change in pressure in the portion receiver (from excess, within 3 bars to rarefaction up to –850 mbar). The analysis of individual stages of the dosing process is described, followed by the elaboration of accepted assumptions. During the tests of the computer model of the hybrid mechatronic dosing and packaging module, the accuracy of repetitions of dose formation was determined within ±0.22 % and 0.9 % of the set value of the dose mass of 50…200 ml.
An experimental bench was designed, which could provide an opportunity to check the results obtained from the computer model. The research results would allow using digital control and measuring equipment to check the accuracy of dosing of the product from 50 ml to 200 ml.
In the course of computer simulation, the effects of the given parameters of the dosing process on the accuracy of the product dose formation were determined, as well as the laws of the necessary distribution of compressed air pressure were formed to maintain the given productivity. The research results could make it possible to improve the designs of liquid product dosing modules and to determine the input parameters for field studies
References
- Lengerke, O., Martínez, C. (2008). Mechatronics Design of a Low-Cost Packaging and Dosing Machine for Doughy Products. ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics, 3, 717–725. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229040784
- Isermann, R. (2023). Designs and Specification of Mechatronic Systems. Springer Handbooks, 287–313. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96729-1_13
- Badiru, A. B., Omitaomu, O. A. (2023). Systems 4.0. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003312277
- Rangappa, S. M., Jyotishkumar, P., Thiagamani, S. M. K., Krishnasamy, S., Siengchin, S. (2020). Food Packaging. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429322129
- Brody, A. L. (2017). Flexible Packaging of Foods. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315151007
- Hocken, R. J., Pereira, P. H. (Eds.) (2016). Coordinate Measuring Machines and Systems. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/b11022
- Wright, T., Gerhart, P. (2009). Fluid Machinery. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/b15836
- Bauer, E. (2016). Pharmaceutical Packaging Handbook. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/9781420012736
- Sukhareva, L. A., Yakovlev, O. A., Legonkova, V. S. (2008). Polymers for Packaging and Containers in Food Industry. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/b12240
- DeMaria, K. (1999). The Packaging Development Process. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482278897
- Klee, H. (2018). Simulation of Dynamic Systems with MATLAB and Simulink. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420044195
- Silva, C. W. de (2022). Modeling of Dynamic Systems with Engineering Applications. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003124474
- Patalano, S., Vitolo, F. (2022). Concurrent Multi-domain Modelling and Simulation for Energy-Efficient Mechatronic Systems. EcoMechatronics, 111–128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07555-1_8
- Vazquez-Santacruz, J. A., Portillo-Velez, R., Torres-Figueroa, J., Marin-Urias, L. F., Portilla-Flores, E. (2023). Towards an integrated design methodology for mechatronic systems. Research in Engineering Design. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00163-023-00416-4
- Ning, S., Long, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Bo, X., Lu, S., Gao, J. (2021). Research on micro-liquid dispensing driven by a syringe pump with the consideration of air volume. Microsystem Technologies, 27 (10), 3653–3666. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05133-9
- Takase, T., Masumoto, N., Shibatani, N., Matsuoka, Y., Tanaka, F., Hirabatake, M. et al. (2022). Evaluating the safety and efficiency of robotic dispensing systems. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences, 8 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40780-022-00255-w
- Singh, A., Asjad, M., Singh, Y. V., Alam, S. (2023). Machine Configuration Based on Machine Reliability and Production Rate Criteria Through Line Balancing Algorithm in Reconfigurable Manufacturing System (RMS). Recent Advances in Intelligent Manufacturing, 157–175. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1308-4_14
- Kartmann, S., Koltay, P., Zengerle, R., Ernst, A. (2015). Pressure Transducer for Medical Applications Employing Radial Expansion of a Low-cost Polymer Tube. Procedia Engineering, 120, 1213–1216. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.08.832
- Gavva, O., Kryvoplias-Volodina, L., Yakymchuk, M. (2017). Structural-parametric synthesis of hydro-mechanical drive of hoisting and lowering mechanism of package-forming machines. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (7 (89)), 38–44. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.111552
- Vavrík, V., Fusko, M., Bučková, M., Gašo, M., Furmannová, B., Štaffenová, K. (2022). Designing of Machine Backups in Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems. Applied Sciences, 12 (5), 2338. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052338
- Furmann, R., Furmannová, B., Więcek, D. (2017). Interactive Design of Reconfigurable Logistics Systems. Procedia Engineering, 192, 207–212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.06.036
- Gavva, O., Kryvoplias-Volodina, L., Blazhenko, S., Tokarchuk, S., Derenivska, A. (2021). Synthesis of precision dosing system for liquid products based on electropneumatic complexes. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (114)), 125–135. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.247187
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Oleksandr Gavva, Liudmyla Kryvoplias-Volodina, Andrii Marinin, Sergii Tokarchuk, Sergii Blazhenko, Oleksandr Volodin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








