Degradation of oil and oil products by microorganisms isolated from the Azerbaijani coast of the Caspian Sea at low temperatures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287467Keywords:
biodegradation of microorganisms, oil and oil products, Caspian Sea, low temperature, liquid chromatographyAbstract
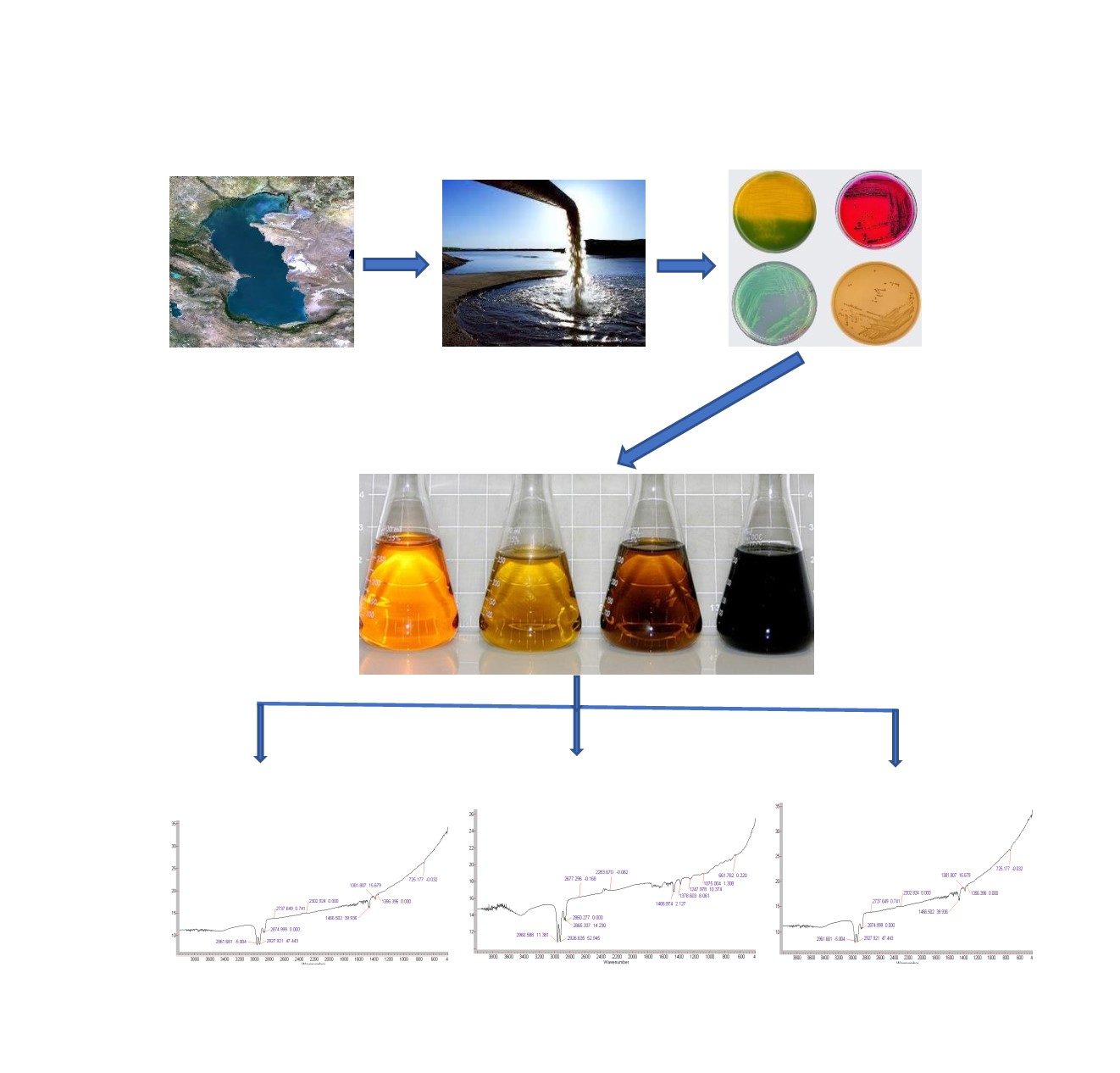
The object of the study is microorganisms isolated from the Azerbaijani territory of the Caspian Sea, capable of decomposing oil and oil products at low temperatures of 4–6 °C. The purpose of this work was to study bacteria and fungi capable of actively assimilating oil, gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel at a temperature of 4–6 °C in order to solve the problem of environmental pollution in this region.
The studied most effective biodestructors are combined into associations that can be used to create an active biological product based on native microorganisms with its further use for water bioremediation, as well as treatment of tanks and other containers used for long-term storage of petroleum products at a temperature of 4–6 °C.
The process of degradation of samples of used oils at the molecular level of the selected compounds was studied by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. As a result of chromatographic and spectroscopic studies, it was found that almost all microorganisms decompose the tested oil products. Only weak peaks remained on the chromatogram, which is a clear indicator of the deep biodegradation carried out by these microorganisms. Thanks to the chromatographic and spectral analysis of oil and products of its decomposition, an oxidation sequence has been established, indicating the decomposition of the last aromatic fraction. As a result, a general picture was obtained on the amount of degradation products containing carboxyl, keto-, hydroxyl groups, which is not enough to determine the processes of transformation of initial products into final ones. All this testifies to the multidirectionality of biodegradation processes
References
- Udod, V., Vildman, I., Zhukova, E. (2014). The development of modern biocenotic control methods for the ecological state of aquatic ecosystems of rivers. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (10 (71)), 4–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2014.28003
- Blyashyna, M., Zhukova, V., Sabliy, L. (2018). Processes of biological wastewater treatment for nitrogen, phosphorus removal by immobilized microorganisms. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (10 (92)), 30–37. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.127058
- Korshunova, T. Yu., Chetverikov, S .P., Bakaeva, M. D., Kuzina, E. V., Rafikova, G. F., Chetverikova, D. V., Loginov, O. N. (2019). Microorganisms in the elimination of oil pollution consequences. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 55 (4), 338–349. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s0555109919040093
- Artyukh, E. A., Mazur, A. S., Ukraintseva, T. V., Kostyuk, L. V. (2014). Looking forward to biosorbents future application for ponds’ cleaning after emergency oil spills. Izvestiya Sankt-Peterburgskogo gosudarstvennogo tekhnologicheskogo instituta (tekhnicheskogo universiteta), 26, 58–66. Available at: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/perspektivy-primeneniya-biosorbentov-dlya-ochistki-vodoemov-pri-likvidatsii-avariynyh-razlivov-nefti
- Bernatska, N. (2015). Establishing the optimal conditions of the process of water treatment by ultrasound. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (10 (76)), 8–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2015.46495
- Pikula, K. S., Zakharenko, A. M., Gulkov, A. N. (2016). Psychrophilic bacteria and their use for bioremediation of Arctic ecosystems polluted with oil and oil products. International Student Research Bulletin, 4, 254–255. Available at: https://eduherald.ru/ru/article/view?id=16205
- Stepanova, A. Y., Gladkov, E. A., Osipova, E. S., Gladkova, O. V., Tereshonok, D. V. (2022). Bioremediation of Soil from Petroleum Contamination. Processes, 10 (6), 1224. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10061224
- Veliev, M. G., Salmanov, M. A., Babashly, A. A., Alieva, S. R., Bektashi, N. R. (2013). Biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons and phenols by bacteria isolated from Caspian waters and soils. Petroleum Chemistry, 53 (6), 426–430. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s0965544113050101
- Dmitrieva, E. D., Grinevich, V. I., Gertsen, M. M. (2022). Degradation of Oil and Petroleum Products by Biocompositions Based on Humic Acids of Peats and Oil-Degrading Microorganisms. Russian Journal of General Chemistry, 92 (12), 2920–2930. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070363222120453
- Gertsen, M. M., Dmitrieva, E. D. (2020). The influence of humic acids in the presence of oil-degrading microorganisms of the ge-nus rhodococcus on the sowing qualities of cockweed in oil pollution. Chemistry of Plant Raw Material, 2, 291–298. doi: https://doi.org/10.14258/jcprm.2020025552
- Babashli, A., Akhundova, N., Gadimova, N. (2022). Biodegradation of phenols and halogenated derivatives of aromatic carbohydrogens by bacteria specific to the genus Pseudomonas and Arthrobacter. RT&A, 17 (4 (70)), 567–572. doi: https://doi.org/10.24412/1932-2321-2022-470-567-572
- Veliev, M. G., Danielsson, B., Salmanov, M. A., Aliyeva, A. R., Bektashi, N. R. (2008). Biodegradation of Baku oil and hydrocarbons by micromycetes. Petroleum Chemistry, 48 (1), 55–62. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11494-008-1011-y
- Brakstad, O. G., Bonaunet, K. (2006). Biodegradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Seawater at Low Temperatures (0–5 °C) and Bacterial Communities Associated with Degradation. Biodegradation, 17 (1), 71–82. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-3342-8
- Belousova, N. I., Shkidchenko, A. N. (2004). Destruction of petroleum products of various concentrations by microorganisms at finite temperatures. Prikl. biochemistry and microbiology, 40 (3), 312–316.
- Pyrchenkova, I. A., Gafarov, A. B., Puntus, I. F., Filonov, A. E., Boronin, A. M. (2006). Selection and characterization of active psychrotrophic microbial oil-degrading microorganisms. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 42 (3), 263–269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s0003683806030070
- Veliyev, M. G., Salmanov, M. A., Alieva, S. R., Gamidova, K. M., Bektashi, N. R. (2013). Analysis of biodegradation products of individual oil hydrocarbons by high performance liquid chromatography. Biology, Biological Sciences /6. Microbiology. Available at: http://www.rusnauka.com/34_NIEK_2013/Biologia/6_148532.doc.htm
- Goodfellow, M., Kämpfer, P., Busse, H.-J., Trujillo, M. E., Suzuki, K., Ludwig, W., Whitman, W. B. (Eds.) (2012). Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Springer, 2083. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68233-4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Aynur Babashli, Nazilya Akhundova, Natavan Gadimova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








