Improving a procedure of load balancing in distributed IoT systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287790Keywords:
internet of things, load balancing, cloud computing, distributed systems, performance evaluationAbstract
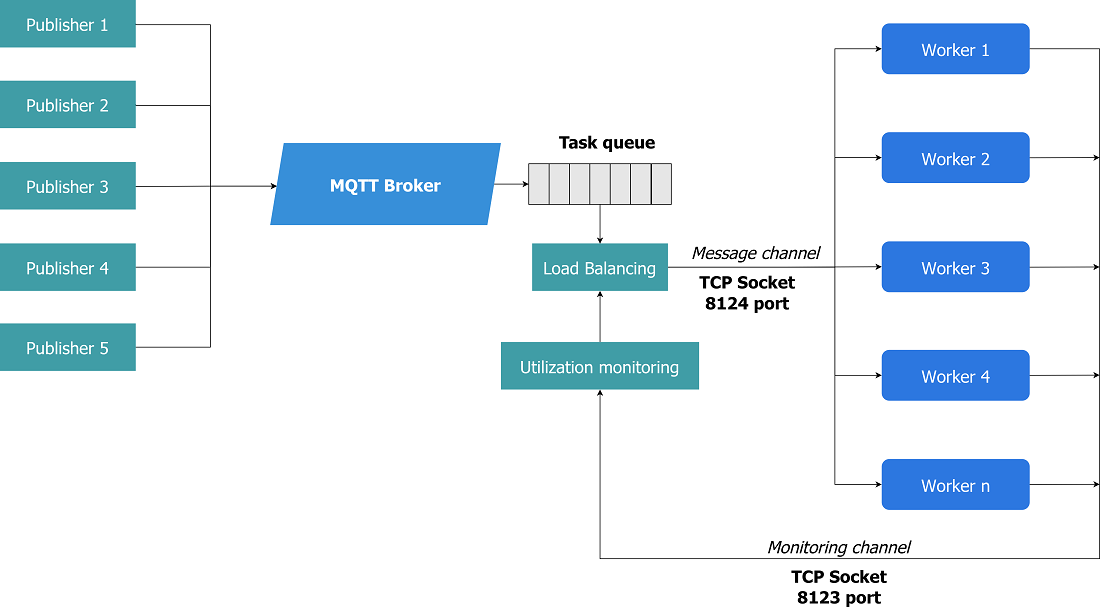
The object of this research is the process of load balancing in distributed Internet of Things (IoT) systems. Within this work, a complex of problems related to efficient load distribution has been addressed. The authors conducted an analysis of existing load-balancing approaches and their drawbacks and proposed an enhanced architecture for the MQTT broker. Additionally, methods and algorithms for load balancing were developed based on multi-criteria server monitoring.
Furthermore, the authors created a mathematical model to assess the uniformity of load distribution in the system and introduced a corresponding metric – the load distribution coefficient. In order to evaluate the proposed load balancing methods, a series of experiments were conducted, including the simulation of a distributed IoT system with non-deterministic load. The main goal of these experiments was to assess the uniformity of MQTT load distribution by the broker.
The results of the experiments confirmed the hypothesis of improved load distribution efficiency through multi-criteria monitoring-based balancing. The utilization of the proposed load-balancing methods allowed for a more efficient utilization of computational resources. It was found that when using the proposed methods, in the case of non-deterministic load in the IoT system, the load distribution coefficient on average exceeded the corresponding indicator of existing methods by 70 %. In addition, the value of this coefficient for the proposed methods remains virtually unchanged throughout the experiment, which is evidence of the stable operation of the system as a whole. The results obtained can be useful in the development of modern IoT systems.
References
- State of IoT – Spring 2023. Available at: https://iot-analytics.com/product/state-of-iot-spring-2023
- Liaqat, M., Naveed, A., Ali, R. L., Shuja, J., Ko, K.-M. (2019). Characterizing Dynamic Load Balancing in Cloud Environments Using Virtual Machine Deployment Models. IEEE Access, 7, 145767–145776. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2945499
- Shafiq, D. A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Abdullah, A., Alzain, M. A. (2021). A Load Balancing Algorithm for the Data Centres to Optimize Cloud Computing Applications. IEEE Access, 9, 41731–41744. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3065308
- Goncalves, D., Puliafito, C., Mingozzi, E., Rana, O., Bittencourt, L., Madeira, E. (2020). Dynamic Network Slicing in Fog Computing for Mobile Users in MobFogSim. 2020 IEEE/ACM 13th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing (UCC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ucc48980.2020.00042
- Yuan, H., Bi, J., Zhou, M. (2022). Geography-Aware Task Scheduling for Profit Maximization in Distributed Green Data Centers. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 10 (3), 1864–1874. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2020.3001051
- Bogdanov, K. L., Reda, W., Maguire, G. Q., Kostić, D., Canini, M. (2018). Fast and Accurate Load Balancing for Geo-Distributed Storage Systems. Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Cloud Computing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3267809.3267820
- Srinivas, J., Qyser, A. A. M., Reddy, B. E. (2015). Exploiting Geo Distributed datacenters of a cloud for load balancing. 2015 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iadcc.2015.7154780
- Shuaib, M., Bhatia, S., Alam, S., Masih, R. K., Alqahtani, N., Basheer, S., Alam, M. S. (2023). An Optimized, Dynamic, and Efficient Load-Balancing Framework for Resource Management in the Internet of Things (IoT) Environment. Electronics, 12 (5), 1104. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051104
- Lim, J. (2021). Scalable Fog Computing Orchestration for Reliable Cloud Task Scheduling. Applied Sciences, 11 (22), 10996. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210996
- Singh, S. P., Kumar, R., Sharma, A., Nayyar, A. (2020). Leveraging energy‐efficient load balancing algorithms in fog computing. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 34 (13). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5913
- Fan, Q., Ansari, N. (2020). Towards Workload Balancing in Fog Computing Empowered IoT. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 7 (1), 253–262. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tnse.2018.2852762
- Kim, H.-Y., Kim, J.-M. (2016). A load balancing scheme based on deep-learning in IoT. Cluster Computing, 20 (1), 873–878. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0667-5
- Gomez, C., Shami, A., Wang, X. (2018). Machine Learning Aided Scheme for Load Balancing in Dense IoT Networks. Sensors, 18 (11), 3779. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113779
- Adil, M. (2021). Congestion free opportunistic multipath routing load balancing scheme for Internet of Things (IoT). Computer Networks, 184, 107707. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107707
- Tonguz, O. K Yanmaz, E. (2008). The Mathematical Theory of Dynamic Load Balancing in Cellular Networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7 (12), 1504–1518. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tmc.2008.66
- Latchoumi, T. P., Parthiban, L. (2021). Quasi Oppositional Dragonfly Algorithm for Load Balancing in Cloud Computing Environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 122 (3), 2639–2656. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09022-w
- Zakutynskyi, I. (2023). Finding the Optimal Number of Computing Containers in IoT Systems: Application of Mathematical Modeling Methods. Electronics and Control Systems, 2 (76), 9–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.18372/1990-5548.76.17661
- Alakbarov, R. (2022). An Optimization Model for Task Scheduling in Mobile Cloud Computing. International Journal of Cloud Applications and Computing, 12 (1), 1–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcac.297102
- Kaveri, P. R., Chavan, V. (2013). Mathematical model for higher utilization of database resources in cloud computing. 2013 Nirma University International Conference on Engineering (NUiCONE). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/nuicone.2013.6780095
- Zakutynskyi, I., Sibruk, L., Rabodzei, I. (2023). Performance evaluation of the cloud computing application for IoT-based public transport systems. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (9 (124)), 6–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.285514
- MQTT Shared Subscriptions – MQTT 5 Essentials Part 7. Available at: https://www.hivemq.com/blog/mqtt5-essentials-part7-shared-subscriptions/
- MQTT Version 5.0. OASIS Standard. Available at: https://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v5.0/os/mqtt-v5.0-os.html
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ihor Zakutynskyi, Ihor Rabodzei, Stanislav Burmakin, Oleksandr Kalishuk, Vitalii Nebylytsia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








