Vehicle routing problem optimization with machine learning in imbalanced classification vehicle route data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.288280Keywords:
vehicle routing problem, machine learning, classification, unbalanced dataAbstract
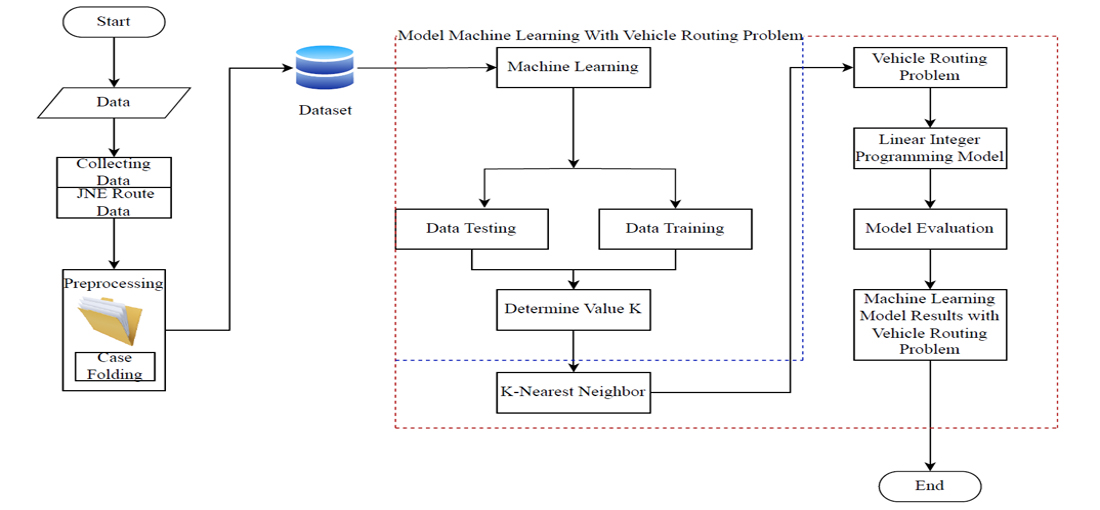
The object of this research is a combinatorial optimization problem arising in the problem of the route of goods delivery vehicles. In this study, the proposed method for solving combinatorial optimization problems consists of several stages: Data Cleaning, Data Preprocessing, K-NN and Cavacity Vehicle Routing Problem model. The results show that the machine learning approach can optimise combinatorial optimization problems, especially in generating vehicle route points and delivery capacity. The characteristics in determining vehicle routes by considering latitude and longitude points. This research builds a framework and implements it in a multi-class optimization model to reduce overfitting and misclassification results caused by unbalanced multiclassification from the influence of the number of 'nodes' on vehicle routes with machine learning. The purpose of the model in general is to gain an understanding of the mechanism in the problem so that it can classify unbalanced vehicle route data based on Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir delivery routes. So that with the availability of the model can be a model in determining vehicle routes based on the capacity limit of the number of shipments of goods. The results of research with machine learning models and vehicle routing problems with testing K values 11, 13, 15. Where it has a percentage of K=11 accuracy 57.3265 % and K=13 accuracy 57.3265 % and K=15 accuracy 81.8645 %. From the test results with odd K values have better accuracy and the K 15 K=15 value is better with a percentage of 81.8645 % compared to K 11 K=11, and 13 K=13. As a result, the developed model in terms of accuracy of the cavacity vehicle routing problem model has an accuracy of 93.80 % and the time series achieves an average precision of 93.31 % and with a recall value of 93.80 %. The results obtained can be useful in developing a more modern model, Cavacity Vehicle Routing Problem with Machine Learning
References
- Soenandi, I. A., Marpaung, B., Ginting, M. (2017). Optimasi Vehicle Routing Problem (Vrp)Dengan Pendekatan Metaheuristik(Studi Kasus Distribusi Bahan Baku Makanan). Jurnal Ilmiah Teknik Industri, 2 (2). doi: https://doi.org/10.24912/jitiuntar.v2i2.487
- Juliandri, D., Mawengkang, H., Bu’ulolo, F. (2018). Discrete Optimization Model for Vehicle Routing Problem with Scheduling Side Cosntraints. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 300, 012024. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/300/1/012024
- Liong, C.-Y., Wan, I., Omar, K. (2008). Vehicle routing problem: Models and solutions. Journal of Quality Measurement and Analysis, 4 (1), 205–218. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313005083_Vehicle_routing_problem_Models_and_solutions
- Alweshah, M., Almiani, M., Almansour, N., Al Khalaileh, S., Aldabbas, H., Alomoush, W., Alshareef, A. (2022). Vehicle routing problems based on Harris Hawks optimization. Journal of Big Data, 9 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-022-00593-4
- Zhu, X., Yan, R., Huang, Z., Wei, W., Yang, J., Kudratova, S. (2020). Logistic Optimization for Multi Depots Loading Capacitated Electric Vehicle Routing Problem From Low Carbon Perspective. IEEE Access, 8, 31934–31947. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2971220
- Jayarathna, D. G. N. D., Lanel, G. H. J., Juman, Z. A. M. S. (2022). Industrial vehicle routing problem: a case study. Journal of Shipping and Trade, 7 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41072-022-00108-7
- Faiz, A., Subiyanto, S., Arief, U. M. (2018). A Modified Meta-Heuristic Approach for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Pickup and Delivery. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2 (2), 81. doi: https://doi.org/10.29099/ijair.v2i2.71
- Basso, R., Kulcsár, B., Sanchez-Diaz, I. (2021). Electric vehicle routing problem with machine learning for energy prediction. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 145, 24–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trb.2020.12.007
- Amelia, A., Zarlis, M., Suherman, S., Efendi, S. (2023). Vehicle detection system based on shape, color, and time-motion. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence (IJ-AI), 12 (3), 1070. doi: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v12.i3.pp1070-1082
- Ajie Sukarno, S., Erdani, Y. (2020). Desain Antarmuka Pada Vehicle Routing Problem Untuk Manajemen Armada Multi-Drone. Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Komputer, 6 (2), 7–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.35329/jiik.v6i2.150
- Ramadhanti, N. S., Kusuma, W. A., Annisa, A. (2020). Optimasi Data Tidak Seimbang pada Interaksi Drug Target dengan Sampling dan Ensemble Support Vector Machine. Jurnal Teknologi Informasi Dan Ilmu Komputer, 7 (6), 1221. doi: https://doi.org/10.25126/jtiik.2020762857
- Bujang, S. D. A., Selamat, A., Ibrahim, R., Krejcar, O., Herrera-Viedma, E., Fujita, H., Ghani, N. A. Md. (2021). Multiclass Prediction Model for Student Grade Prediction Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access, 9, 95608–95621. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3093563
- Gurcan, F. (2018). Multi-Class Classification of Turkish Texts with Machine Learning Algorithms. 2018 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ismsit.2018.8567307
- Genkin, M. (2020). Zero-Shot Machine Learning Technique for Classification of Multi-User Big Data Workloads. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/bigdata50022.2020.9378023
- von Rueden, L., Mayer, S., Beckh, K., Georgiev, B., Giesselbach, S., Heese, R. et al. (2021). Informed Machine Learning - A Taxonomy and Survey of Integrating Prior Knowledge into Learning Systems. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 1–1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2021.3079836
- Furian, N., O’Sullivan, M., Walker, C., Çela, E. (2021). A machine learning-based branch and price algorithm for a sampled vehicle routing problem. OR Spectrum, 43 (3), 693–732. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-020-00615-8
- Hirst, J. D., Boobier, S., Coughlan, J., Streets, J., Jacob, P. L., Pugh, O. et al. (2023). ML meets MLn: Machine learning in ligand promoted homogeneous catalysis. Artificial Intelligence Chemistry, 1 (2), 100006. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aichem.2023.100006
- Bansal, M., Goyal, A., Choudhary, A. (2022). A comparative analysis of K-Nearest Neighbor, Genetic, Support Vector Machine, Decision Tree, and Long Short Term Memory algorithms in machine learning. Decision Analytics Journal, 3, 100071. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2022.100071
- Jin, H., Kim, Y.-G., Jin, Z., Rushchitc, A. A., Al-Shati, A. S. (2022). Optimization and analysis of bioenergy production using machine learning modeling: Multi-layer perceptron, Gaussian processes regression, K-nearest neighbors, and Artificial neural network models. Energy Reports, 8, 13979–13996. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.10.334
- Cardarilli, G. C., Di Nunzio, L., Fazzolari, R., Nannarelli, A., Re, M., Spano, S. (2020). N -Dimensional Approximation of Euclidean Distance. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 67 (3), 565–569. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2019.2919545
- Wazery, Y. M., Saber, E., Houssein, E. H., Ali, A. A., Amer, E. (2021). An Efficient Slime Mould Algorithm Combined With K-Nearest Neighbor for Medical Classification Tasks. IEEE Access, 9, 113666–113682. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3105485
- Sumayli, A. (2023). Development of advanced machine learning models for optimization of methyl ester biofuel production from papaya oil: Gaussian process regression (GPR), multilayer perceptron (MLP), and K-nearest neighbor (KNN) regression models. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 16 (7), 104833. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104833
- Habib, Y., Filchenkov, A. (2022). Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning For Multi Vehicles One-commodity Vehicle Routing Problem. Procedia Computer Science, 212, 418–428. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.11.026
- Margossian, H., Deconinck, G., Sachau, J. (2015). Distribution network protection considering grid code requirements for distributed generation. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 9 (12), 1377–1381. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2014.0987
- Núñez-Mata, O., Palma-Behnke, R., Valencia, F., Urrutia-Molina, A., Mendoza-Araya, P., Jiménez-Estévez, G. (2019). Coupling an adaptive protection system with an energy management system for microgrids. The Electricity Journal, 32 (10), 106675. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tej.2019.106675
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Muhammad Syahputra Novelan, Syahril Efendi, Poltak Sihombing, Herman Mawengkang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








