Enhancing vehicle wheel suspension test equipment through Taguchi method for optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.288476Keywords:
Taguchi method, vertical dynamic loads, vehicle body weight, suspension, fast Fourier transformAbstract
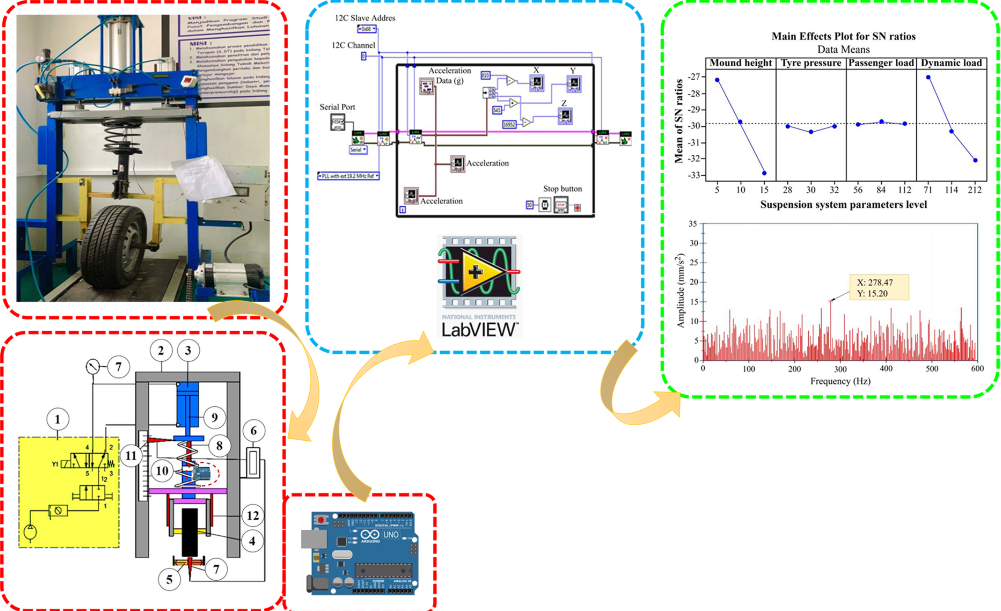
The study demonstrates a significant advancement in vehicle suspension testing by utilizing the Taguchi method for optimization. The suspension system determines a vehicle’s performance, directly affecting ride comfort, handling, and safety. The research presented in this study highlights a potentially effective method for enhancing suspension testing. The research systematically investigates the complex network of factors influencing suspension behavior using the Taguchi method, a robust optimization technique. The analysis includes examining road surface conditions, passenger weight variations, and tire pressure fluctuations. The objective is to design a suspension system that provides both comfort and stability without making any concessions, regardless of the obstacles encountered on the road. The car utilized for this research is an Altis sedan equipped with tires with a 205/55 R16 profile. The study’s findings indicate that factor A, which represents embankment height, significantly impacts 56 % of road irregularity management and the maintenance of a stable driving experience. The dynamic load factor (Factor D) contributes significantly to the vehicle’s overall stability and ride quality, accounting for 43 % in different scenarios. Based on the given framework, it can be observed that the variables B (tire pressure) and C (passenger weight) significantly influence suspension vibration, resulting in a reduction of below 0.1 %. While the research results presented here only cover a subset of automobiles, the methodology employed can be used to deal with similar problems in other vehicles.
References
- Xu, T., Liang, M., Li, C., Yang, S. (2015). Design and analysis of a shock absorber with variable moment of inertia for passive vehicle suspensions. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 355, 66–85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.05.035
- Fleps-Dezasse, M., Brembeck, J. (2016). LPV Control of Full-Vehicle Vertical Dynamics using Semi-Active Dampers. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 49 (11), 432–439. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.08.064
- Akkuş, H., Yaka, H. (2021). Experimental and statistical investigation of the effect of cutting parameters on surface roughness, vibration and energy consumption in machining of titanium 6Al-4V ELI (grade 5) alloy. Measurement, 167, 108465. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108465
- Dushchenko, V., Vorontsov, S., Masliyev, V., Agapov, O., Nanivskyi, R., Cherevko, Y., Masliiev, A. (2021). Comparing the physical principles of action of suspension damping devices based on their influence on the mobility of wheeled vehicles. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (5 (112)), 51–60. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.237312
- Kaka, S. (2018). Shock Absorber And Spring Contribution Reduces Vertical Vehicle Loads That Burden The Road Structure. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 13 (2), 8686–8692.
- Gopinath, S., Golden Renjith, R. J., Dineshkumar, J. (2014). Design and fabrication of magnetic shock absorber. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 3 (2), 208. doi: https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v3i2.1831
- Pankaj, S., Rushikesh, A., Sanket, W., Viraj, J., Kaushal, P. (2017). Design and analysis of helical compression spring used in suspension system by finite element analysis method. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 04 (04), 2959–2969. Available at: https://dokumen.tips/documents/design-and-analysis-of-helical-all-these-types-of-springs-leaf-springs-and.html?page=11
- Abed, S. A., Khalaf, A. A., Mnati, H. M., Hanon, M. M. (2022). Optimization of mechanical properties of recycled polyurethane waste microfiller epoxy composites using grey relational analysis and taguchi method. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (12 (115)), 48–58. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.252719
- Akkuş, H. (2018). Optimising the effect of cutting parameters on the average surface roughness in a turning process with the Taguchi method. Materiali in Tehnologije, 52 (6), 781–785. doi: https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2018.110
- Hamzaçebi, C. (2021). Taguchi Method as a Robust Design Tool. Quality Control - Intelligent Manufacturing, Robust Design and Charts. doi: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.94908
- Ka’ka, S., Kambuno, D., Tangkemanda, A. (2022). Damping transformation modeling on wheel suspension using pneumatic cylinder thrust force as a substitute for vehicle weight. Journal of Vibroengineering, 25 (2), 363–376. doi: https://doi.org/10.21595/jve.2022.22619
- Xiong, J. (2022). Vibration test and robust optimization analysis of vehicle suspension system based on Taguchi method. SN Applied Sciences, 5 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-022-05236-0
- Sert, E., Boyraz, P. (2016). Enhancement of Vehicle Handling Based on Rear Suspension Geometry Using Taguchi Method. SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles, 9 (1), 1–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-9020
- Mitra, A. C., Jawarkar, M., Soni, T., Kiranchand, G. R. (2016). Implementation of Taguchi Method for Robust Suspension Design. Procedia Engineering, 144, 77–84. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.05.009
- Lu, W., Li, W., Chen, X. (2021). Design Optimization of an Integrated E-Type Multilink Suspension Wheel-Side Drive System and Improvement of Vehicle Ride Comfort. Shock and Vibration, 2021, 1–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1462980
- Ka’ka, S., Himran, S., Renreng, I., Sutresman, O. (2018). The Pneumatic Actuators As Vertical Dynamic Load Simulators On Medium Weighted Wheel Suspension Mechanism. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 962, 012022. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/962/1/012022
- Sreekar Reddy, M. B. S., Vigneshwar, P., RajaSekhar, D., Akhil, K., Lakshmi Narayana Reddy, P. (2016). Optimization Study on Quarter Car Suspension System by RSM and Taguchi. Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal, Networks, Computing, and Systems, 261–271. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-3589-7_29
- Li, S., Xu, J., Gao, H., Tao, T., Mei, X. (2020). Safety probability based multi-objective optimization of energy-harvesting suspension system. Energy, 209, 118362. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118362
- Mario, H., Dietrich, W., Gfrerrer, A., Lang, J. (2013). Integrated Computer-Aided Design in Automotive Development. Springer, 466. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11940-8
- Badr, M. F., Abdullah, Y., Jaliel, A. K. (2017). Position control of the pneumatic actuator employing ON/OFF solenoids valve. International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering, 17 (2), 29–37.
- Simon, C. G., Hardinsi, F. A., Paliling, F. (2023). Comparison of the Effect of Variable Helix Angle Geometry Tools on CNC Vertical Milling Machines on Chatter using a microcontroller Based on SLD. INTEK: Jurnal Penelitian, 10 (1), 26. doi: https://doi.org/10.31963/intek.v10i1.4265
- Ulrich, K. T., Eppinger, S. D., Yang, M. C. (2008). Product design and development. McGraw-Hill.
- Krishnaiah, K., Shahabudeen, P. (2012). Applied design of experiments and Taguchi methods. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., 368.
- Andre Hardinsi, F., Novareza, O., As’ad Sonief, A. (2021). Optimization of variabel helix angle parameters in cnc milling of chatter and surface roughnes using taguchi method. Journal of Engineering and Management in Industrial System, 9 (1), 35–44. doi: https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jemis.2021.009.01.4 4
- Wen, J.-L., Yang, Y.-K., Jeng, M.-C. (2008). Optimization of die casting conditions for wear properties of alloy AZ91D components using the Taguchi method and design of experiments analysis. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 41 (5-6), 430–439. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1499-0
- Thakare, H., Parekh, A., Upletawala, A., Behede, B. (2022). Application of mixed level design of Taguchi method to counter flow vortex tube. Materials Today: Proceedings, 57, 2242–2249. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.12.444
- Yang, W. H., Tarng, Y. S. (1998). Design optimization of cutting parameters for turning operations based on the Taguchi method. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 84 (1-3), 122–129. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-0136(98)00079-x
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Christof Geraldi Simon, Festo Andre Hardinsi, Sallolo Suluh, Formanto Paliling, Rigel Sampelolo, Agus Widyianto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








