Designing tools for assessing the reliability of electric motor torque measurements by using identifiers of anomalous deviations in a noisy signal system
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.292187Keywords:
assessment procedure, torque, electric motor parameters, neural network, fuzzy logicAbstract
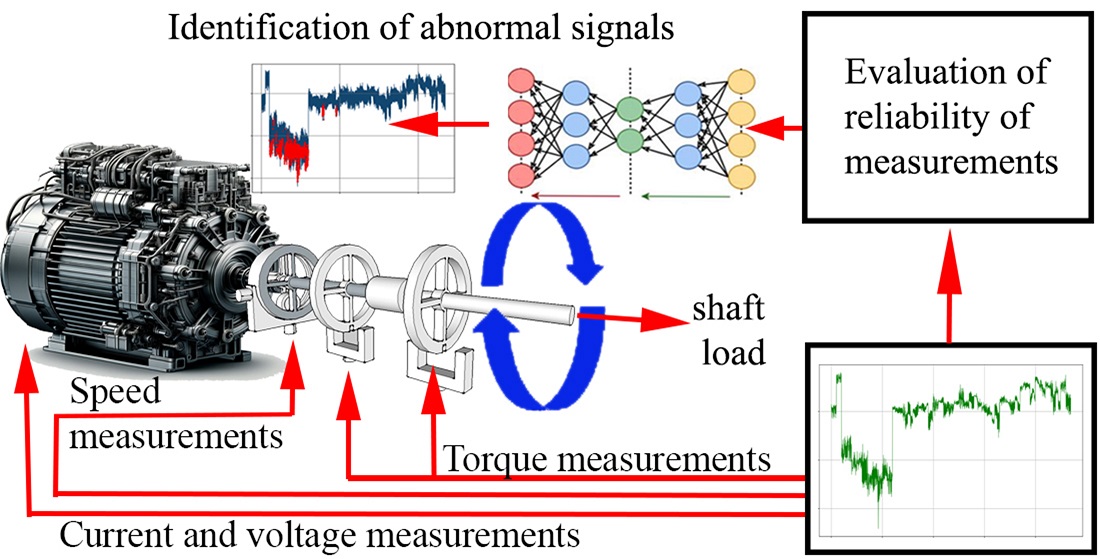
The problem of the reliability of measurements of rotational parameters of electric motors was solved, which was focused on the development of an algorithm for evaluating measurements under conditions of additional noise. An analysis of methodological approaches and mathematical tools used to process and interpret the uncertainty of measurement results was carried out. Cases where they may not be effective due to high noise levels were considered. To detect anomalies in the signal, an algorithm for assessing the reliability of measurements using fuzzy logic was proposed. A structural diagram of the model for measuring the torque of an electric motor under the conditions of a noisy signal was developed, where transfer functions were used to model the angular velocity and torque parameters. A method for detecting anomalies in noisy signals is presented, which identifies the amplitude and time characteristics of spiking pulses. The method includes the application of a wide range of analytical tools for deep analysis of signals and is particularly effective for detecting anomalies that may be hidden in background noise. A prototype of a measuring bench was developed, which uses neural networks to detect anomalies when measuring the rotational parameters of electric motors, which made it possible to obtain a training sample using a sample electric motor and apply it to evaluate the parameters of another electric motor. In a practical aspect, the developed methods and technological solutions for improving the reliability of measurements of rotational parameters of electric motors could be used to make corrections in existing systems. In particular, they could be used in industry, electric transport, as well as in the aerospace and military sectors where the reliability of measuring systems is important
References
- Xin, Q.-Y., Pei, Y.-C., Luo, M.-Y., Wang, Z.-Q., He, L., Liu, J.-Y. et al. (2023). A generalized precision measuring mechanism and efficient signal processing algorithm for the eccentricity of rotary parts. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 204, 110791. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110791
- Gan, C., Wu, J., Sun, Q., Kong, W., Li, H., Hu, Y. (2018). A Review on Machine Topologies and Control Techniques for Low-Noise Switched Reluctance Motors in Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Access, 6, 31430–31443. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2837111
- Hovda, S. (2018). Automatic detection of abnormal torque while reaming. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 166, 13–24. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.02.050
- Kükrer, O., İnce, E. A. (2023). Frequency estimation of multiple complex sinusoids using noise suppressing predictive FIR filter. Digital Signal Processing, 143, 104235. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2023.104235
- Herrera, M. R. S., Märquez, J. M. A., Borrero, A. M., Sänchez, M. A. M. (2013). Testing Bench for Remote Practical Training in Electric Machines. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 46 (17), 357–362. doi: https://doi.org/10.3182/20130828-3-uk-2039.00076
- Avramenko, V. V., Konoplyanchenko, A. E., Prohnenko, Yu. I. (2016). Recognition of the reference signals at interference generation and loss at random times. ScienceRise, 3 (2 (20)), 38–42. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2313-8416.2016.64500
- Avramenko, V. V., Slepushko, N. Ju. (2009). Raspoznavanie etalonnyh signalov pri nepolnoy informacii o harakteristikah pomeh. Vestnik SumGU. Tehnicheskie nauki, 3, 13–19.
- Li, P., Pei, Y., Li, J. (2023). A comprehensive survey on design and application of autoencoder in deep learning. Applied Soft Computing, 138, 110176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110176
- Gao, Y., Cheong, B., Bozhko, S., Wheeler, P., Gerada, C., Yang, T. (2023). Surrogate role of machine learning in motor-drive optimization for more-electric aircraft applications. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 36 (2), 213–228. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2022.08.011
- Python Control Systems Library (Version 0.9.4). Available at: https://python-control.readthedocs.io/en/0.9.4/
- Tran, M., Amer, M., Dababat, A., Abdelaziz, A. Y., Dai, H.-J., Liu, M.-K., Elsisi, M. (2023). Robust fault recognition and correction scheme for induction motors using an effective IoT with deep learning approach. Measurement, 207, 112398. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.112398
- Rahman, T. A. Z., Chek, L. W., Ramli, N. (2022). Intelligent Vibration-based Anomaly Detection for Electric Motor Condition Monitoring. Conference: 2022 9th Iranian Joint Congress on Fuzzy and Intelligent Systems (CFIS2022). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357459169_Intelligent_Vibration-based_Anomaly_Detection_for_Electric_Motor_Condition_Monitoring
- Mian, T., Choudhary, A., Fatima, S., Panigrahi, B. K. (2023). Artificial intelligence of things based approach for anomaly detection in rotating machines. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 109, 108760. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2023.108760
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Volodymyr Kvasnikov, Dmytro Kvashuk, Mykhailo Prygara, Jaroslav Legeta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








