Determining vertical oscillations of front-plow tractor without support wheel
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.296842Keywords:
plow unit, front attachment mechanism, "push-pull", front plow, tire stiffness coefficient, tire damping coefficientAbstract
The object of this study is a tractor with a front plow without a support wheel. One way to avoid the use of ballast is to use front-mounted plows that operate under the "push" mode. As a rule, such plows are equipped with at least one supporting wheel. The presence of the latter complicates the structure of the plow and, of course, affects the degree of vertical load on the steered wheels of the mobile vehicle.
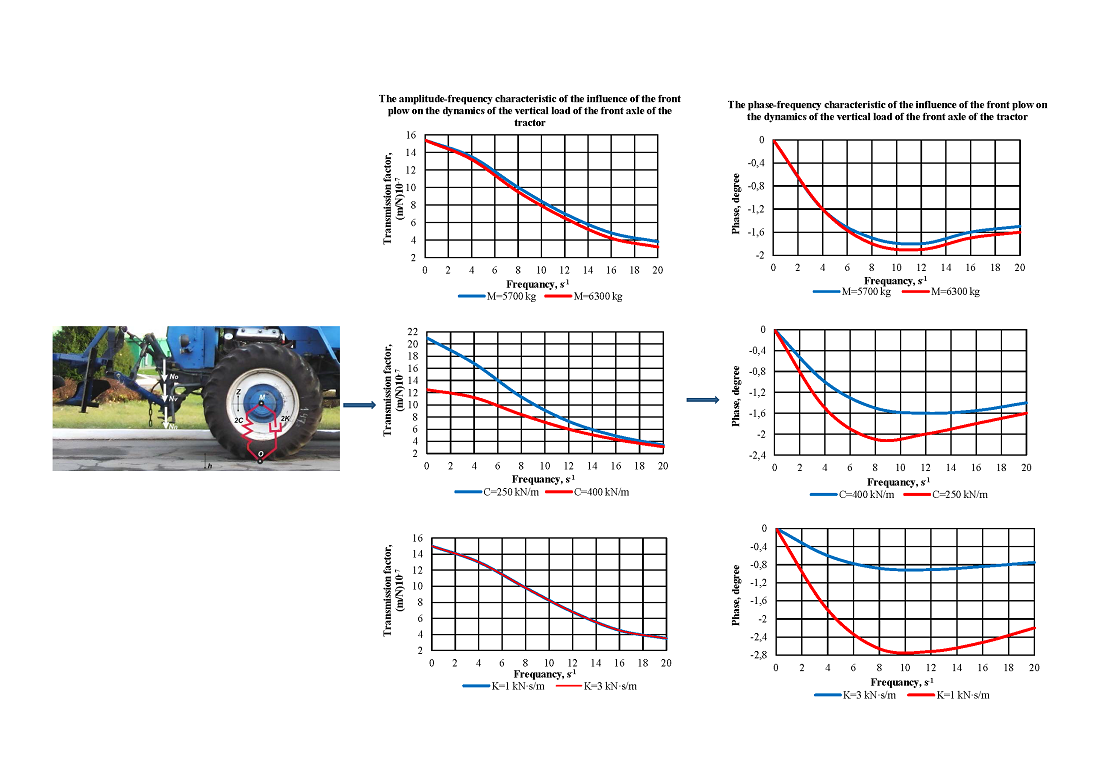
With the help of the constructed mathematical model and the corresponding amplitude and phase frequency characteristics, the dynamics of vertical oscillations of the front axle of a tractor with a front mounted plow without a support wheel were investigated. Vertical fluctuations of the total force acting on the tractor from the side of the plow were considered as a disturbing influence. According to the simulation results, an increase in the vertical load of the front axle of the tractor by 600 kg causes a desired decrease in the value of the amplitude and an increase in the phase of external disturbances of the dynamic system. The higher the frequency of disturbance oscillations, the more acceptable these characteristics become. It was established that in order to improve the response of the studied dynamic system to disturbances, it is necessary to reduce the stiffness coefficient of the tires of the front wheels. In practice, this is achieved by adjusting the air pressure in the tires. The amplitude-frequency characteristics of the system almost do not change when the damping coefficient of the tires of the front wheels of the tractor is increased in the range from 1 to 3 kN·s/m, while the phase-frequency characteristics improve. This is especially noticeable at the frequencies of oscillations of the disturbing influence in the range of 0–10 s-1.
The results could be used as a basis for evaluating the efficiency of tractors with a front plow without a support wheel in tillage operations. Such efficiency can be achieved under the condition of practical implementation of the recommendations proposed in this paper regarding the selection of design parameters of tires for the front wheels of the tractor
References
- Liu, K., Sozzi, M., Gasparini, F., Marinello, F., Sartori, L. (2023). Combining simulations and field experiments: Effects of subsoiling angle and tillage depth on soil structure and energy requirements. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 214, 108323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.108323
- Kraut-Cohen, J., Zolti, A., Shaltiel-Harpaz, L., Argaman, E., Rabinovich, R., Green, S. J., Minz, D. (2020). Effects of tillage practices on soil microbiome and agricultural parameters. Science of The Total Environment, 705, 135791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135791
- Ren, Z., Han, X., Feng, H., Wang, L., Ma, G., Li, J. et al. (2024). Long-term conservation tillage improves soil stoichiometry balance and crop productivity based on a 17-year experiment in a semi-arid area of northern China. Science of The Total Environment, 908, 168283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168283
- Ambike, S. S., Schmiedeler, J. P. (2007). Application of Geometric Constraint Programming To The Kinematic Design of Three-Point Hitches. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 23 (1), 13–21. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.22325
- Bulgakov, V., Ivanovs, S., Nadykto, V., Petrov, G. (2023). Investigation of front plough functioning stability conditions without support wheel. Engineering for Rural Development. https://doi.org/10.22616/erdev.2023.22.tf116
- Gluckauf, Z. W. (1989). Operating experience with a plough for difficult seams (in German). International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 26 (6), 321. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(89)91711-7
- ASAE Standards AD730: 2012, 2012. Agricultural wheeled tractors – Rear-mounted three-point linkage – Categories 1N, 1, 2N, 2, 3N, 3, 4N AND 4. St. Joseph, Michigan: ASAE.
- ASAE Standards S513, 2003. Agricultural wheeled tractors - Front-hitched three-point linkage. St. Joseph, Michigan: ASAE.
- Macmillan, R. H. (2002). The Mechanics of Tractor Implement Performance: Theory and Worked Examples. University of Melbourne.
- Askari, M., Komarizade, M. H., Nikbakht, A. M., Nobakht, N., Teimourlou, R. F. (2011). A novel three-point hitch dynamometer to measure the draft requirement of mounted implements. Research in Agricultural Engineering, 57 (4), 128–136. https://doi.org/10.17221/16/2011-rae
- Jagan, T., Ponpaul, R. S. (2022). Utilization of Tractor Power using Front Three Point Linkage. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2272 (1), 012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2272/1/012004
- Portes, P., Bauer, F., Cupera, J. (2013). Laboratory-experimental verification of calculation of force effects in tractor’s three-point hitch acting on driving wheels. Soil and Tillage Research, 128, 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2012.10.007
- Prasanna Kumar, G. V. (2015). Geometric performance parameters of three-point hitch linkage system of a 2WD Indian tractor. Research in Agricultural Engineering, 61 (1), 47–53. https://doi.org/10.17221/79/2012-rae
- Kumar, A., Pranav, P. K., Kumar, S. (2018). Computer simulation of three-point linkage parameters for virtual hitch point and optimum depth of operation. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 11 (3), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eaef.2018.02.006
- Tatíček, M., Bauer, F., Sedlák, P., Čupera, J. (2014). The effect of setup of three point linkage on energetic and performance parameters of tractor aggregate. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 59 (5), 253–262. https://doi.org/10.11118/actaun201159050253
- Bulgakov, V., Nadykto, V., Kyurchev, S., Nesvidomin, V., Ivanovs, S., Olt, J. (2019). Theoretical background for increasing grip properties of wheeled tractors based on their rational ballasting. Agraarteadus: Journal of Agricultural Science, 30 (2), 78–84. https://doi.org/10.15159/jas.19.07
- Mamkagh, A. M. (2018). Effect of Tillage Speed, Depth, Ballast Weight and Tire Inflation Pressure on the Fuel Consumption of the Agricultural Tractor: A Review. Journal of Engineering Research and Reports, 3 (2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.9734/jerr/2018/v3i216871
- Zhang, S., Ren, W., Xie, B., Luo, Z., Wen, C., Chen, Z. et al. (2023). A combined control method of traction and ballast for an electric tractor in ploughing based on load transfer. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 207, 107750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.107750
- Zhang, S., Xie, B., Wen, C., Zhao, Y., Du, Y., Zhu, Z. et al. (2022). Intelligent ballast control system with active load-transfer for electric tractors. Biosystems Engineering, 215, 143–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2022.01.008
- Singh, N., Pandey, K. (2017). Development of Visual Basic Program to Design Front Mounted Three-Point Linkage for Higher Power Tractors. Advances in Research, 11 (2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.9734/air/2017/35767
- Zheng, E., Zhong, X., Zhu, R., Xue, J., Cui, S., Gao, H., Lin, X. (2019). Investigation into the vibration characteristics of agricultural wheeled tractor-implement system with hydro-pneumatic suspension on the front axle. Biosystems Engineering, 186, 14–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.05.004
- Bauer, F., Porteš, P., Slimařík, D., Čupera, J., Fajman, M. (2017). Observation of load transfer from fully mounted plough to tractor wheels by analysis of three point hitch forces during ploughing. Soil and Tillage Research, 172, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.05.007
- Havrysh, V. I., Bondarenko, V. O. (2011). Osnovy teoriyi rozrakhunku mobilnykh enerhetychnykh zasobiv. Mykolaiv: MDAU, 284.
- Zeidman, P., Friston, K., Parr, T. (2023). A primer on Variational Laplace (VL). NeuroImage, 279, 120310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120310
- Aizerman, M. A. (1963). Theory of automatic control. A volume in Adiwes International Series in the Engineering Sciences. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2013-0-01720-3
- Ogata, K. (2010). Modern Control Engineering. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc., 912.
- Sorin-Stefan, B., Valenti, V. (2012). Use of Finite Element Method to Determine the Influence of Land Vehicles Traffic on Artificial Soil Compaction. Water Stress. https://doi.org/10.5772/30189
- Franklin, G. F., Powell, J. D., Emami-Naeini, A. (2019). Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems. New York: Pearson.
- Nise, N. S. (2011). Control Systems Engineering. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Zhang, J., Yao, H., Chen, L., Zheng, E., Zhu, Y., Xue, J. (2022). Vibration characteristics analysis and suspension parameter optimization of tractor/implement system with front axle suspension under ploughing operation condition. Journal of Terramechanics, 102, 49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jterra.2022.05.001
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Volodymyr Nadykto, Gennadii Golub, Volodymyr Kyurchev, Nataliya Tsyvenkova, Gennadii Petrov, Yaroslav Yarosh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








