Increasing the reliability of diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy based on machine learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.297849Keywords:
fundus images, diabetic retinopathy, neural network, image preprocessing, medical image analysisAbstract
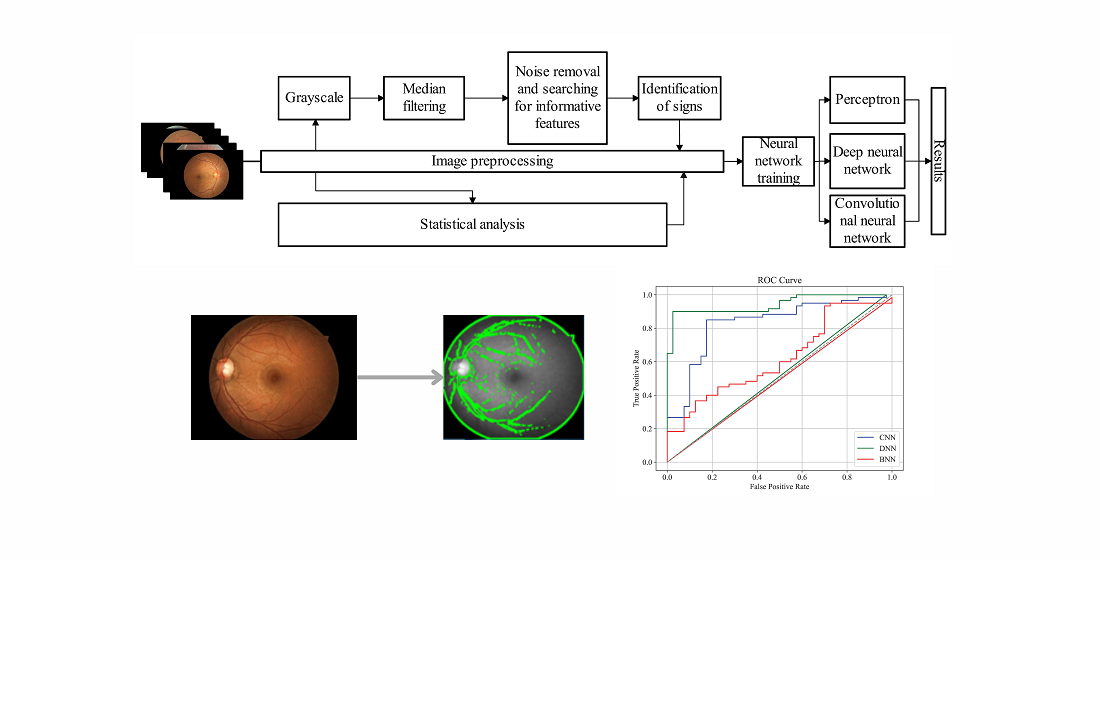
This paper discusses the method of measuring and analyzing the parameters of the retina with subsequent diagnosis based on them of pathological changes due to diabetic retinopathy, which is crucial in the field of medicine to help doctors in timely detection and treatment of the disease. The main problem of biomedical image data analysis is insufficient pre-processing of images for further clear determination of informative indicators. This paper explores the application of machine learning and image processing techniques to develop an effective method for the diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy. The main focus is on obtaining the optimal model using machine learning and different types of neural networks. This paper considered and analyzed such methods of image preprocessing as: median filtering, grayscale conversion, cropping of non-informative areas of the image, selection of contours. The classification results of three rules (Classical Neural Networks (CNNs), Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) were analyzed, and through experimental studies it was determined that the ANN performed the task best (accuracy=87.1 %, reliability=84.6 %, sensitivity=91.6 %, specificity=84 %). An information model was obtained to support decision-making in assessing the condition of the retina using the processing of the obtained microscopic images and further analysis of informative parameters, and a database of more than 35,000 samples and informative features of the retina was formed. Given the sufficient quality of classification and the availability of software and hardware, this method can be developed and applied in practice in medical institutions after conducting all the necessary clinical studies
References
- Diabetes. WHO. Available at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1
- Burton, M. J., Ramke, J., Marques, A. P., Bourne, R. R. A., Congdon, N., Jones, I. et al. (2021). The Lancet Global Health Commission on Global Eye Health: vision beyond 2020. The Lancet Global Health, 9 (4), e489–e551. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30488-5
- GBD Results. Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Available at: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/
- Diabetes Now Affects One in 10 Adults Worldwide. International Diabetes Federation. Available at: https://idf.org/news/diabetes-now-affects-one-in-10-adults-worldwide/
- Kropp, M., Golubnitschaja, O., Mazurakova, A., Koklesova, L., Sargheini, N., Vo, T.-T. K. S. et al. (2023). Diabetic retinopathy as the leading cause of blindness and early predictor of cascading complications – risks and mitigation. EPMA Journal, 14 (1), 21–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13167-023-00314-8
- Bhatwadekar, A. D., Shughoury, A., Belamkar, A., Ciulla, T. A. (2021). Genetics of Diabetic Retinopathy, a Leading Cause of Irreversible Blindness in the Industrialized World. Genes, 12 (8), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081200
- Chabba, N., Silwal, P. R., Bascaran, C., McCormick, I., Goodman, L., Gordon, I. et al. (2024). What is the coverage of retina screening services for people with diabetes? Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open, 14 (1), e081123. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081123
- Jonas, J. B., Sabanayagam, C. (2019). Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy and Cardiovascular Disease, 20–37. https://doi.org/10.1159/000486262
- Ursin, F., Timmermann, C., Orzechowski, M., Steger, F. (2021). Diagnosing Diabetic Retinopathy With Artificial Intelligence: What Information Should Be Included to Ensure Ethical Informed Consent? Frontiers in Medicine, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.695217
- Artificial Neural Networks/Neural Network Basics. Wikibooks. Available at: https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Artificial_Neural_Networks/Neural_Network_Basics
- Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. Kaggle. Available at: https://www.kaggle.com/c/diabetic-retinopathy-detection/data
- Li, T., Gao, Y., Wang, K., Guo, S., Liu, H., Kang, H. (2019). Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for diabetic retinopathy screening. Information Sciences, 501, 511–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.011
- Decencière, E., Zhang, X., Cazuguel, G., Lay, B., Cochener, B., Trone, C. et al. (2014). Feedback on a publicly distributed image database: the messidor database. Image Analysis & Stereology, 33 (3), 231. https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.1155
- Li, W., Bian, L., Ma, B., Sun, T., Liu, Y., Sun, Z. et al. (2024). Interpretable Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy, Retinal Vein Occlusion, Age-Related Macular Degeneration, and Other Fundus Conditions. Diagnostics, 14 (2), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14020121
- Kumar, N. S., Balasubramanian, R. K., Phirke, M. R. (2023). Image Transformers for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection from Fundus Datasets. Revue d’Intelligence Artificielle, 37 (6), 1617–1627. https://doi.org/10.18280/ria.370626
- Vandana, Laxmi, V. (2023). The Detection and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy using the Architectures of Deep Learning. International Journal For Multidisciplinary Research, 5 (6). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2023.v05i06.10837
- Sanamdikar, S. T., Patil, S. A., Patil, D. O., Borawake, M. P. (2023). Enhanced Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Ensemble Machine Learning: A Comparative Study. Ingénierie Des Systèmes d Information, 28 (6), 1663–1668. https://doi.org/10.18280/isi.280624
- Dai, L., Sheng, B., Chen, T., Wu, Q., Liu, R., Cai, C. et al. (2024). A deep learning system for predicting time to progression of diabetic retinopathy. Nature Medicine, 30 (2), 584–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02702-z
- Zago, G. T., Andreão, R. V., Dorizzi, B., Teatini Salles, E. O. (2020). Diabetic retinopathy detection using red lesion localization and convolutional neural networks. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 116, 103537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103537
- Qummar, S., Khan, F. G., Shah, S., Khan, A., Shamshirband, S., Rehman, Z. U. et al. (2019). A Deep Learning Ensemble Approach for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. IEEE Access, 7, 150530–150539. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2947484
- Bakator, M., Radosav, D. (2018). Deep Learning and Medical Diagnosis: A Review of Literature. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 2 (3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2030047
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Orken Mamyrbayev, Sergii Pavlov, Oleksandr Karas, Yosip Saldan, Kymbat Momynzhanova, Sholpan Zhumagulova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








