Determining the influence of relative humidity on the working parameters of a gas sensor based on zinc oxide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.307234Keywords:
gas sensor, zinc oxide, magnetron sputtering, relative humidity, standard conditionsAbstract
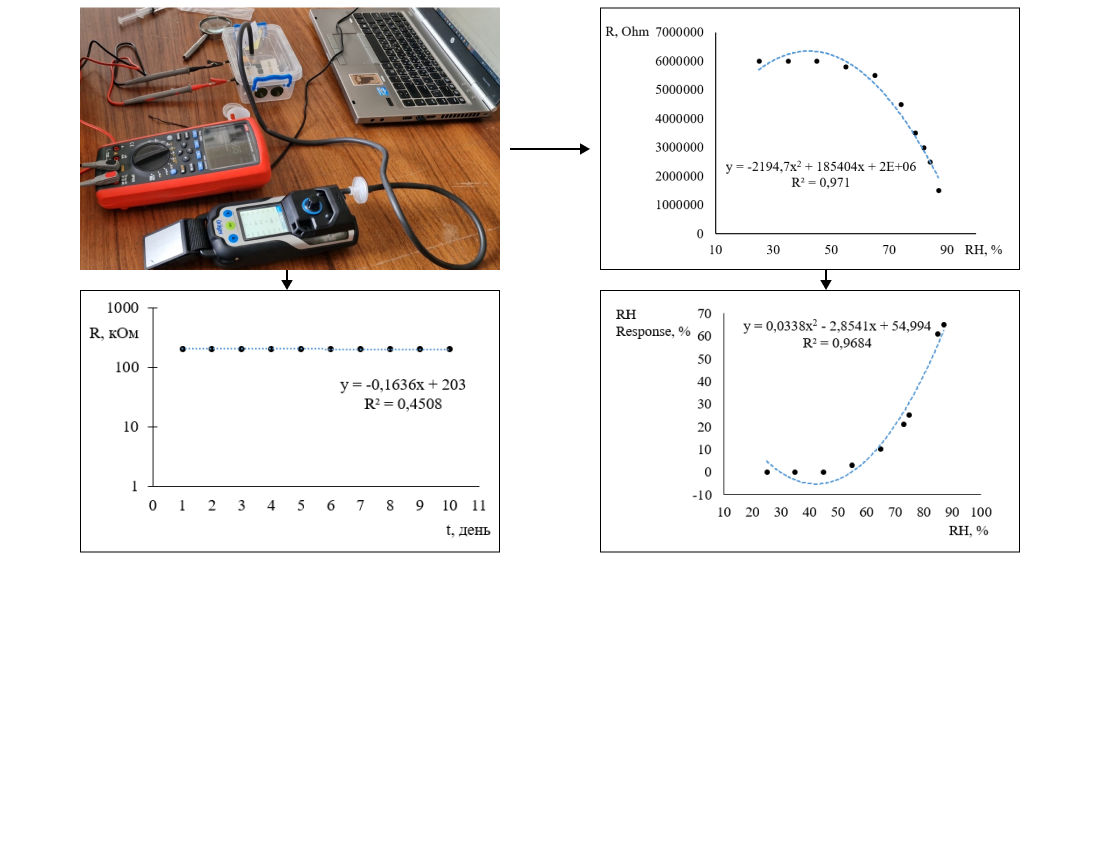
This paper investigates the dependence of operating parameters of a gas sensor based on zinc oxide obtained by the method of direct current magnetron sputtering. The production of gas sensor films was carried out using a VUP-5M vacuum unit with an original material-saving magnetron. The study of the dependence of the working parameters of the gas sensor was carried out under standard conditions. It was found that with increasing humidity, the electrical resistance of the gas sensor decreases and, accordingly, the sensitivity to the target gas decreases. A significant reaction of the gas sensor to an increase in humidity was observed in the range of 65–80 % relative humidity. The mechanism of influence of relative humidity on the sensitivity of a gas sensor based on ZnO was investigated. The change in resistance of the gas sensor is caused by trapped electrons on adsorbed oxygen molecules on the surface of the sensitive layer. The capture of electrons from the conduction zone leads to bending of the conduction zone and an increase in the space charge zone, respectively, to a change in the resistance of the sensitive layer of the gas sensor. In the atmosphere, when O2 molecules are adsorbed on the ZnO surface, they remove an electron from the conduction band. The reaction of oxygen adsorbed on the ZnO surface with reducing gases and the replacement of adsorbed oxygen with other molecules changes the bending of the conduction band and reduces the area of space charge. Adsorption of water on the surface of zinc oxide occurs according to the dissociation mechanism, which consists in the adsorption of steam molecules or hydroxyl groups with the subsequent displacement of previously adsorbed oxygen and free electrons and, accordingly, leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of the gas sensor. In addition, the adsorption of water vapor (H2O) molecules leads to less chemisorption of oxygen species on the ZnO surface due to the reduction of the surface area, which is responsible for the sensor response. Approaches to reduce the influence of relative humidity on the sensitivity of a gas sensor based on zinc oxide have been proposed
References
- Deng, X., Sang, S., Li, P., Li, G., Gao, F., Sun, Y. et al. (2013). Preparation, Characterization, and Mechanistic Understanding of Pd-Decorated ZnO Nanowires for Ethanol Sensing. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2013, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/297676
- Buryy, O., Ubizskii, S. В. (2017). Nanostructured gas sensors: the state of the art and perspectives for research. Visnyk Natsionalnoho universytetu «Lvivska politekhnika». Seriya: Radioelektronika ta telekomunikatsiyi, 885, 113–131. Available at: https://science.lpnu.ua/sites/default/files/journal-paper/2018/jun/13517/17.pdf
- Popov, O., Ivaschenko, T., Markina, L., Yatsyshyn, T., Iatsyshyn, A., Lytvynenko, O. (2023). Peculiarities of Specialized Software Tools Used for Consequences Assessment of Accidents at Chemically Hazardous Facilities. Systems, Decision and Control in Energy V, 779–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35088-7_45
- Parihar, V., Raja, M., Paulose, R. (2018). A Brief Review of Structural, Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Reviews On Advanced Materials Science, 53 (2), 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1515/rams-2018-0009
- Ryzhikov, A., Jońca, J., Kahn, M., Fajerwerg, K., Chaudret, B., Chapelle, A. et al. (2015). Organometallic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for gas sensing: towards selectivity through nanoparticles morphology. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 17 (7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3086-2
- Kumar, R., Al-Dossary, O., Kumar, G., Umar, A. (2014). Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for NO2 Gas–Sensor Applications: A Review. Nano-Micro Letters, 7 (2), 97–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-014-0023-3
- Pospelov, B., Rybka, E., Meleshchenko, R., Krainiukov, O., Harbuz, S., Bezuhla, Y. et al. (2020). Use of uncertainty function for identification of hazardous states of atmospheric pollution vector. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (10 (104)), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.200140
- Harun, K., Mansor, N., Ahmad, Z. A., Mohamad, A. A. (2016). Electronic Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-gel Method: A LDA+U Calculation and Experimental Study. Procedia Chemistry, 19, 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.03.125
- Minska, N., Ponomarenko, R., Shevchenko, R., Antoshkin, O. (2023). Optimization of the Technology of Creating Sensitive Gas Sensors Based on Zinc Oxide. Materials Science Forum, 1096, 81–86. https://doi.org/10.4028/p-lm4qpy
- Minska, N., Hvozd, V., Shevchenko, O., Slepuzhnikov, Y., Murasov, R., Khrystych, V. et al. (2023). Devising technological solutions for gas sensors based on zinc oxide for use at critical infrastructure facilities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (5 (124)), 34–40. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286546
- Agarwal, S., Rai, P., Gatell, E. N., Llobet, E., Güell, F., Kumar, M., Awasthi, K. (2019). Gas sensing properties of ZnO nanostructures (flowers/rods) synthesized by hydrothermal method. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 292, 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.083
- Dral, A. P., ten Elshof, J. E. (2018). 2D metal oxide nanoflakes for sensing applications: Review and perspective. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 272, 369–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.157
- Danchenko, Y., Andronov, V., Barabash, E., Obigenko, T., Rybka, E., Meleshchenko, R., Romin, A. (2017). Research of the intramolecular interactions and structure in epoxyamine composites with dispersed oxides. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (12 (90)), 4–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.118565
- Bian, H., Ma, S., Sun, A., Xu, X., Yang, G., Yan, S. et al. (2016). Improvement of acetone gas sensing performance of ZnO nanoparticles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 658, 629–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.217
- Yan, H., Song, P., Zhang, S., Yang, Z., Wang, Q. (2016). Facile synthesis, characterization and gas sensing performance of ZnO nanoparticles-coated MoS2 nanosheets. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 662, 118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.066
- Umar, A., Khan, M. A., Kumar, R., Algarni, H. (2018). Ag-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Enhanced Ethanol Gas Sensing Application. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 18 (5), 3557–3562. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14651
- Zhang, D., Yang, Z., Li, P., Zhou, X. (2019). Ozone gas sensing properties of metal-organic frameworks-derived In2O3 hollow microtubes decorated with ZnO nanoparticles. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 301, 127081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127081
- Miasoiedova, A., Minska, N., Shevchenko, R., Azarenkо, O., Lukashenko, V., Kyrychenko, O. et al. (2023). Improving the manufacturing technology of sensing gas sensors based on zinc oxide by using the method of magnetron sputtering on direct current. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (5 (122)), 31–37. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.277428
- Deyneko, N., Kovalev, P., Semkiv, O., Khmyrov, I., Shevchenko, R. (2019). Development of a technique for restoring the efficiency of film ITO/CdS/CdTe/Cu/Au SCs after degradation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (5 (97)), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.156565
- Khrypunov, G., Vambol, S., Deyneko, N., Sychikova, Y. (2016). Increasing the efficiency of film solar cells based on cadmium telluride. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (5 (84)), 12–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2016.85617
- Deyneko, N., Kryvulkin, I., Matiushenko, M., Tarasenko, O., Khmyrov, I., Khmyrova, A., Shevchenko, R. (2019). Investigation of photoelectric converters with a base cadmium telluride layer with a decrease in its thickness for tandem and two-sided sensitive instrument structures. EUREKA: Physics and Engineering, 5, 73–80. https://doi.org/10.21303/2461-4262.2019.001002
- Hübner, M., Simion, C. E., Tomescu-Stănoiu, A., Pokhrel, S., Bârsan, N., Weimar, U. (2011). Influence of humidity on CO sensing with p-type CuO thick film gas sensors. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 153 (2), 347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.10.046
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Natalia Minska, Alexander Levterov, Olga Shevchenko, Andrii Sihaiov, Oleksii Shcherbak, Serhii Poliakov, Vasyl Rotar, Oleksandr Rebrov, Volodymyr Kradozhon, Nataliia Zobenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








