Large language model (LLM) comparison between GPT-3 and PaLM-2 to produce Indonesian cultural content
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.309972Keywords:
large language model, generative artificial intelligence, GPT-3, PaLM-2, BERTScore EvaluationAbstract
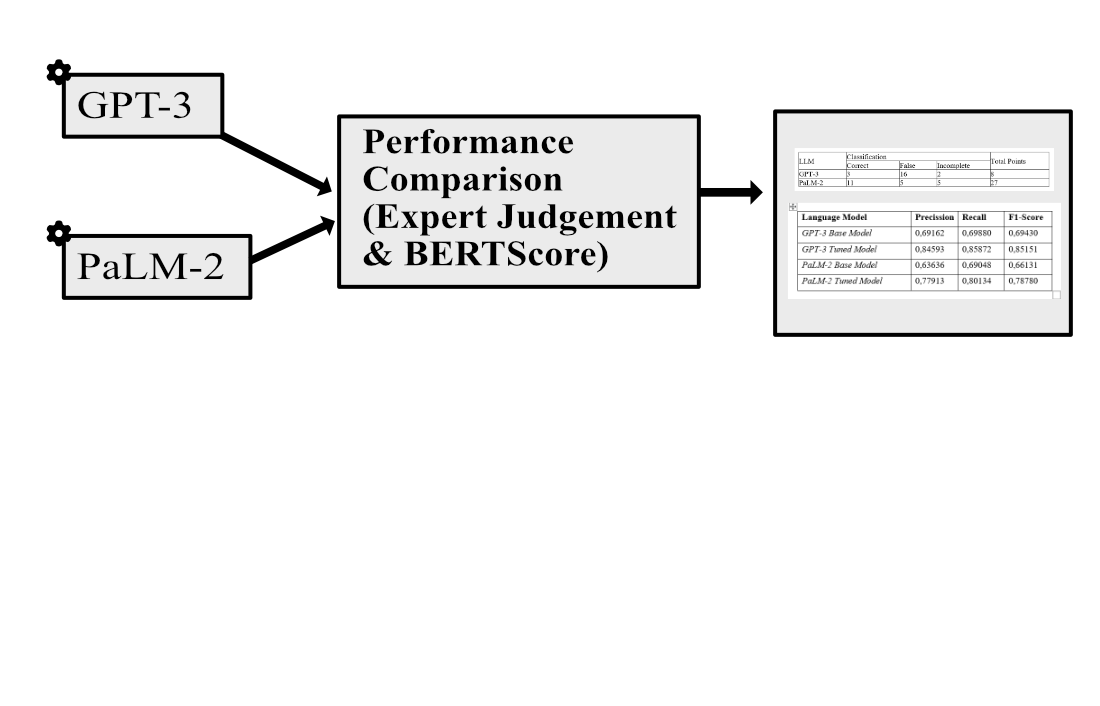
Large language models can help to compile content with a cultural theme. However, any information generated by large language models needs to be evaluated to see the truth/fact of the information generated. With many studies discussing the comparison of the capabilities of large language models, there is not much research that directly discusses the comparison of the performance of large language models in producing Indonesian cultural content. This research compares the correctness of the information generated by the large language model using the expert judgment method when creating Indonesian cultural content and its fine-tuning capabilities evaluated using BERTScore. The evaluation method was successfully applied and the results show that in this case, PaLM-2 included less misinformation while GPT-3 excelled in fine-tuning. Using the combination of expert judgment and BERTScore makes it possible to evaluate large language models and obtain additional valid training data to correct deficiencies. The results showed that PaLM-2 produced more valid content with a score of 27 points, while GPT-3 scored 8 points. For training on new datasets/fine-tuning, it was found that the GPT-3 language model was able to learn the dataset more quickly, with a time of 50 minutes and a cost of IDR 27,000, while PaLM-2 took 2 hours 10 minutes and a cost of IDR 1,377,204. For the training dataset evaluation results, GPT-3 is superior with an average of all scores reaching 0.85205. Meanwhile, the PaLM-2 Tuned Model got an average overall score of 0.78942. In this case, the GPT-3 Tuned Model is superior by 8 %. In practice, this method can be used if the assessment is descriptive and requires direct assessment from experts
Supporting Agency
- Thank you to the Palembang City Culture Service for being a resource for the data in this research.
References
- Wijaya, J. H. (2023). Lifestyle Transformation in Indonesia: The Impact of Foreign Cultures in the Era of Globalization. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4511264
- Adnan, N. (2014). Character Building Through Traditional Dance As Developing Identity Belongings: A Study Of Indonesia-Malaysia. Proceeding of the Third International Seminar on Languages and Arts. Padang. Available at: https://ejournal.unp.ac.id/index.php/isla/article/view/5412/
- Barbier, E. B., Burgess, J. C. (2017). The Sustainable Development Goals and the systems approach to sustainability. Economics, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.5018/economics-ejournal.ja.2017-28
- Yamasaki, K., Yamada, T. (2022). A framework to assess the local implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 11. Sustainable Cities and Society, 84, 104002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.104002
- Negara, E., Hidayanto, A., Andryani, R., Syaputra, R. (2021). Survey of Smart Contract Framework and Its Application. Information, 12 (7), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12070257
- Lyu, Y., Zhang, H., Niu, S., Cai, J. (2024). A Preliminary Exploration of YouTubers’ Use of Generative-AI in Content Creation. Extended Abstracts of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. https://doi.org/10.1145/3613905.3651057
- Zhang, C., Lu, Y. (2021). Study on artificial intelligence: The state of the art and future prospects. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 23, 100224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2021.100224
- Koteluk, O., Wartecki, A., Mazurek, S., Kołodziejczak, I., Mackiewicz, A. (2021). How Do Machines Learn? Artificial Intelligence as a New Era in Medicine. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11 (1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010032
- Shabbir, J., Anwer, T. (2018). Artificial Intelligence and its Role in Near Future. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.01396
- Ahmed, I., Roy, A., Kajol, M., Hasan, U., Datta, P. P., Reza, Md. R. (2023). ChatGPT vs. Bard: A Comparative Study. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.168923529.98827844/v1
- Shidiq, M. (2023). The Use Of Artificial Intelligence-Based Chat-gpt And Its Challenges For The World Of Education; From The Viewpoint Of The Development Of Creative Writing Skills. Proceeding of International Conference on Education, Society and Humanity, 353–357. Available at: https://ejournal.unuja.ac.id/index.php/icesh/article/view/5614
- González García, C., Núñez-Valdez, E., García-Díaz, V., Pelayo G-Bustelo, C., Cueva-Lovelle, J. M. (2019). A Review of Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 5 (4), 9. https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2018.03.004
- Jan, Z., Ahamed, F., Mayer, W., Patel, N., Grossmann, G., Stumptner, M., Kuusk, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0: Systematic review of applications, challenges, and opportunities. Expert Systems with Applications, 216, 119456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119456
- Hasan, A. R. (2022). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Accounting & Auditing: A Literature Review. Open Journal of Business and Management, 10 (01), 440–465. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojbm.2022.101026
- Hughes, R. T., Zhu, L., Bednarz, T. (2021). Generative Adversarial Networks–Enabled Human–Artificial Intelligence Collaborative Applications for Creative and Design Industries: A Systematic Review of Current Approaches and Trends. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2021.604234
- Tri Julianto, I., Kurniadi, D., Septiana, Y., Sutedi, A. (2023). Alternative Text Pre-Processing using Chat GPT Open AI. Jurnal Nasional Pendidikan Teknik Informatika (JANAPATI), 12 (1), 67–77. https://doi.org/10.23887/janapati.v12i1.59746
- Naveed, H., Khan, A. U., Qiu, S., Saqib, M., Anwar, S., Usman, M. et al. (2023). A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. arXiv. Available: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.06435
- Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P. et al. (2023). Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.14165
- Chowdhery, A., Narang, S., Devlin, J., Bosma, M., Mishra, G., Roberts, A. et al. (2022). PaLM: Scaling Language Modeling with Pathways. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2204.02311
- Andryani, R., Surya Negara, E., Syaputra, R., Erlansyah, D. (2023). Analysis of Academic Social Networks in Indonesia. Qubahan Academic Journal, 3 (4), 409–421. https://doi.org/10.58429/qaj.v3n4a289
- Negara, E. S., Keni, K., Andryani, R., Syaputra, R. S., Widyanti, Y. (2023). Social network analysis to detect influential actors with Indonesian hastags using the centrality method. Sixth International Conference of Mathematical Sciences (ICMS 2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0126819
- Negara, E. S., Andryani, R., Erlansyah, D., Syaputra, R. (2020). Analysis of Indonesian Motorcycle Gang with Social Network Approach. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 11 (12). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2020.0111224
- Nurhachita, N., Negara, E. S. (2021). A comparison between deep learning, naïve bayes and random forest for the application of data mining on the admission of new students. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence (IJ-AI), 10 (2), 324. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v10.i2.pp324-331
- Anil, R., Dai, A. M., Firat, O., Johnson, M., Lepikhin, D., Passoset, A. et al. (2023). PaLM 2 Technical Report. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.10403
- Porter, J. (2023). ChatGPT continues to be one of the fastest-growing services ever. The Verge. Available at: https://www.theverge.com/2023/11/6/23948386/chatgpt-active-user-count-openai-developer-conference
- Aydin, Ö., Karaarslan, E. (2023). Is ChatGPT Leading Generative AI? What is Beyond Expectations? Academic Platform Journal of Engineering and Smart Systems, 11 (3), 118–134. https://doi.org/10.21541/apjess.1293702
- Farquhar, S., Varma, V., Kenton, Z., Gasteiger, J., Mikulik, V., Shah, R. (2024). Challenges with unsupervised LLM knowledge discovery. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.10029
- Floridi, L., Chiriatti, M. (2020). GPT-3: Its Nature, Scope, Limits, and Consequences. Minds and Machines, 30 (4), 681–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11023-020-09548-1
- Chae, Y., Davidson, T. (2023). Large Language Models for Text Classification: From Zero-Shot Learning to Instruction-Tuning. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/sthwk
- Bi, B., Li, C., Wu, C., Yan, M., Wang, W., Huang, S. et al. (2020). PALM: Pre-training an Autoencoding&Autoregressive Language Model for Context-conditioned Generation. Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.700
- Schubert, M. C., Wick, W., Venkataramani, V. (2023). Performance of Large Language Models on a Neurology Board–Style Examination. JAMA Network Open, 6 (12), e2346721. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.46721
- Chen, L., Chen, P., Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2988510
- Koto, F., Aisyah, N., Li, H., Baldwin, T. (2023). Large Language Models Only Pass Primary School Exams in Indonesia: A Comprehensive Test on IndoMMLU. Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.emnlp-main.760
- Dao, X.-Q. (2023). Performance Comparison of Large Language Models on VNHSGE English Dataset: OpenAI ChatGPT, Microsoft Bing Chat, and Google Bard. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.02288
- Ouyang, L., Wu, J., Jiang, X., Almeida, D., Wainwright, C. L., Mishkin, P. (2022). Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.02155
- Milani Fitria, K. (2023). Information Retrieval Performance in Text Generation using Knowledge from Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT-3). Jambura Journal of Mathematics, 5 (2), 327–338. https://doi.org/10.34312/jjom.v5i2.20574
- Rofiq, M. A., Azhar, A. (2022). Hazards Identification and Risk Assessment In Welding Confined Space Ship Reparation PT. X With Job Safety Analysis Method. BERKALA SAINSTEK, 10 (4), 175. https://doi.org/10.19184/bst.v10i4.32669
- Bill, D., Eriksson, T. (2023). Fine-Tuning A Llm Using Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback For A Therapy Chatbot Application. KTH. Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1782678/FULLTEXT01.pdf
- Zhang, T., Kishore, V., Wu, F., Weinberger, K. Q., Artzi, Y. (2020). BERTScore: Evaluating Text Generation with BERT. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1904.09675
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Deni Erlansyah, Amirul Mukminin, Dedek Julian, Edi Surya Negara, Ferdi Aditya, Rezki Syaputra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









