Development of Fe-Cr-C alloys with high Mn content for bone implant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.312442Keywords:
Fe-Cr-C alloy, biomaterials, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, Mn content, orthopedic implantsAbstract
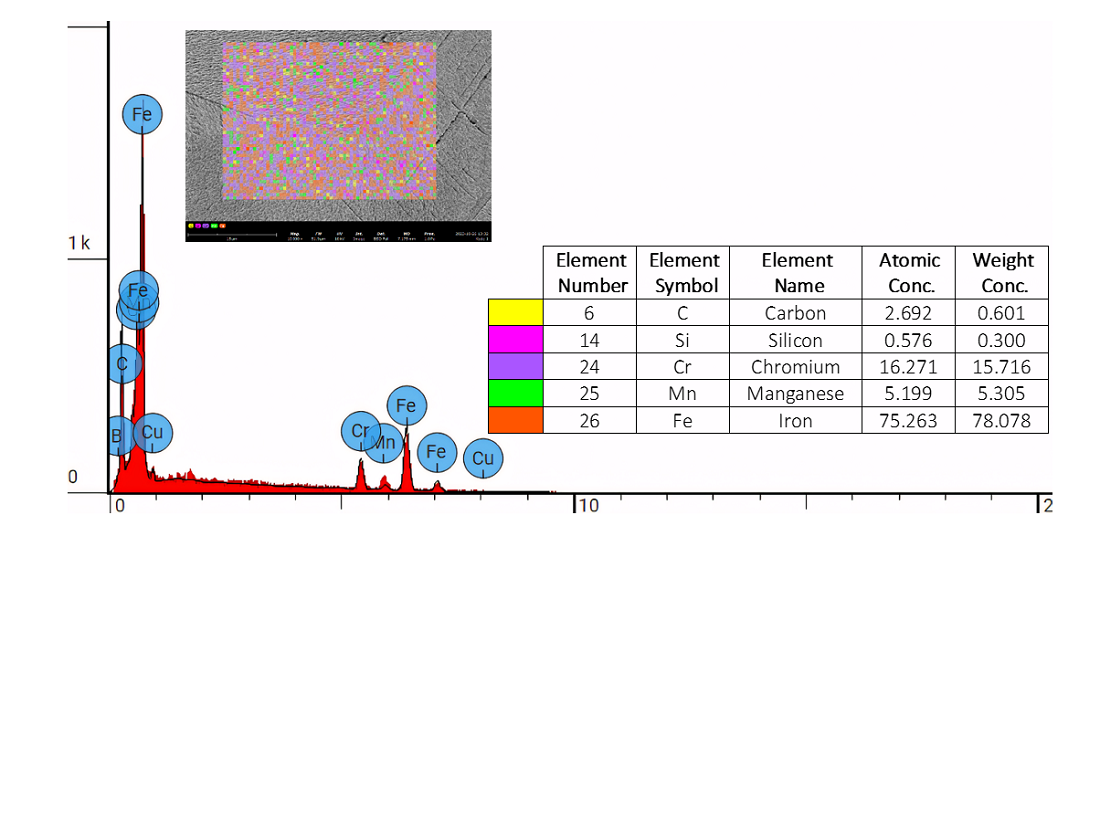
The object of this study is to combine the properties of Mn and the advantages of Fe-Cr-C to improve biomaterial compatible characteristics. Three alloys of Fe-Cr-C with compositions of 12 wt. % Mn, 16 wt. % Mn, and 20 wt. % Mn, were investigated. Microstructural analysis was carried out using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and a Vickers hardness test kit was used to evaluate the hardness. The pin-on-disc method was used for the dry slide wear test, and the corrosion test was carried out using the three-electrode cell polarization method. The hardness value of Fe-Cr-C alloy increased by 28.7 % with the increase of Mn content from 12 wt. % (231.8 VHN) to 20 wt. % (298.4 VHN). The tensile strength value increased by 30.3 % with an increase in Mn content from 12 wt. % (522.69 MPa) to 20 wt. % (680.89 MPa), while the strain value decreased by 30.9 %. However, impact toughness did somewhat decline, from 0.213 J/mm2 at 12 wt. % Mn to 0.169 J/mm2 at 20 wt. % Mn. The wear rate results for Fe-Cr-C 20 wt. % Mn 0.000156 mm3/kg. show a reduction of more than 15 wt. % when compared to Fe-Cr-C 12 wt. % Mn because of an increase in the hard-intermetallic area. Additionally, corrosion resistance improved significantly, with the corrosion rate decreasing from 0.005814 mm/yr at 12 wt. % Mn to 0.001780 mm/yr at 20 wt. % Mn, demonstrating that higher Mn content reduces material degradation in corrosive environments. Based on the experimental results, Fe-Cr-C 20 wt % Mn alloy has the highest mechanical and corrosion resistance of the three types of alloys. Fe-Cr-C with high Mn alloys are promising candidates for application as biomaterials for bone implants by optimizing the Mn content and corrosion resistance
References
- Wang, W., Ouyang, Y., Poh, C. K. (2011). Orthopaedic Implant Technology: Biomaterials from Past to Future. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore, 40 (5), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.v40n5p237
- Poinescu, A. A., Ion, R.-M. (2018). 316L Stainless Steel/Hydroxyapatite Composite Materials for Biomedical Applications. Hydroxyapatite - Advances in Composite Nanomaterials, Biomedical Applications and Its Technological Facets. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71490
- Ali, S., Abdul Rani, A. M., Mufti, R. A., Hastuty, S., Hussain, M., Shehzad, N. et al. (2019). An Efficient Approach for Nitrogen Diffusion and Surface Nitriding of Boron-Titanium Modified Stainless Steel Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Metals, 9 (7), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070755
- Salahinejad, E., Hadianfard, M. J., Macdonald, D. D., Sharifi-Asl, S., Mozafari, M., Walker, K. J. et al. (2013). In Vitro Electrochemical Corrosion and Cell Viability Studies on Nickel-Free Stainless Steel Orthopedic Implants. PLoS ONE, 8 (4), e61633. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061633
- Kartikasari, R., Subardi, A., Muhfidin, R., Aziz, I., Effendy, M., Triyono, T., Diharjo, K. (2023). Development of Fe-13.8Cr-8.9Mn alloy for steel biomaterials. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (12 (126)), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.293009
- Mahmoud, E. R. I., Shaharoun, A., Gepreel, M. A., Ebied, S. (2022). Phase Prediction, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe–Mn–Ni–Cr–Al–Si High Entropy Alloys. Metals, 12 (7), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071164
- Tiwar, S., Mishra, S. B. (2018). Corrosion of Stainless Steel and its Prevention through Surface Modification for Biomedical Application: A Review. Asian Journal of Engineering and Applied Technology, 7 (2), 60–66. https://doi.org/10.51983/ajeat-2018.7.2.954
- Nagarajan, S., Mohana, M., Sudhagar, P., Raman, V., Nishimura, T., Kim, S. et al. (2012). Nanocomposite Coatings on Biomedical Grade Stainless Steel for Improved Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4 (10), 5134–5141. https://doi.org/10.1021/am301559r
- Talha, M., Behera, C. K., Sinha, O. P. (2013). A review on nickel-free nitrogen containing austenitic stainless steels for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 33 (7), 3563–3575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.06.002
- Gregorutti, R. W., Grau, J. E., Sives, F., Elsner, C. I. (2015). Mechanical, electrochemical and magnetic behaviour of duplex stainless steel for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Technology, 31 (15), 1818–1824. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284715y.0000000017
- Al-Zoubi, N., Li, X., Schönecker, S., Johansson, B., Vitos, L. (2014). Influence of manganese on the bulk properties of Fe-Cr-Mn alloys: a first-principles study. Physica Scripta, 89 (12), 125702. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/89/12/125702
- Ha, H.-Y., Jang, M.-H., Lee, T.-H. (2016). Influences of Mn in solid solution on the pitting corrosion behaviour of Fe-23 wt%Cr-based alloys. Electrochimica Acta, 191, 864–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.01.118
- Yuan, Y., Wu, Y., Yang, Z., Liang, X., Lei, Z., Huang, H. et al. (2019). Formation, structure and properties of biocompatible TiZrHfNbTa high-entropy alloys. Materials Research Letters, 7 (6), 225–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2019.1584592
- Allain, J. P., Echeverry-Rendón, M. (2018). Surface treatment of metallic biomaterials in contact with blood to enhance hemocompatibility. Hemocompatibility of Biomaterials for Clinical Applications, 279–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-100497-5.00008-2
- Rasouli, D., Kermanpur, A., Najafizadeh, A. (2019). Developing high-strength, ductile Ni-free Fe–Cr–Mn–C–N stainless steels by interstitial-alloying and thermomechanical processing. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 8 (3), 2846–2853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.12.026
- Kartikasari, R., Effendy, M. (2021). Surface characterization of Fe–10Al–25Mn alloy for biomaterial applications. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 15, 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.08.006
- Eliaz, N. (2019). Corrosion of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review. Materials, 12 (3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030407
- Borgioli, F., Galvanetto, E., Bacci, T. (2016). Low temperature nitriding of AISI 300 and 200 series austenitic stainless steels. Vacuum, 127, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.02.009
- Yang, K., Ren, Y. (2010). Nickel-free austenitic stainless steels for medical applications. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 11 (1), 014105. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/11/1/014105
- Muñoz, A., Costa, M. (2012). Elucidating the mechanisms of nickel compound uptake: A review of particulate and nano-nickel endocytosis and toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 260 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.12.014
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ratna Kartikasari, Sugiarto Kadiman, Rivan Muhfidin, Ihwanul Aziz, Triyono Triyono

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








