Defining a pattern in the loss of integrity by ribbed plates under fire conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313935Keywords:
fire resistance of reinforced concrete ribbed slabs, fire modeling, through cracks, loss of integrityAbstract
This paper reports a study aimed at assessing fire resistance of reinforced concrete ribbed slabs at the onset of integrity loss limit state. EN 1992-1-2 lacks calculation methodology for determining the limit of fire resistance of reinforced concrete slabs when the limit state of integrity loss occurs. Scientific works are focused on two limit states of fire resistance: load-bearing capacity and heat-insulating capacity. Experimental tests are criticized because of difficulties in registering signs of the onset of the limit state of loss of integrity, in particular due to the need to control the unheated surface of the ribbed plate during a fire under the action of mechanical load. Therefore, there is no calculation methodology for assessing the fire resistance of reinforced concrete ribbed slabs upon the onset of the limit state of loss of integrity. At the same time, to ensure the safe evacuation of people in the event of a fire, to prevent the spread of fire, as well as to carry out the effective work of rescuers, it is necessary to use building structures with guaranteed fire resistance classes.
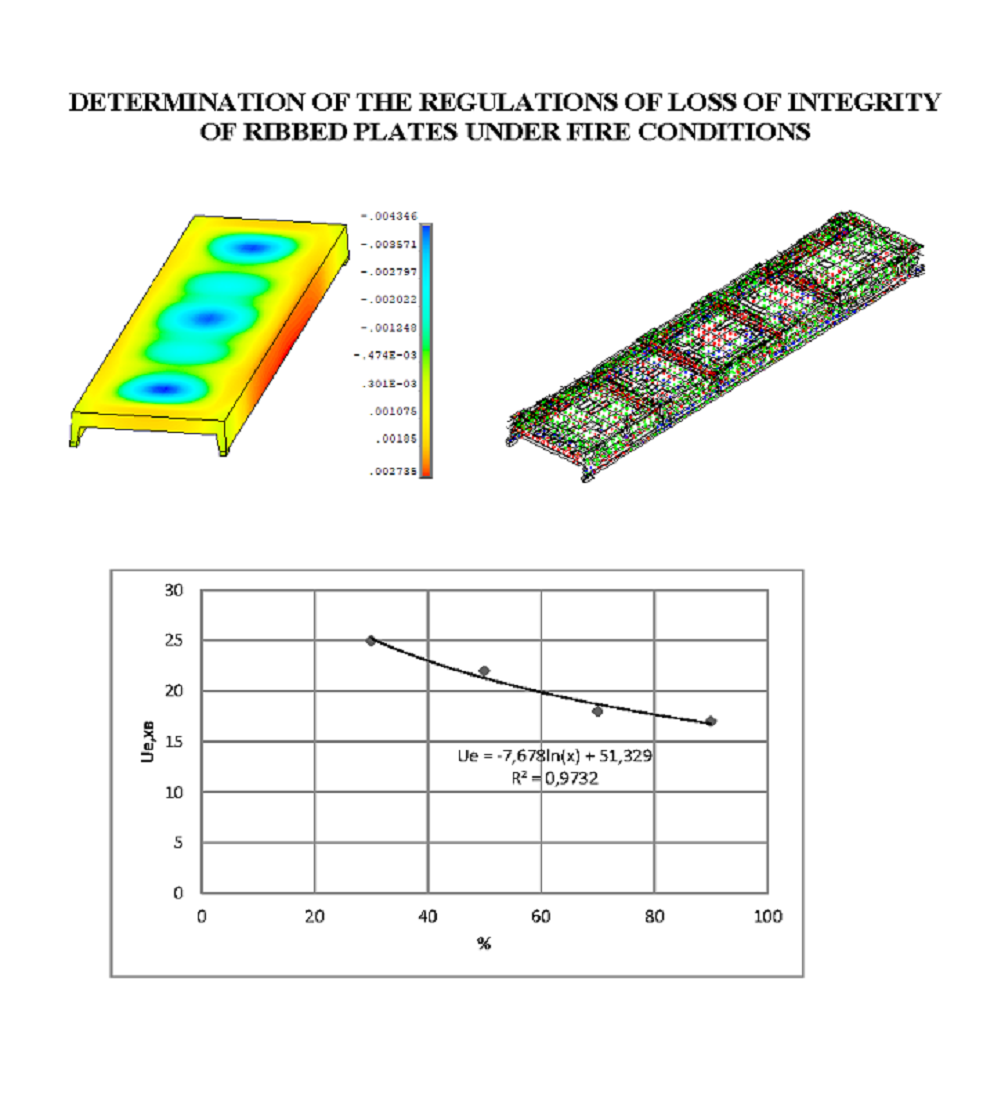
The paper reports the results of solving thermal engineering and static problems, which relate to the temperature distribution and stress-strain state of the investigated ribbed plate. Conducting research into the fire resistance of reinforced concrete ribbed slabs, taking into account the onset of the limit state of loss of integrity, made it possible to establish the dependence of the fire resistance limit of these structures on the loss of integrity on the level of applied mechanical load. The resulting dependence plot makes it possible to evaluate reinforced concrete ribbed slabs according to the criterion of the onset of the limit state of loss of integrity, which provides an opportunity to determine fire resistance more objectively
References
- Hu, R., Chen, K., Jiang, W., Luo, H. (2024). IFC data extension for real-time safety monitoring of automated construction in high-rise building projects. Automation in Construction, 162, 105408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105408
- Salihu, F., Guri, Z., Cvetkovska, M., Pllana, F. (2023). Fire Resistance Analysis of Two-Way Reinforced Concrete Slabs. Civil Engineering Journal, 9 (5), 1085–1104. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2023-09-05-05
- Eurocodes. Background and applications: structural fire design. Worked examples (2014). European Union. https://doi.org/10.2788/85432
- Sidnei, S., Berezovskyi, A., Kasiarum, S., Lytvynenko, O., Chastokolenko, I. (2023). Revealing patterns in the behavior of a reinforced concrete slab in fire based on determining its stressed and deformed state. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (7 (125)), 43–49. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289930
- Vasilchenko, A., Danilin, O., Lutsenko, T., Ruban, A. (2021). Features of Evaluation of Fire Resistance of Reinforced Concrete Ribbed Slab under Combined Effect “Explosion-Fire.” Materials Science Forum, 1038, 492–499. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.1038.492
- Buchanan, A. H., Abu, A. K. (2016). Structural Design for Fire Safety. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118700402
- Dzidic, S. (2023). Fire Resistance of Reinforced Concrete Slabs. Reinforced Concrete Structures - Innovations in Materials, Design and Analysis. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.1001046
- Kildashti, K., Katwal, U., Tao, Z., Tam, V. (2024). Numerical simulation of steel-concrete composite beams and slabs at elevated temperatures. Engineering Structures, 315, 118297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118297
- Nuianzin, O., Kozak, A., Kostenko, V., Kryshtal, M., Nuianzin, V., Nekora, O. (2023). The research of the fire resistance limits of a reinforced concrete slab according to the results of fire tests without mechanical load. Strength of Materials and Theory of Structures, 110, 264–276. https://doi.org/10.32347/2410-2547.2023.110.264-276
- Qin, D., Gao, P., Aslam, F., Sufian, M., Alabduljabbar, H. (2022). A comprehensive review on fire damage assessment of reinforced concrete structures. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 16, e00843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00843
- Sidnei, S., Nuianzin, V., Kostenko, T., Berezovskyi, A., Wąsik, W. (2023). A Method of Evaluating the Destruction of a Reinforced Concrete Hollow Core Slab for Ensuring Fire Resistance. Journal of Engineering Sciences, 10 (2), D1–D7. https://doi.org/10.21272/jes.2023.10(2).d1
- Sidnei, S., Myroshnyk, O., Kovalov, A., Veselivskyi, R., Hryhorenko, K., Shnal, T., Matsyk, I. (2024). Identifying the evolution of through cracks in iron-reinforced hollow slabs under the influence of a standard fire temperature mode. Applied Mechanics, 4 (7 (130)), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.310520
- Perehin, A., Nuianzin, O., Shnal, T., Shchipets, S., Myroshnyk, O. (2023). Improvement of means for assessing fire resistance of fragments of reinforced concrete structures. AIP Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0120061
- Kovalov, A., Otrosh, Y., Ostroverkh, O., Hrushovinchuk, O., Savchenko, O. (2018). Fire resistance evaluation of reinforced concrete floors with fire-retardant coating by calculation and experimental method. E3S Web of Conferences, 60, 00003. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20186000003
- Li, B., Lin, Y. Q., Zhang, H. L., Ma, M. J. (2019). Fire Behavior of the Assembled Monolithic Hollow‐Ribbed Slabs. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8921502
- Zafarullah, N., Ameir, E., Nakayama, A., Muhammad Bilal, H. S. (2022). Determination of structural reliability of a reinforced concrete slab under fire Load. E3S Web of Conferences, 347, 01009. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202234701009
- Law, A., Bisby, L. (2020). The rise and rise of fire resistance. Fire Safety Journal, 116, 103188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2020.103188
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Stanislav Sidnei, Serhii Gonchar, Maxim Zhuravskij, Ihor Matsyk, Ihor Nozhko, Olena Petukhova, Taras Shnal, Viktor Vykhrystenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








