Non-intrusive load monitoring: a cost-effective approach for home appliance identification utilizing machine learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.316694Keywords:
non-intrusive, monitoring, appliance, identification, kNN, smart, grid, energy, logger, power, consumerAbstract
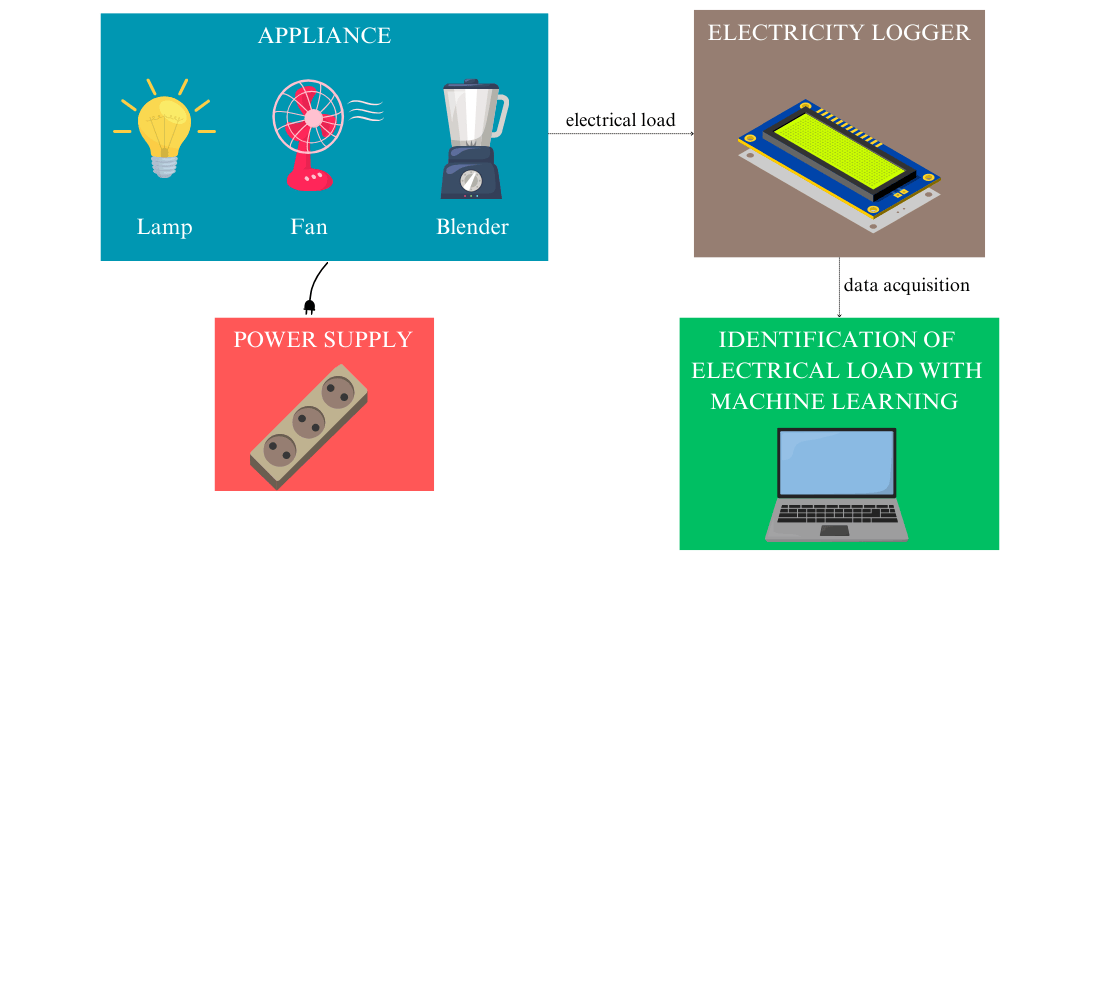
This research focuses on developing a cost-effective non-intrusive load monitoring system (NILM) to identify household appliances using machine learning, specifically the k-nearest neighbors (kNN) algorithm which is not disturbing the existing system. The object of this research is the process of appliance identification based on power consumption characteristics in residential energy monitoring. The main problem to be solved is the lack of accessible, affordable, and efficient tools for monitoring household electricity consumption, as existing solutions are often costly or require complex installations. Existing solutions are expensive or require complicated setup. This research seeks to design a low-cost NILM that can identify household appliances without invasive system while ensuring high accuracy. This study successfully designed and implemented an electrical recording device that integrates machine learning algorithms, achieving an identification accuracy of 83.33 % across six test scenarios involving various household appliances. The findings of this study show that utilizing active power and power factor as classification parameters allows for effective equipment identification. The moderate accuracy of the system indicates that the proposed design is quite promising but can be improved with more advanced algorithms and additional sensor data. The resulting system is cost-effective due to its inexpensive components which are achieved due to the modular design and the use of inexpensive components, such as the Wemos D1 mini and PZEM-004T V3 sensors, which simplify implementation and enhance system scalability. Its built-in LCD provides real-time monitoring without the need for internet connectivity. This research demonstrates the feasibility of a scalable and cost-effective NILM system, which can be further improved with advanced algorithms and additional sensor data for broader applications in smart energy management
References
- Khan, I. (2019). Household factors and electrical peak demand: a review for further assessment. Advances in Building Energy Research, 15 (4), 409–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512549.2019.1575770
- Zuki, N. A. M., Othman, R. N. F. K. R., Shukor, F. A. A., Ahmad, S. R. C. (2023). Analysis of linear motor with symmetrical EMF vector for household elevator application. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS), 14 (1), 51. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v14.i1.pp51-59
- Divina, F., García Torres, M., Goméz Vela, F. A., Vázquez Noguera, J. L. (2019). A Comparative Study of Time Series Forecasting Methods for Short Term Electric Energy Consumption Prediction in Smart Buildings. Energies, 12 (10), 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101934
- Marangoni, G., Tavoni, M. (2021). Real-time feedback on electricity consumption: evidence from a field experiment in Italy. Energy Efficiency, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-020-09922-z
- Hussein, H. I., Abdullah, A. N., Jafar, A. S. J. (2023). A novel online monitoring system of frequency oscillations based intelligence phasor measurement units. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS), 14 (3), 1589. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v14.i3.pp1589-1596
- Eirinaki, M., Varlamis, I., Dahihande, J., Jaiswal, A., Pagar, A. A., Thakare, A. (2022). Real-time recommendations for energy-efficient appliance usage in households. Frontiers in Big Data, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdata.2022.972206
- Mohammed, N., A. Danapalasingam, K., Majed, A. (2018). Design, Control and Monitoring of an Offline Mobile Battery Energy Storage System for a Typical Malaysian Household Load Using PLC. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems (IJPEDS), 9 (1), 180. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v9.i1.pp180-188
- Tundis, A., Faizan, A., Mühlhäuser, M. (2019). A Feature-Based Model for the Identification of Electrical Devices in Smart Environments. Sensors, 19 (11), 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112611
- Welikala, S., Dinesh, C., Ekanayake, M. P. B., Godaliyadda, R. I., Ekanayake, J. (2019). Incorporating Appliance Usage Patterns for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring and Load Forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 10 (1), 448–461. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsg.2017.2743760
- Ghosh, S., Chatterjee, A., Chatterjee, D. (2019). Improved non‐intrusive identification technique of electrical appliances for a smart residential system. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 13 (5), 695–702. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2018.5475
- Wójcik, A., Łukaszewski, R., Kowalik, R., Winiecki, W. (2019). Nonintrusive Appliance Load Monitoring: An Overview, Laboratory Test Results and Research Directions. Sensors, 19 (16), 3621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163621
- Cannas, B., Carcangiu, S., Carta, D., Fanni, A., Muscas, C. (2021). Selection of Features Based on Electric Power Quantities for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. Applied Sciences, 11 (2), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020533
- Garcia, F. D., Souza, W. A., Diniz, I. S., Marafão, F. P. (2020). NILM-based approach for energy efficiency assessment of household appliances. Energy Informatics, 3 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42162-020-00131-7
- Schirmer, P. A., Mporas, I. (2023). Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 14 (1), 769–784. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsg.2022.3189598
- Cimen, H., Cetinkaya, N., Vasquez, J. C., Guerrero, J. M. (2021). A Microgrid Energy Management System Based on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring via Multitask Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 12 (2), 977–987. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsg.2020.3027491
- Wang, A. L., Chen, B. X., Wang, C. G., Hua, D. (2018). Non-intrusive load monitoring algorithm based on features of V–I trajectory. Electric Power Systems Research, 157, 134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2017.12.012
- Laouali, I., Ruano, A., Ruano, M. da G., Bennani, S. D., Fadili, H. E. (2022). Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring of Household Devices Using a Hybrid Deep Learning Model through Convex Hull-Based Data Selection. Energies, 15 (3), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15031215
- Mataloto, B., Ferreira, J. C., Resende, R. P. (2023). Long Term Energy Savings Through User Behavior Modeling in Smart Homes. IEEE Access, 11, 44544–44558. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3272888
- Aboulian, A., Green, D. H., Switzer, J. F., Kane, T. J., Bredariol, G. V., Lindahl, P. et al. (2019). NILM Dashboard: A Power System Monitor for Electromechanical Equipment Diagnostics. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15 (3), 1405–1414. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2018.2843770
- Chen, Y.-Y., Chen, M.-H., Chang, C.-M., Chang, F.-S., Lin, Y.-H. (2021). A Smart Home Energy Management System Using Two-Stage Non-Intrusive Appliance Load Monitoring over Fog-Cloud Analytics Based on Tridium’s Niagara Framework for Residential Demand-Side Management. Sensors, 21 (8), 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082883
- Chen, C., Geng, G., Yu, H., Liu, Z., Jiang, Q. (2023). An End-Cloud Collaborated Framework for Transferable Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 11 (2), 1157–1169. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2021.3132929
- Zhang, R., Wang, Y., Song, Y. (2022). Nonintrusive Load Monitoring Method Based on Color Encoding and Improved Twin Support Vector Machine. Frontiers in Energy Research, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2022.906458
- Chen, S., Zhao, B., Zhong, M., Luan, W., Yu, Y. (2023). Nonintrusive Load Monitoring Based on Self-Supervised Learning. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 72, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2023.3246504
- Li, W., Kong, D., Wu, J. (2017). A Novel Hybrid Model Based on Extreme Learning Machine, k-Nearest Neighbor Regression and Wavelet Denoising Applied to Short-Term Electric Load Forecasting. Energies, 10 (5), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050694
- Hasan, I. J., Waheib, B. M., Jalil Salih, N. A., Abdulkhaleq, N. I. (2021). A global system for mobile communications-based electrical power consumption for a non-contact smart billing system. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), 11 (6), 4659. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v11i6.pp4659-4666
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Levin Halim, Reyvaldo Barthez, Nico Saputro

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








