Development of multifunctional polymer composites with high red mud content
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.317952Keywords:
Abstract
Red mud (RM) is one of the large-scale by-products of alumina production, posing significant environmental challenges due to its high alkalinity, toxicity, and substantial accumulation volumes. The object of this study is polymer composite based on styrene-butadiene aqueous dispersion with RM and chamotte (Pa2) as fillers at high concentrations (up to 90 wt. %). The primary problem addressed in this research is finding effective ways to utilize RM as secondary raw material to enhance its recycling efficiency and create multifunctional materials with adjustable properties.
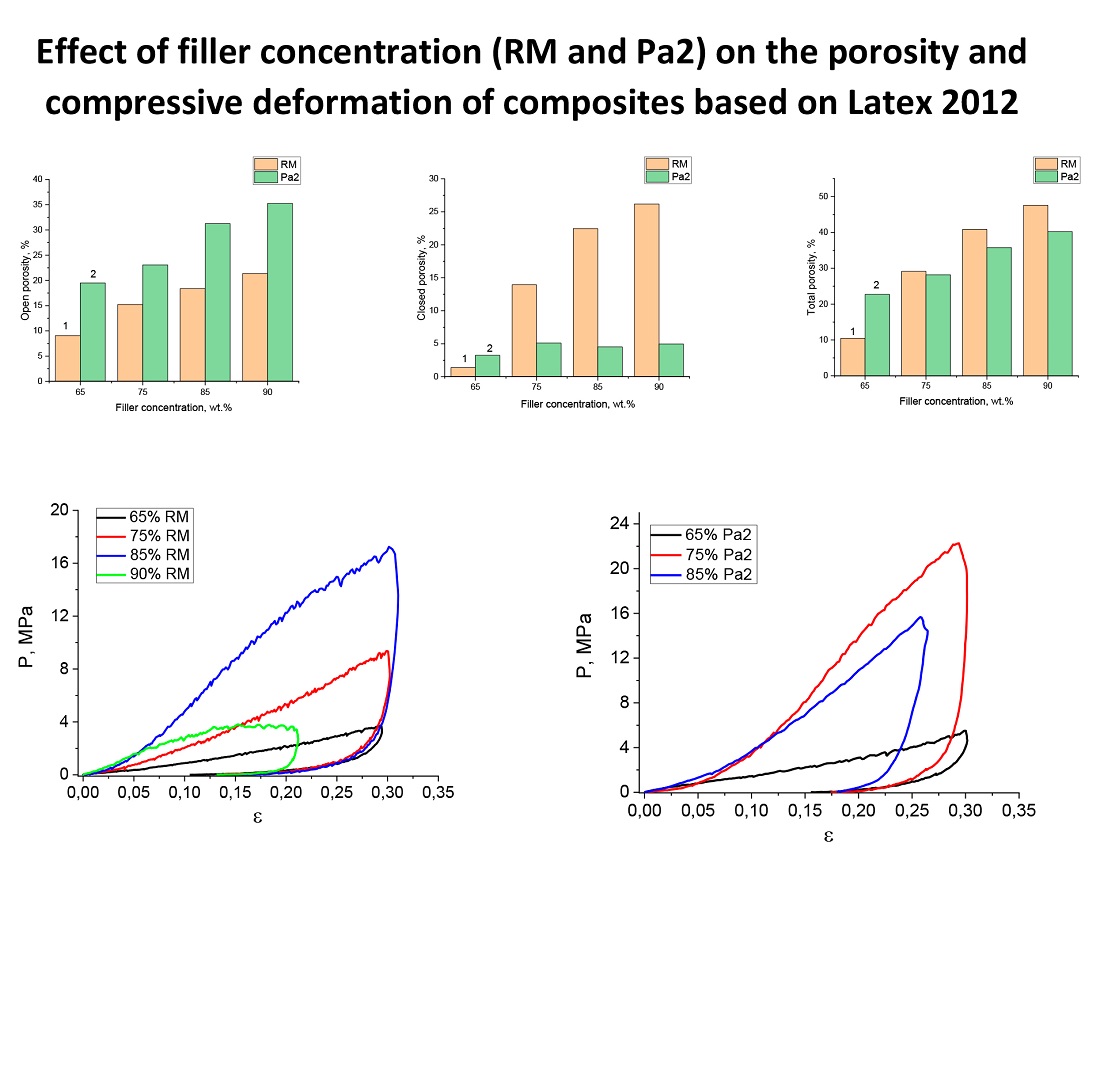
The study established that RM has an irregular plate-like structure with a high active surface area, which facilitates the formation of an open porous composite structure, while Pa2 forms a dense matrix due to its aluminosilicate content. Infrared spectral analysis confirmed the presence of functional groups (OH, Si–O, Al–O) that ensure the interaction of fillers with the polymer matrix. Thermogravimetric analysis demonstrated that RM and Pa2 exhibit similar behavior under heating. Mechanical tests revealed that RM-based composites exhibit high plasticity and energy absorption capacity, whereas Pa2-based composites are characterized by greater stiffness and strength (elastic modulus up to 129.8 MPa).
The results indicate that the choice of filler type and concentration effectively regulates composite properties. The proposed approach enables the recycling of industrial waste and the development of multifunctional materials suitable for use in construction, protective coatings, and the production of structural elements capable of withstanding significant loads
References
- Ahmed, S., Meng, T., Taha, M. (2020). Utilization of red mud for producing a high strength binder by composition optimization and nano strengthening. Nanotechnology Reviews, 9 (1), 396–409. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2020-0029
- Power, G., Gräfe, M., Klauber, C. (2011). Bauxite residue issues: I. Current management, disposal and storage practices. Hydrometallurgy, 108 (1-2), 33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.02.006
- Liu, S., Guan, X., Zhang, S., Dou, Z., Feng, C., Zhang, H., Luo, S. (2017). Sintered bayer red mud based ceramic bricks: Microstructure evolution and alkalis immobilization mechanism. Ceramics International, 43 (15), 13004–13008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.036
- Zhang, M., Zhao, M., Zhang, G., Mann, D., Lumsden, K., Tao, M. (2016). Durability of red mud-fly ash based geopolymer and leaching behavior of heavy metals in sulfuric acid solutions and deionized water. Construction and Building Materials, 124, 373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.07.108
- Liu, R.-X., Poon, C.-S. (2016). Utilization of red mud derived from bauxite in self-compacting concrete. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.049
- Mišík, M., Burke, I. T., Reismüller, M., Pichler, C., Rainer, B., Mišíková, K. et al. (2014). Red mud a byproduct of aluminum production contains soluble vanadium that causes genotoxic and cytotoxic effects in higher plants. Science of The Total Environment, 493, 883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.052
- Mesgari Abbasi, S., Rashidi, A., Ghorbani, A., Khalaj, G. (2016). Synthesis, processing, characterization, and applications of red mud/carbon nanotube composites. Ceramics International, 42 (15), 16738–16743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.146
- Liu, Y., Naidu, R. (2014). Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): Recovery of metals. Waste Management, 34 (12), 2662–2673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.003
- Liu, W., Yang, J., Xiao, B. (2009). Review on treatment and utilization of bauxite residues in China. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 93 (3-4), 220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2009.08.005
- Mukiza, E., Zhang, L., Liu, X., Zhang, N. (2019). Utilization of red mud in road base and subgrade materials: A review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 141, 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.031
- Abdel-Raheem, M., Santana, L. M. G., Cordava, M. A. P., Martínez, B. O. (2017). Uses of Red Mud as a Construction Material. AEI 2017, 388–399. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784480502.032
- Carneiro, J., Tobaldi, D. M., Capela, M. N., Novais, R. M., Seabra, M. P., Labrincha, J. A. (2018). Synthesis of ceramic pigments from industrial wastes: Red mud and electroplating sludge. Waste Management, 80, 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.032
- Mi, H., Yi, L., Wu, Q., Xia, J., Zhang, B. (2021). Preparation of high-strength ceramsite from red mud, fly ash, and bentonite. Ceramics International, 47 (13), 18218–18229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.141
- Chen, Y., Li, A., Jiang, S. (2024). Wettability and Mechanical Properties of Red Mud–Al2O3 Composites. Materials, 17 (5), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17051095
- Melnyk, L., Svidersky, V., Chernyak, L., Dorogan, N. (2018). Aspects of making of a composite material when using red mud. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (6 (92)), 23–28. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.125702
- Hendricks, H. L., Buchanan, V. E. (2020). Effect of material parameters on the mechanical properties of chemically treated red mud HDPE composites. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 29 (8), 1126–1134. https://doi.org/10.1177/0967391120954064
- Bhat, A. H., Abdul, H. P. S., K., A. (2011). Thermoplastic Polymer based Modified Red Mud Composites Materials. Advances in Composite Materials - Ecodesign and Analysis. https://doi.org/10.5772/14377
- Melnyk, L. I. (2023). Kompozyt na osnovi system sopolimer – chervonyi shlam. Modern science: challenges of today. Bratislava, 6–38. Available at: https://ela.kpi.ua/handle/123456789/67229
- Melnyk, L. I., Cherniak, L. P., Yevpak, V. V. (2024). Composites based on fly ash with different polymer matrixes. Scientific Notes of Taurida National V.I. Vernadsky University. Series: Technical Sciences, 2 (1), 106–112. https://doi.org/10.32782/2663-5941/2024.1.2/18
- Melnyk, L. (2024). Formation of composite with variation of dispersity of filler and type of binder. Technical Sciences and Technologies, 1 (35), 198–203. https://doi.org/10.25140/2411-5363-2024-1(35)-198-203
- Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60 (2), 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
- Bodnar, R. T. (2016). Ekspres-metod vyznachennia kraiovoho kuta zmochuvannia porystykh til. Metody ta prylady kontroliu yakosti, 1 (36), 30–38.
- Vovchenko, L., Matzui, L., Zhuravkov, A., Samchuk, A. (2006). Electrical resistivity of compacted TEG and TEG-Fe under compression. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 67 (5-6), 1168–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2006.01.042
- Hubina, V. H., Kadoshnikov, V. M. (2005). Red mud from the Mykolaiv Alumina Plant – A valuable technogenic raw material. Geological and Mineralogical Bulletin, 2, 122–126.
- Palmer, S. J., Reddy, B. J., Frost, R. L. (2009). Characterisation of red mud by UV–vis–NIR spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 71 (5), 1814–1818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2008.06.038
- Wang, Q., Wang, D., Chen, H. (2017). The role of fly ash microsphere in the microstructure and macroscopic properties of high-strength concrete. Cement and Concrete Composites, 83, 125–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.07.021
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Liubov Melnyk, Valentin Sviderskyy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








