Determining the impact of blockchain technologies on the grain supply chain tracking system in the EU
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.318931Keywords:
blockchain technologies, supply chains, grain industry, automation, document flow, economic effect, investment returnAbstract
The object of this paper is blockchain technology in the tracking system of grain supply chains.
The current study considers the task of determining the impact of blockchain technology introduction on the tracking system of grain supply chains.
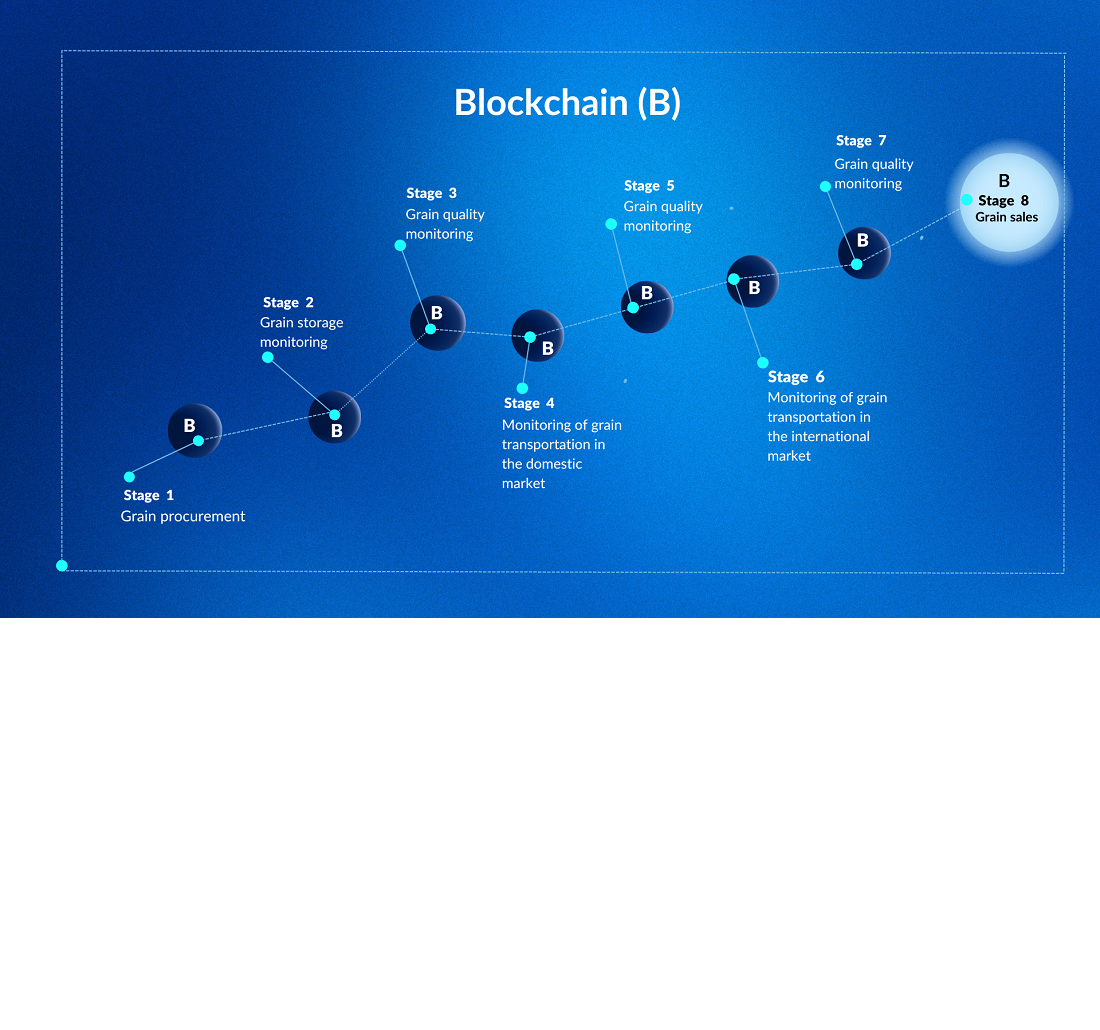
The key problems in the system of grain supply chains have been identified and the tasks to solve them have been proposed. The characteristics of key technologies in the implementation of blockchain in the system of grain supply chains have been defined, such as smart contracts, the Internet of Things (IoT), interplanetary file system (IPFS), contactless tags (RFID), Ethereum platform (identified as the best for supply chain tracking). The influence of factors on the introduction of blockchain technologies into the grain supply chain tracking system was determined using a SWOT analysis. Strengths include transparency, increased trust, automation of processes and protection against falsification. Weaknesses include high implementation costs, difficulty scaling, and the need for staff training. Opportunities that open up through the use of blockchain include attracting new partners, increasing competitiveness, and developing new markets. Threats include legal difficulties, technical failures, high energy costs, and resistance from market participants. An assessment of the investment attractiveness of introducing blockchain technology into the grain supply chain tracking system was carried out by calculating such indicators as economic effect; net present value (NPV) of implementing blockchain technologies; payback period of investments. According to the results of analysis, the following data were obtained: NPV (150439 a.u.)>0, the payback period of investments is 2.8 years, which is acceptable for large agricultural holdings. Prospects for development have been determined, in particular, the unification of agricultural holdings for the joint implementation of blockchain technologies in the tracking system of grain supply chains, which would be a strategically beneficial solution for all participants in the supply chain
References
- Chung, S., Hwang, J.-T., Park, S.-H. (2022). Physiological Effects of Bioactive Compounds Derived from Whole Grains on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Applied Sciences, 12 (2), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020658
- Yakoviyk, I. V., Zhukov, I. M., Tsvelikh, M. P. (2023). The impact of the grain crisis on food security of Ukraine and the European Union. Topical issues of law: theory and practice, 2 (46), 21–31. https://doi.org/10.33216/2218-5461/2023-46-2-21-31
- Carey, R., Coleman, C. G., White, T. M. (2024). The Impact of Blockchain on Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Review. Journal of Procurement and Supply Chain Management, 3 (1), 1–11. Available at: https://gprjournals.org/journals/index.php/JPSCM/article/view/235
- Arena, A., Bianchini, A., Perazzo, P., Vallati, C., Dini, G. (2019). BRUSCHETTA: An IoT Blockchain-Based Framework for Certifying Extra Virgin Olive Oil Supply Chain. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), 173–179. https://doi.org/10.1109/smartcomp.2019.00049
- Lambert, D. M.; Monczka, R. M., Handfield, R. B., Giunipero, L. C., Patterson, J. L. (Eds.) (2008). La cadena de suministro. Administración estratégica de la cadena de suministro. Pearson Educación, 27–61.
- Wamba, S. F., Queiroz, M. M. (2020). Industry 4.0 and the supply chain digitalisation: a blockchain diffusion perspective. Production Planning & Control, 33 (2-3), 193–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2020.1810756
- Abdel-Basset, M., Manogaran, G., Mohamed, M. (2018). RETRACTED: Internet of Things (IoT) and its impact on supply chain: A framework for building smart, secure and efficient systems. Future Generation Computer Systems, 86, 614–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.04.051
- Ali Syed, T., Alzahrani, A., Jan, S., Siddiqui, M. S., Nadeem, A., Alghamdi, T. (2019). A Comparative Analysis of Blockchain Architecture and its Applications: Problems and Recommendations. IEEE Access, 7, 176838–176869. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2957660
- Pournader, M., Shi, Y., Seuring, S., Koh, S. C. L. (2019). Blockchain applications in supply chains, transport and logistics: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Production Research, 58 (7), 2063–2081. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1650976
- Kayikci, Y., Subramanian, N., Dora, M., Bhatia, M. S. (2020). Food supply chain in the era of Industry 4.0: blockchain technology implementation opportunities and impediments from the perspective of people, process, performance, and technology. Production Planning & Control, 33 (2-3), 301–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2020.1810757
- Moosavi, J., Naeni, L. M., Fathollahi-Fard, A. M., Fiore, U. (2021). Blockchain in supply chain management: a review, bibliometric, and network analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13094-3
- Bukhari, I. R. (2023). Impact of Blockchain Technology on Supply Chain Management. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373900041_Impact_of_Blockchain_Technology_on_Supply_Chain_Management
- Rating of the main exporters of grain from Ukraine according to the results of the 2022/23 MR. Available at: https://graintrade.com.ua/en/novosti/rejting-osnovnih-eksporteriv-zerna-z-ukraini-za-pidsumkami-202223-mr.html
- Mahmudnia, D., Arashpour, M., Yang, R. (2022). Blockchain in construction management: Applications, advantages and limitations. Automation in Construction, 140, 104379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104379
- Chen, C., Yang, B., Gao, A., Li, L., Dong, X., Zhao, F.-J. (2022). Suppression of methanogenesis in paddy soil increases dimethylarsenate accumulation and the incidence of straighthead disease in rice. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 169, 108689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108689
- Jiang, Y., Zheng, W. (2021). Coupling mechanism of green building industry innovation ecosystem based on blockchain smart city. Journal of Cleaner Production, 307, 126766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126766
- Malik, M., Mahmood, S., Noreen, S., Abid, R., Ghaffar, S., Zahra, S. Et al. (2021). Lead contamination affects the primary productivity traits, biosynthesis of macromolecules and distribution of metal in durum wheat (Triticumdurum L.). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28 (9), 4946–4956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.093
- Peng, X., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Xu, J., Li, H., Zhao, Z., Qi, Z. (2022). A Refined Supervision Model of Rice Supply Chain Based on Multi-Blockchain. Foods, 11 (18), 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182785
- Xiong, W., Xiong, L. (2021). Anti-collusion data auction mechanism based on smart contract. Information Sciences, 555, 386–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.10.053
- Lei, M., Xu, L., Liu, T., Liu, S., Sun, C. (2022). Integration of Privacy Protection and Blockchain-Based Food Safety Traceability: Potential and Challenges. Foods, 11 (15), 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152262
- Qu, Z., Zhang, Z., Zheng, M. (2022). A quantum blockchain-enabled framework for secure private electronic medical records in Internet of Medical Things. Information Sciences, 612, 942–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.09.028
- Xu, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, H., Deng, W. (2023). ABC-GSPBFT: PBFT with grouping score mechanism and optimized consensus process for flight operation data-sharing. Information Sciences, 624, 110–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.12.068
- Mohammed, A. H., Abdulateef, A. A., Abdulateef, I. A. (2021). Hyperledger, Ethereum and Blockchain Technology: A Short Overview. 2021 3rd International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/hora52670.2021.9461294
- Zhang, Y., Wu, X., Ge, H., Jiang, Y., Sun, Z., Ji, X. et al. (2023). A Blockchain-Based Traceability Model for Grain and Oil Food Supply Chain. Foods, 12 (17), 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173235
- Chibba, A., Rundquist, J. (2009). Effective Information Flow in the Internal Supply Chain: Results from a Snowball Method to Map Information Flows. Journal of Information & Knowledge Management, 08 (04), 331–343. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219649209002439
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Halyna Kupalova, Nazar Didukh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








