A scalable model for Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem with Pickup and Delivery under dynamic constraints using adaptive heuristic-based ant colony optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.319733Keywords:
adaptive heuristic-based ant colony optimization, capacitated vehicle routing problem, dynamic constraints, traffic congestion, adverse weather, urban logisticsAbstract
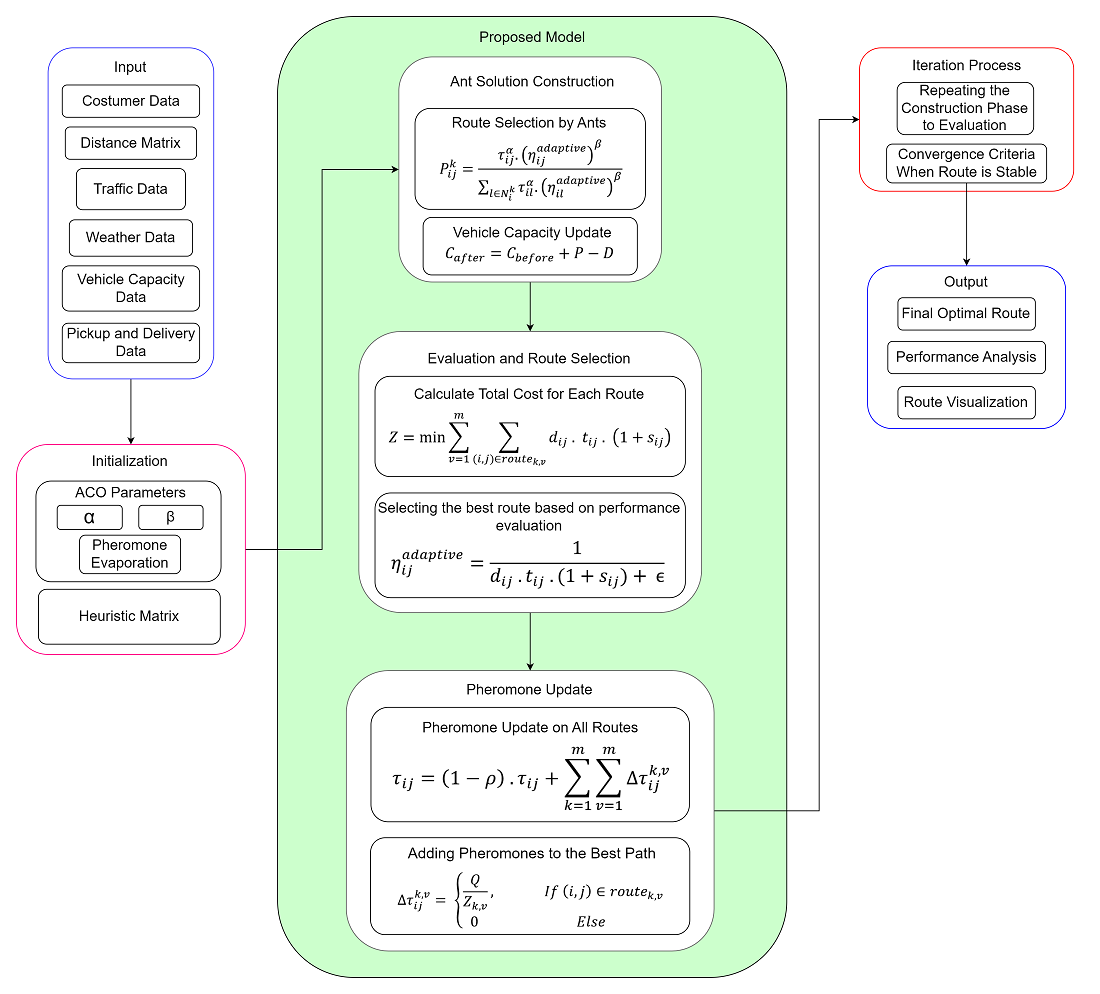
This study addresses the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem with Pickup and Delivery (CVRPPD), a core challenge in urban logistics involving the optimization of vehicle routes under dynamic constraints. Traditional algorithms predominantly focus on static variables like distance, failing to account for real-world factors such as traffic congestion, adverse weather, and vehicle capacity limitations. To solve this problem, the Adaptive Heuristic-Based Ant Colony Optimization (AHB-ACO) algorithm was developed, incorporating these dynamic constraints into the routing optimization process. The AHB-ACO algorithm minimizes total travel costs while ensuring adherence to vehicle capacity limits and improving route safety. Simulation tests were conducted on datasets with 50, 100, and 200 customers to evaluate performance under varying levels of complexity. The results demonstrate that AHB-ACO outperforms traditional ACO, particularly in dynamic scenarios, achieving a total cost of 4155.82 with an execution time of 1639.68 seconds for the 200-customer dataset. The algorithm’s adaptive heuristic formula integrates distance, traffic congestion, and weather penalties, enabling the generation of safer and more realistic routes. These results are explained by the algorithm’s ability to dynamically adjust to constraints, ensuring robust performance in complex environments. The findings highlight AHB-ACO’s practical applicability in urban logistics, offering scalability and adaptability for real-world delivery and pickup challenges, especially in areas affected by fluctuating traffic and weather conditions
References
- Song, M., Li, J., Li, L., Yong, W., Duan, P. (2018). Application of Ant Colony Algorithms to Solve the Vehicle Routing Problem. Intelligent Computing Theories and Application, 831–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95930-6_83
- Yu, W., Liu, Z., Bao, X. (2019). Distance Constrained Vehicle Routing Problem to Minimize the Total Cost. Computing and Combinatorics, 639–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26176-4_53
- Akkerman, F., Mes, M. (2022). Distance approximation to support customer selection in vehicle routing problems. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04674-8
- Zhu, Z., Qian, Y., Zhang, W. (2021). Research on UAV Searching Path Planning Based on Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. 2021 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology (ICCASIT), 1319–1323. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccasit53235.2021.9633591
- Xiang, A., Wang, L. (2021). Research on Path Planning of UAV Forest Fire Fighting Based on Improved Ant Colony Algorithm. 2021 7th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 289–295. https://doi.org/10.1145/3467707.3467751
- Jang, J., Kim, M., Lee, J. (2019). Improvement of Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm to Solve Traveling Salesman Problem. Journal of Society of Korea Industrial and Systems Engineering, 42 (3), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.11627/jkise.2019.42.3.001
- Frías, N., Johnson, F., Valle, C. (2023). Hybrid Algorithms for Energy Minimizing Vehicle Routing Problem: Integrating Clusterization and Ant Colony Optimization. IEEE Access, 11, 125800–125821. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3325787
- Ky Phuc, P. N., Phuong Thao, N. L. (2021). Ant Colony Optimization for Multiple Pickup and Multiple Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Window and Heterogeneous Fleets. Logistics, 5 (2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics5020028
- Pan, T., Pan, H., Gao, J. (2015). An improved ant colony algorithm based on vehicle routing problem. 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), 2747–2752. https://doi.org/10.1109/chicc.2015.7260059
- Ren, T., Luo, T., Jia, B., Yang, B., Wang, L., Xing, L. (2023). Improved ant colony optimization for the vehicle routing problem with split pickup and split delivery. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 77, 101228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2023.101228
- Huang, Y.-H., Blazquez, C. A., Huang, S.-H., Paredes-Belmar, G., Latorre-Nuñez, G. (2019). Solving the Feeder Vehicle Routing Problem using ant colony optimization. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 127, 520–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.10.037
- Peng, Y., Pan, Y., Qin, Z., Li, D. (2015). An adaptive hybrid ant colony optimization algorithm for solving Capacitated Vehicle Routing. Proceedings of the 2015 International Industrial Informatics and Computer Engineering Conference. https://doi.org/10.2991/iiicec-15.2015.132
- Dhanya, K. M., Kanmani, S. (2017). Dynamic Vehicle Routing Problem: Solution by Ant Colony Optimization with Hybrid Immigrant Schemes. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications, 9 (7), 52–60. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijisa.2017.07.06
- Fatimah Mohamad Ayop, S., Shahizan Othman, M., Mi Yusuf, L. (2020). Ant Colony Optimization Using Different Heuristic Strategies for Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 864 (1), 012082. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/864/1/012082
- Guo, N., Qian, B., Na, J., Hu, R., Mao, J.-L. (2022). A three-dimensional ant colony optimization algorithm for multi-compartment vehicle routing problem considering carbon emissions. Applied Soft Computing, 127, 109326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109326
- Thymianis, M., Tzanetos, A., Osaba, E., Dounias, G., Del Ser, J. (2022). Electric Vehicle Routing Problem: Literature Review, Instances and Results with a Novel Ant Colony Optimization Method. 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/cec55065.2022.9870373
- Wu, H., Gao, Y. (2023). An ant colony optimization based on local search for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup–delivery and time window. Applied Soft Computing, 139, 110203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110203
- Siddalingappa, P., Basavaraj, P., Basavaraj, P., Gowramma, P. (2023). Route optimization via improved ant colony algorithm with graph network. International Journal of Reconfigurable and Embedded Systems (IJRES), 12 (3), 403. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijres.v12.i3.pp403-413
- Setyati, E., Juniwati, I. (2022). Ant Colony Optimization Ant Colony Optimization untuk menyelesaikan perutean distribusi Snack dengan Vehicle Routing Problem. Jurnal Teknologi Informasi Dan Terapan, 9 (2), 111–117. https://doi.org/10.25047/jtit.v9i2.296
- Alwabli, A., Kostanic, I., Malky, S. (2020). Dynamic Route Optimization For Waste Collection and Monitering smart bins Using Ant colony Algorithm. 2020 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Control, Optimization and Computer Science (ICECOCS), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/icecocs50124.2020.9314571
- Han, J., Mozhdehi, A., Wang, Y., Sun, S., Wang, X. (2022). Solving a multi-trip VRP with real heterogeneous fleet and time windows based on ant colony optimization. Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Computational Transportation Science, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1145/3557991.3567776
- Kyriakakis, N. A., Marinaki, M., Marinakis, Y. (2021). A hybrid ant colony optimization-variable neighborhood descent approach for the cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem. Computers & Operations Research, 134, 105397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2021.105397
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Imam Muslem R, Mahyuddin K. M. Nasution, Sutarman Sutarman, Suherman Suherman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








