Improving of intelligent decision support systems for planning a balanced diet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322316Keywords:
decision tree, deep learning, efficiency, matrix factorization, recommender systemAbstract
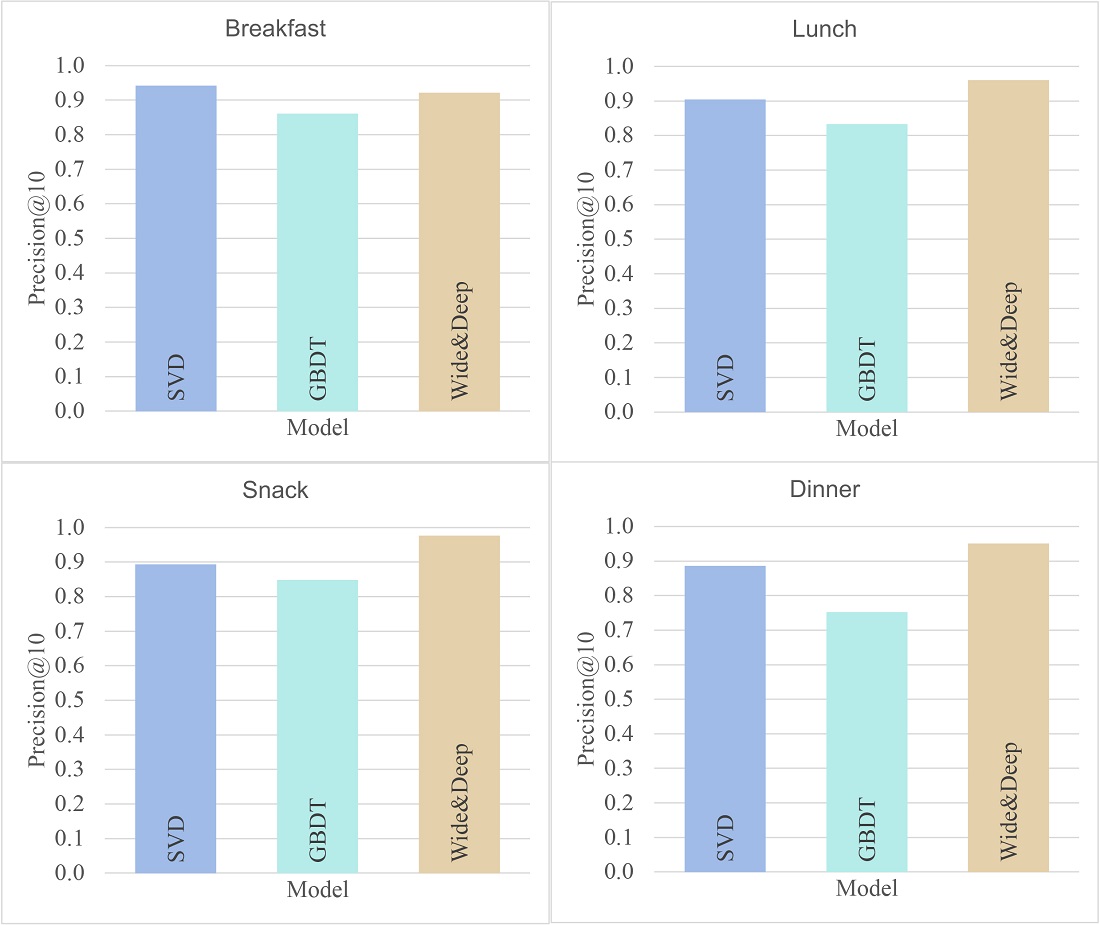
The object of this study is the process of creating a personalized menu. The subject of the study is recommendation systems for generating breakfast, lunch, snack, and dinner menus. The task solved was the development of an effective system for supporting the decisions by a wide range of users in planning a balanced diet. To form a menu of dishes of different categories of meals in a hybrid system for planning a balanced human diet, it is proposed to use different recommendation systems based on different models of artificial intelligence. The choice of the singular matrix decomposition model, the gradient boosting model of decision trees, and the wide and deep learning models for recommendation systems for forming a menu of dishes has been substantiated by the results of analysis. Based on the results of the experiment with these artificial intelligence models, it was determined which of them are more effective in solving the problem of forming a menu of meals for different categories of meals. The effectiveness of all models was evaluated by such test indicators as Precision@K, mean absolute and root mean square error. The feasibility of choosing the singular matrix decomposition model for generating breakfast menus and the wide and deep learning models for generating snack, lunch, and dinner menus was evaluated by the Precision@K values. The singular matrix decomposition model, compared to the other models studied in this paper, showed the highest Precision@K for breakfast, namely 0.942. The wide and deep learning models demonstrated the highest Precision@K for lunch, snack, and dinner: 0.961, 0.977, and 0.951, respectively. In practice, the results could be used to develop highly efficient personalized meal planning services in mobile and online platforms
References
- Overweight and obesity - BMI statistics. Eurostat. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Overweight_and_obesity_-_BMI_statistics
- Misra, A., Jayawardena, R., Anoop, S. (2019). Obesity in South Asia: Phenotype, Morbidities, and Mitigation. Current Obesity Reports, 8 (1), 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-019-0328-0
- Powell-Wiley, T. M., Poirier, P., Burke, L. E., Després, J.-P., Gordon-Larsen, P., Lavie, C. J. et al. (2021). Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation, 143 (21). https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000973
- Adair, T., Lopez, A. D. (2020). The role of overweight and obesity in adverse cardiovascular disease mortality trends: an analysis of multiple cause of death data from Australia and the USA. BMC Medicine, 18 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01666-y
- Liu, J., Rehm, C. D., Onopa, J., Mozaffarian, D. (2020). Trends in Diet Quality Among Youth in the United States, 1999-2016. JAMA, 323 (12), 1161. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.0878
- Pecune, F., Callebert, L., Marsella, S. (2020). A Socially-Aware Conversational Recommender System for Personalized Recipe Recommendations. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Human-Agent Interaction, 78–86. https://doi.org/10.1145/3406499.3415079
- Papastratis, I., Konstantinidis, D., Daras, P., Dimitropoulos, K. (2024). AI nutrition recommendation using a deep generative model and ChatGPT. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-65438-x
- Stefanidis, K., Tsatsou, D., Konstantinidis, D., Gymnopoulos, L., Daras, P., Wilson-Barnes, S. et al. (2022). PROTEIN AI Advisor: A Knowledge-Based Recommendation Framework Using Expert-Validated Meals for Healthy Diets. Nutrients, 14 (20), 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14204435
- Zioutos, K., Kondylakis, H., Stefanidis, K. (2023). Healthy Personalized Recipe Recommendations for Weekly Meal Planning. Computers, 13 (1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010001
- Majumder, B. P., Li, S., Ni, J., McAuley, J. (2019). Generating Personalized Recipes from Historical User Preferences. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), 5975–5981. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/d19-1613
- Mohan, A., Singh, S., Kalpana, Dr. A. V. (2023). Meal Plan Monitoring and Recommendation System. Recent Trends in Data Science and Its Applications, 595–602. https://doi.org/10.13052/rp-9788770040723.117
- Zhang, S., Yao, L., Sun, A., Tay, Y. (2019). Deep Learning Based Recommender System. ACM Computing Surveys, 52 (1), 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1145/3285029
- Ladyzhets, V., Yeremenko, B., Terenchuk, S. (2024). Candidate Generation for Meal Recommendation System. 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST), 560–564. https://doi.org/10.1109/sist61555.2024.10629517
- Pu, L., Faltings, B. (2013). Understanding and improving relational matrix factorization in recommender systems. Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1145/2507157.2507178
- Li, D., Jin, R., Gao, J., Liu, Z. (2020). On Sampling Top-K Recommendation Evaluation. Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. https://doi.org/10.1145/3394486.3403262
- Manety, S., Khider, D., Heiser, C., McKay, N., Emile-Geay, J., Routson, C. (2022). PaleoRec: A sequential recommender system for the annotation of paleoclimate datasets. Environmental Data Science, 1. https://doi.org/10.1017/eds.2022.3
- Hug, N. (2020). Surprise: A Python library for recommender systems. Journal of Open Source Software, 5 (52), 2174. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02174
- Guolin, K. et al. (2017). LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Available at: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/6449f44a102fde848669bdd9eb6b76fa-Paper.pdf
- Abadi, M. et al. (2015). TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1603.04467
- Jiao, J., Zhang, X., Li, F., Wang, Y. (2020). A Novel Learning Rate Function and Its Application on the SVD++ Recommendation Algorithm. IEEE Access, 8, 14112–14122. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2960523
- Mat Amin, M., Yep Ai Lan, J., Makhtar, M., Rasid Mamat, A. (2018). A Decision Tree Based Recommender System for Backpackers Accommodations. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7 (2.15), 45. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i2.15.11210
- Cheng, H.-T., Koc, L., Harmsen, J., Shaked, T., Chandra, T., Aradhye, H. et al. (2016). Wide & Deep Learning for Recommender Systems. Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems. https://doi.org/10.1145/2988450.2988454
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Viktor Ladyzhets, Svitlana Terenchuk, Iryna Aznaurіan, Antonina Makhynia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








