Identifying the impact of the complexity of datasets in Bayesian optimized XGBoost on the performance of classifications for imbalanced class distribution datasets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322626Keywords:
Bayesian optimization, eXtreme gradient boosting, imbalanced datasets, complexity of datasets, classification, confusion matrix, resampling techniques, hyperparameter tuning, performance evaluation, minority class identificationAbstract
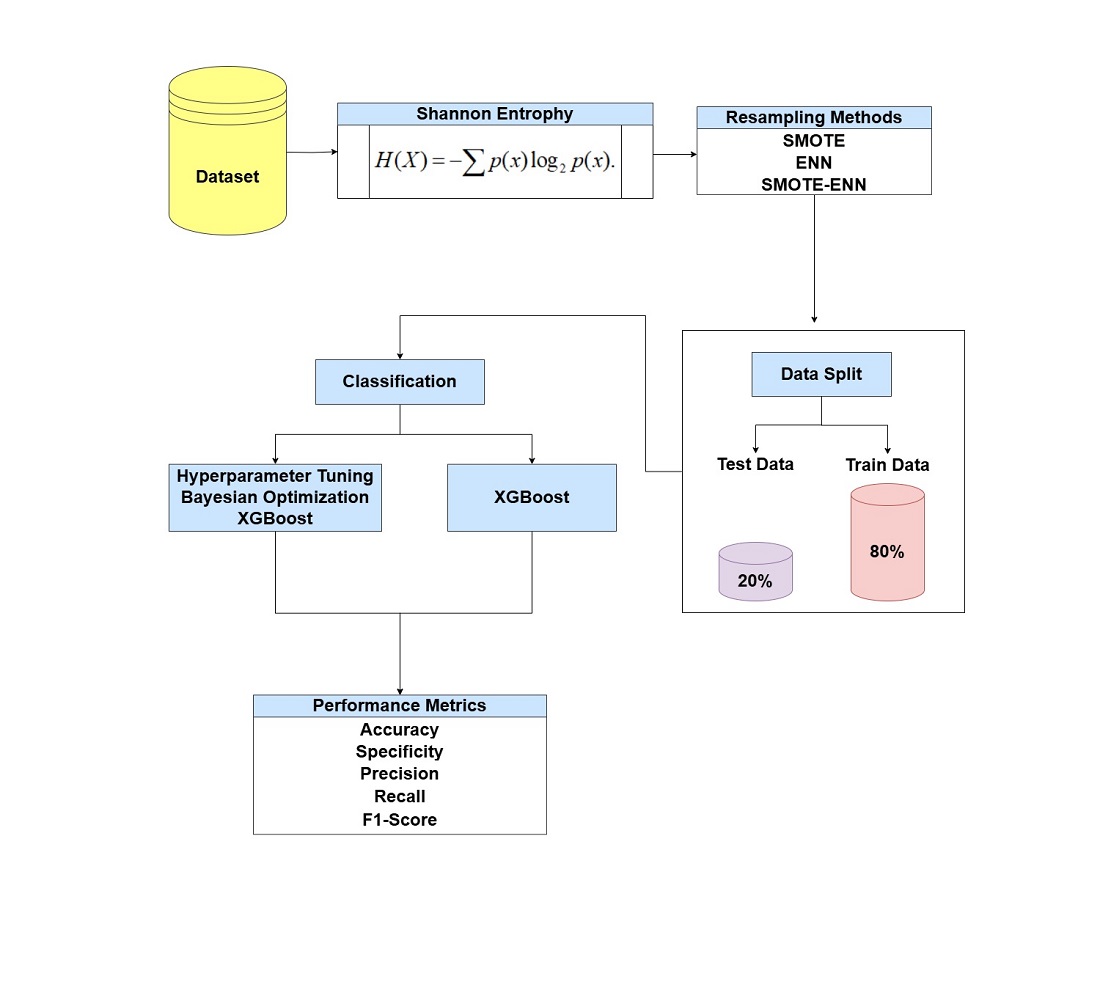
This study explores how dataset complexity affects the performance of XGBoost models optimized using Bayesian methods, focusing on datasets characterized by imbalanced class distributions. The main challenge is accurately identifying minority classes, which are often misdiagnosed due to the dominance of majority classes, impairing predictive power. Additionally, dataset complexity, as indicated by the coefficient of variation (14.64 % to 85.68 %), does not consistently correlate with improved model performance, highlighting the need for more targeted methods. High-dimensional datasets may not be as accurate as simpler ones and require the use of advanced approaches. By using Bayesian optimization, it is possible to fine-tune hyperparameters and improve classification performance on different types of datasets. This indicates that the selection of appropriate resampling techniques to match the characteristics of the dataset is critical, and that hyperparameter optimization plays an important role in building models with high accuracy. The applications extend to areas such as fraud detection and other fields where the categorization of minority groups is important. Through the use of efficient resampling techniques and advanced optimization methods, this study offers a comprehensive solution to the challenges of imbalanced datasets, enhancing the reliability of machine learning solutions. The variation in resampling techniques and optimizing model performance metrics can be attributed to the distribution of classes, the number of features, the complexity, and the characteristics of the datasets
References
- Ghosh, K., Bellinger, C., Corizzo, R., Branco, P., Krawczyk, B., Japkowicz, N. (2022). The class imbalance problem in deep learning. Machine Learning, 113 (7), 4845–4901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-022-06268-8
- Rezvani, S., Wang, X. (2023). A broad review on class imbalance learning techniques. Applied Soft Computing, 143, 110415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110415
- Moniz, N., Cerqueira, V. (2021). Automated imbalanced classification via meta-learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 178, 115011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115011
- Magris, M., Iosifidis, A. (2023). Bayesian learning for neural networks: an algorithmic survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 56 (10), 11773–11823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10443-1
- Pereira, R. M., Costa, Y. M. G., Silla, C. N. (2021). Handling imbalance in hierarchical classification problems using local classifiers approaches. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 35 (4), 1564–1621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-021-00762-8
- Ye, H.-J., Chen, H.-Y., Zhan, D.-C., Chao, W.-L. (2020). Identifying and Compensating for Feature Deviation in Imbalanced Deep Learning. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.01385
- Guan, S., Fu, N. (2022). Class imbalance learning with Bayesian optimization applied in drug discovery. Scientific Reports, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05717-7
- Banchhor, C., Srinivasu, N. (2021). Analysis of Bayesian optimization algorithms for big data classification based on Map Reduce framework. Journal of Big Data, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00464-4
- Albahli, S. (2023). Efficient hyperparameter tuning for predicting student performance with Bayesian optimization. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83 (17), 52711–52735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17525-w
- Wang, X., Jin, Y., Schmitt, S., Olhofer, M. (2023). Recent Advances in Bayesian Optimization. ACM Computing Surveys, 55 (13s), 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1145/3582078
- Nayak, J., Naik, B., Dash, P. B., Vimal, S., Kadry, S. (2022). Hybrid Bayesian optimization hypertuned catboost approach for malicious access and anomaly detection in IoT nomalyframework. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 36, 100805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2022.100805
- Guembe, B., Misra, S., Azeta, A. (2024). Federated Bayesian optimization XGBoost model for cyberattack detection in internet of medical things. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 193, 104964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2024.104964
- Yan, S., Zhao, Z., Liu, S., Zhou, M. (2024). BO-SMOTE: A Novel Bayesian-Optimization-Based Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 54 (4), 2079–2091. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2023.3335241
- Davis, D., Rodriguez, L. (2024). Enhancing algorithm interpretability and accuracy with borderline-SMOTE and Bayesian optimization. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3 (2), 6–13. Available at: https://ashpress.org/index.php/jcts/article/view/24
- Bates, J. E., Shepard, H. K. (1993). Measuring complexity using information fluctuation. Physics Letters A, 172 (6), 416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(93)90232-o
- Wang, L. (2022). Imbalanced credit risk prediction based on SMOTE and multi-kernel FCM improved by particle swarm optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 114, 108153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108153
- Wilson, D. R., Martinez, T. R. (2000). Reduction Techniques for Instance-Based Learning Algorithms. Machine Learning, 38, 257–286. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007626913721
- Yang, F., Wang, K., Sun, L., Zhai, M., Song, J., Wang, H. (2022). A hybrid sampling algorithm combining synthetic minority over-sampling technique and edited nearest neighbor for missed abortion diagnosis. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 22 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-022-02075-2
- Snoek, J., Larochelle, H., Adams, R. P. (2012). Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1206.2944
- Frazier, P. I. (2018). A Tutorial on Bayesian Optimization. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.02811
- Klein, A., Falkner, S., Bartels, S., Hennig, P., Hutter, F. (2017). Fast Bayesian optimization of machine learning hyperparameters on large datasets. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1605.07079
- Akiba, T., Sano, S., Yanase, T., Ohta, T., Koyama, M. (2019). Optuna. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 2623–2631. https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330701
- Chen, T., Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
- Szeghalmy, S., Fazekas, A. (2023). A Comparative Study of the Use of Stratified Cross-Validation and Distribution-Balanced Stratified Cross-Validation in Imbalanced Learning. Sensors, 23 (4), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042333
- Vujovic, Ž. Ð. (2021). Classification Model Evaluation Metrics. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 12 (6). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2021.0120670
- Salmi, M., Atif, D., Oliva, D., Abraham, A., Ventura, S. (2024). Handling imbalanced medical datasets: review of a decade of research. Artificial Intelligence Review, 57 (10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10884-2
- Khadka, K., Chandrasekaran, J., Lei, Y., Kacker, R. N., Kuhn, D. R. (2024). A Combinatorial Approach to Hyperparameter Optimization. Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 3rd International Conference on AI Engineering - Software Engineering for AI, 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1145/3644815.3644941
- Chai, P., Hou, L., Zhang, G., Tushar, Q., Zou, Y. (2024). Generative adversarial networks in construction applications. Automation in Construction, 159, 105265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105265
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sutarman Sutarman, Putri Khairiah Nasution, Katrin Jenny Sirait, Cindy Novita Yolanda Panjaitan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








