Determining working parameters for the Hall-effect thruster with permanent magnets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322814Keywords:
Hall-effect thruster, permanent magnets, engine thrust, specific impulse, engine efficiencyAbstract
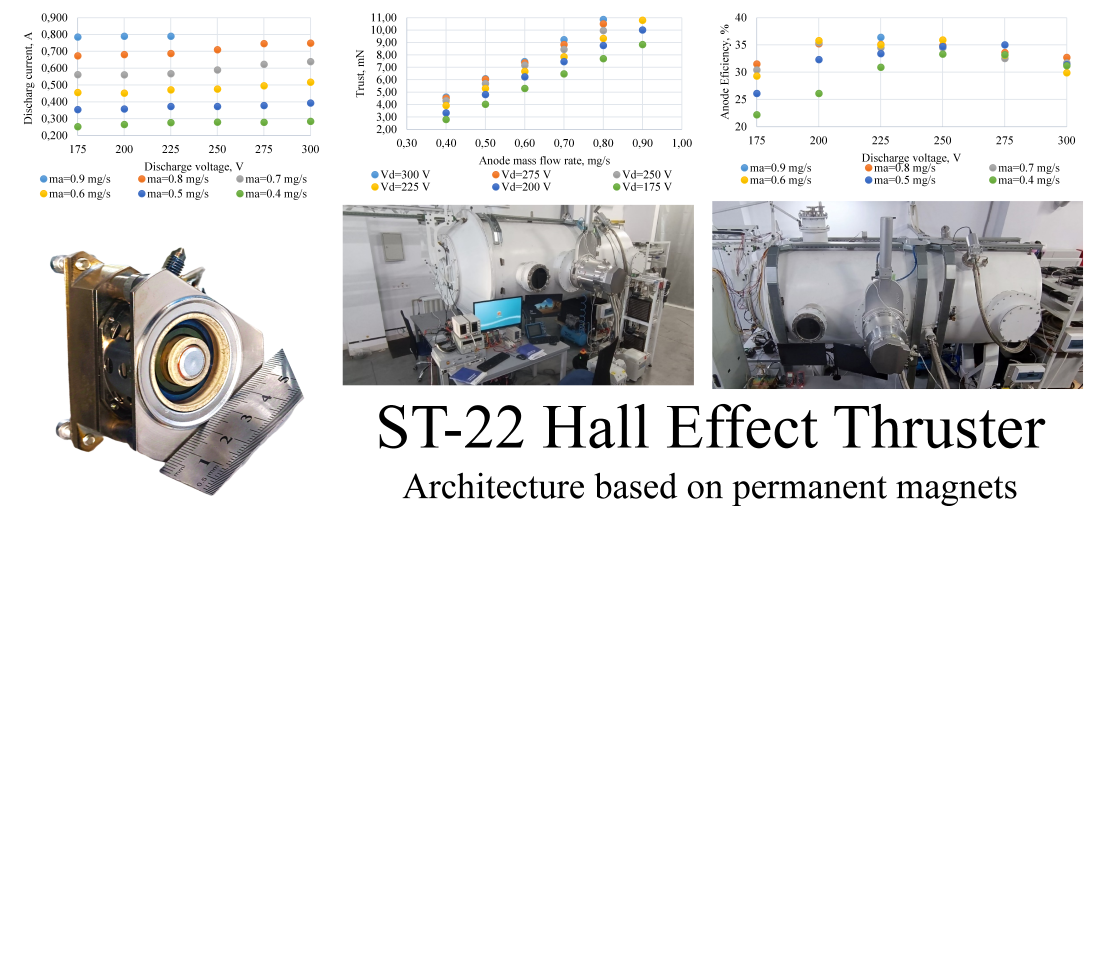
The object of this study is a Hall-effect thruster with a magnetic system on permanent magnets with minimal power consumption of electric energy, designed by Flight Control LLC (Ukraine). The task addressed in the study was to minimize the power consumed by the engine by excluding electromagnets from the engine’s magnetic system and using only permanent magnets in the magnetic system. To solve this task, a laboratory model of a Hall-effect thruster with permanent magnets was built and the operating parameters and characteristics of the engine were experimentally determined. As a result of laboratory studies of the operating parameters of the engine with permanent magnets, the volt-ampere characteristics of the engine discharge were obtained at fixed working gas (xenon) flow rates. The dependences of engine thrust on the mass flow rate of the working gas at fixed discharge voltages were also obtained. Based on the experimental data, the dependences of specific impulse of the engine anode block on the discharge voltage, as well as the dependences of efficiency of the engine anode block on discharge voltage and the working substance flow rates were calculated. The studies have shown that in Hall-effect thrusters of low thrust, in order to minimize the specific power as part of the magnetic system, it is quite possible to use permanent magnets. In particular, for the power range (100–200) W, the values of thrust (3–10) mN, specific impulse (700–1350) s, and efficiency of the anode block (25–37) % were achieved, which corresponds to the parameters of the considered prototypes with the conventional and combined structure of the magnetic system. The results of the work could be used in practice when designing Hall-effect thrusters of low specific power
References
- Mazouffre, S., Hallouin, T., Inchingolo, M., Gurciullo, A., Lascombes, P., Maria, J.-L. (2019). Characterization of miniature Hall thruster plume in the 50 - 200 W power range. 8th European Conference For Aeronautics and Space Sciences (EUCASS). Available at: https://doi.org/10.13009/EUCASS2019-214
- Mazouffre, S. (2016). Electric propulsion for satellites and spacecraft: established technologies and novel approaches. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 25 (3), 033002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/25/3/033002
- Boeuf, J.-P. (2017). Tutorial: Physics and modeling of Hall thrusters. Journal of Applied Physics, 121 (1). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972269
- Voronovsky, D. K., Kulagin, S. N., Maslov, V. V., Petrenko, O. N., Tolok, S. V. (2021). Hall-Effect Thruster ST-25 With Permanent Magnet. Journal of Rocket-Space Technology, 28 (4), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.15421/452005
- Alekseenko, O., Andrey, K., Maslov, V., Petrenko, O. (2021). Cyclograms of the ST-25 Hall Thruster Starting. Journal of Rocket-Space Technology, 29 (4), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.15421/452105
- Petrenko, O., Pererva, V., Maslov, V. (2024). Determining the effect of laboratory testing conditions on working parameters of the ST-25 hall thruster. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (5 (128)), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.301162
- Misuri, T., Albertoni, R., Ducci, C. et al. (2015). MEPS: A Low Power Electric Propulsion System for Small Satellites. IAA-B10-1103. 10th IAA Symposium on Small Satellites for Earth Observation. Berlin. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301678871_MEPS_A_Low_Power_Electric_Propulsion_System_for_Small_Satellites
- Misuri, T., Ducci, C., Gregucci, S., Pedrini, D., Cannelli, F., Cesari, U. et al. (2019). SITAEL HT100 Thruster unit, full ground qualification. International Electric Propulsion Conference. Vienna. Available at: https://electricrocket.org/2019/655.pdf
- Lascombes, P. (2018). Electric Propulsion For Small Satellites Orbit Control And Deorbiting: The Example Of A Hall Effect Thruster. 2018 SpaceOps Conference. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2018-2729
- Grimaud, L., Mazouffre, S. (2018). Performance comparison between standard and magnetically shielded 200 W Hall thrusters with BN-SiO2 and graphite channel walls. Vacuum, 155, 514–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.06.056
- Yeo, S. H., Ogawa, H., Kahnfeld, D., Schneider, R. (2021). Miniaturization perspectives of electrostatic propulsion for small spacecraft platforms. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 126, 100742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2021.100742
- Luna, J. P., Lewis, R. A., Park, N., Bosher, J., Guarducci, F., Cannat, F. (2019). T7 Thruster Design and Performance. The 36th International Electric Propulsion Conference. University of Vienna. Available at: https://electricrocket.org/2019/356.pdf
- Mazouffre, S., Grimaud, L. (2018). Characteristics and Performances of a 100-W Hall Thruster for Microspacecraft. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 46 (2), 330–337. https://doi.org/10.1109/tps.2017.2786402
- Voronovkyi, D., Petrenko, O., Kulagin, S., Maslov, V., Yurkov, B. (2023). Low Power Hall Thruster ST-22 With Permanent Magnets. Journal of Rocket-Space Technology, 30 (4), 30–36. https://doi.org/10.15421/452205
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Olexandr Petrenko, Viktor Pererva, Viktor Maslov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








