Development of enhanced method of geospatial electrical intelligence of near-surface soil layers in Northern Kazakhstan for detecting pollution sources
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322818Keywords:
soil electrical conductivity, digital processing, experimental data, coal dust, transport and logistics flows, rail transportationAbstract
This study focuses on the near-surface soil layers in suburban areas of Astana, Northern Kazakhstan, to address the critical issue of soil pollution caused by anthropogenic activities, particularly coal dust dispersion from open railway freight transportation. Existing geophysical methods for soil conductivity measurement lack precision due to interference from upper soil layers and seasonal moisture variations, limiting reliable pollution source identification.
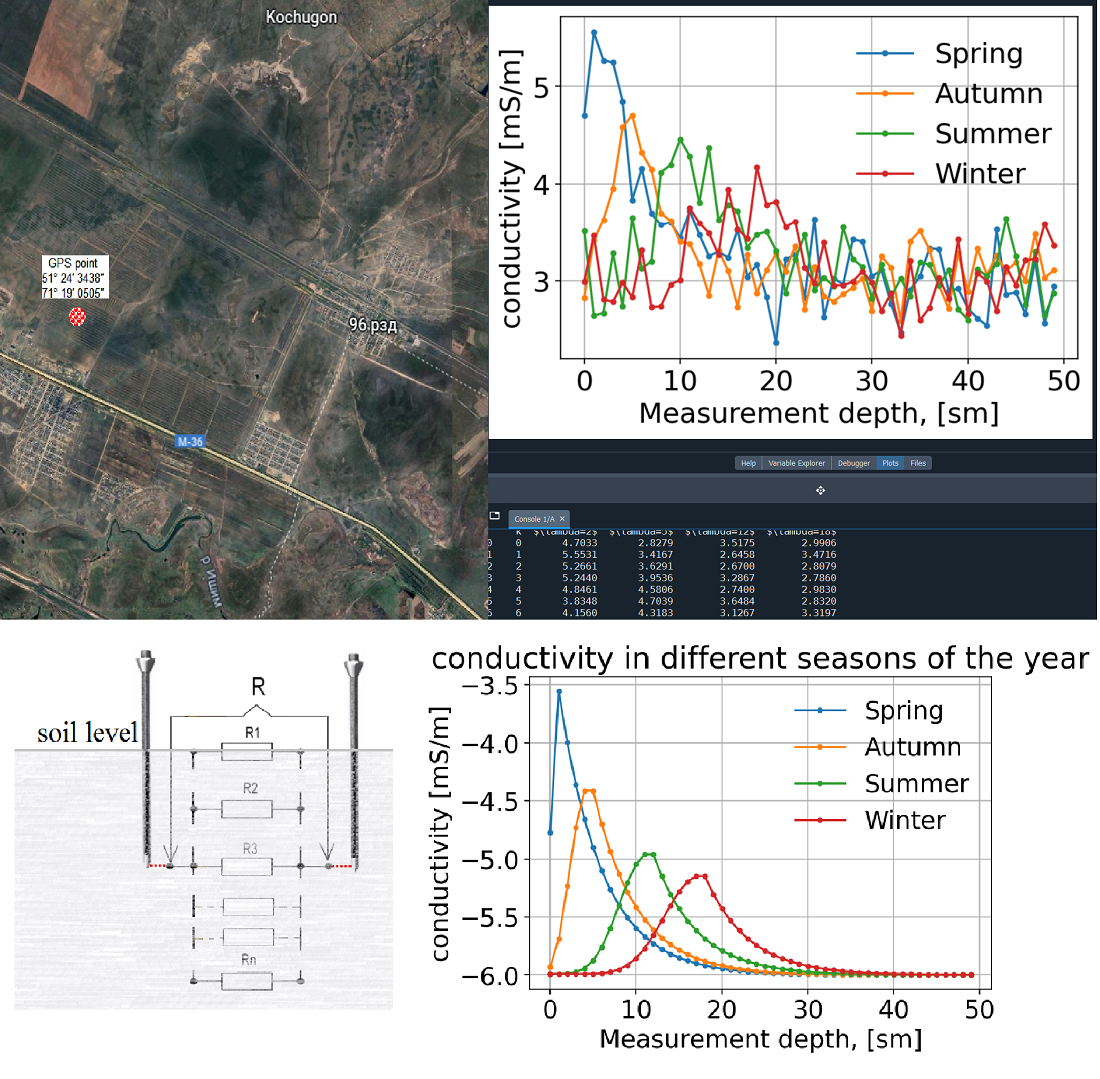
To enhance the precision of measurements, researchers modified the measuring probes. This improvement, combined with geophysical studies and Global Positioning System topographic referencing, allowed for identifying new patterns in pollutant behavior. A strong correlation was established between electromagnetic anomalies and human activities, including transportation, logistics, and urbanization.
The study revealed that soil electrical conductivity near railway tracks was three times higher due to coal dust, with peak values reaching 4.8 mS/m in spring. Modified probes improved measurement accuracy by 28–32 % depending on the season, enabling precise detection of subsurface pollution patterns.
The findings provide insights into urban pollution dynamics and its long-term effects.
Based on experimental data, recommendations were developed such as transition to renewable energy will reduce coal dependency and pollution.
In conclusion, the study highlights key issues surrounding soil pollution and provides recommendations to mitigate its effects. This approach supports sustainable land management, regulatory enforcement, and pollution mitigation strategies in urban-suburban interfaces worldwide
References
- Ariati, A., Arifin, M. Z., Sutikno, F. R., Bowoputro, H., Miftahulkhair, M. (2024). Identifying the influence of traffic management on vehicle emissions and the distribution of air dispersion in the Makassar port area. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (10 (129)), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.307037
- Lupolt, S. N., Santo, R. E., Kim, B. F., Green, C., Codling, E., Rule, A. M. et al. (2021). The Safe Urban Harvests Study: A Community-Driven Cross-Sectional Assessment of Metals in Soil, Irrigation Water, and Produce from Urban Farms and Gardens in Baltimore, Maryland. Environmental Health Perspectives, 129 (11). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp9431
- Romero‐Ruiz, A., Linde, N., Baron, L., Breitenstein, D., Keller, T., Or, D. (2022). Lasting Effects of Soil Compaction on Soil Water Regime Confirmed by Geoelectrical Monitoring. Water Resources Research, 58 (2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021wr030696
- Garré, S., Hyndman, D., Mary, B., Werban, U. (2021). Geophysics conquering new territories: The rise of “agrogeophysics.” Vadose Zone Journal, 20 (4). https://doi.org/10.1002/vzj2.20115
- Blanchy, G., Virlet, N., Sadeghi‐Tehran, P., Watts, C. W., Hawkesford, M. J., Whalley, W. R., Binley, A. (2020). Time‐intensive geoelectrical monitoring under winter wheat. Near Surface Geophysics, 18 (4), 413–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/nsg.12107
- Cassiani, G., Boaga, J., Vanella, D., Perri, M. T., Consoli, S. (2015). Monitoring and modelling of soil-plant interactions: the joint use of ERT, sap flow and eddy covariance data to characterize the volume of an orange tree root zone. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19 (5), 2213–2225. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-2213-2015
- Binley, A. (2015). Tools and Techniques: Electrical Methods. Treatise on Geophysics, 233–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-53802-4.00192-5
- Yao, R., Yang, J., Wu, D., Xie, W., Gao, P., Jin, W. (2016). Digital Mapping of Soil Salinity and Crop Yield across a Coastal Agricultural Landscape Using Repeated Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) Surveys. PLOS ONE, 11 (5), e0153377. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153377
- Brogi, C., Huisman, J. A., Pätzold, S., von Hebel, C., Weihermüller, L., Kaufmann, M. S. et al. (2019). Large-scale soil mapping using multi-configuration EMI and supervised image classification. Geoderma, 335, 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.08.001
- Boaga, J. (2017). The use of FDEM in hydrogeophysics: A review. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 139, 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2017.02.011
- Boaga, J., Ghinassi, M., D’Alpaos, A., Deidda, G. P., Rodriguez, G., Cassiani, G. (2018). Geophysical investigations unravel the vestiges of ancient meandering channels and their dynamics in tidal landscapes. Scientific Reports, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20061-5
- Peneva, S., Le, Q. N. P., Munhoz, D. R., Wrigley, O., Wille, F., Doose, H. et al. (2025). Microplastic analysis in soils: A comparative assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 289, 117428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117428
- McLachlan, P., Blanchy, G., Chambers, J., Sorensen, J., Uhlemann, S., Wilkinson, P., Binley, A. (2021). The Application of Electromagnetic Induction Methods to Reveal the Hydrogeological Structure of a Riparian Wetland. Water Resources Research, 57 (6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2020wr029221
- Akhmadiya, A., Nabiyev, N., Moldamurat, K., Dyussekeyev, K., Atanov, S. (2021). Use of Sentinel-1 Dual Polarization Multi-Temporal Data with Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Textural Parameters for Building Damage Assessment. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 31 (2), 240–250. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1054661821020036
- Corwin, D. L., Scudiero, E. (2020). Field‐scale apparent soil electrical conductivity. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 84 (5), 1405–1441. https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20153
- Qiu, L., Tang, J., Liu, Z. (2024). An improved goal-oriented adaptive finite-element method for 3-D direct current resistivity anisotropic forward modeling using nested tetrahedra. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 231, 105555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2024.105555
- McLachlan, P., Blanchy, G., Binley, A. (2021). EMagPy: Open-source standalone software for processing, forward modeling and inversion of electromagnetic induction data. Computers & Geosciences, 146, 104561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104561
- Flinchum, B. A., Holbrook, W. S., Grana, D., Parsekian, A. D., Carr, B. J., Hayes, J. L., Jiao, J. (2018). Estimating the water holding capacity of the critical zone using near‐surface geophysics. Hydrological Processes, 32 (22), 3308–3326. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13260
- Rahmati, M., Amelung, W., Brogi, C., Dari, J., Flammini, A., Bogena, H. et al. (2024). Soil Moisture Memory: State‐Of‐The‐Art and the Way Forward. Reviews of Geophysics, 62 (2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2023rg000828
- Carrera, A., Peruzzo, L., Longo, M., Cassiani, G., Morari, F. (2024). Electromagnetic and DC-current geophysics for soil compaction assessment. https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2024-1587
- Tret' godovyh passazhirskih zh/d perevozok Nacperevozchika prihoditsya na letniy period. Available at: https://rail-news.kz/ru/passenger-transportation/15084-tret-godovyx-passazirskix-zd-perevozok-nacperevozcika-prixoditsia-na-letnii-period.html
- Bolee 40% ob'ema perevozok KTZh zanimaet ugol'. Available at: https://ktzh-gp.kz/ru/media/news/news_main_section_ru/18017/
- Itogi raboty KEW/KEF 2023. Available at: https://kazenergyforum.com/kew-kef-2023/results/
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Kuandyk Akshulakov, Dauren Kassenov, Marat Samatov, Sabyrzhan Atanov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








