Multi-objective optimization of a two-stage helical gearbox with double gears in second stage using saw technique to reduce bottom area and enhance efficiency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322992Keywords:
SAW method, MEREC method, helical gearbox, gear ratio, gearbox efficiency, gearbox bottom area, MCDM, MOOPAbstract
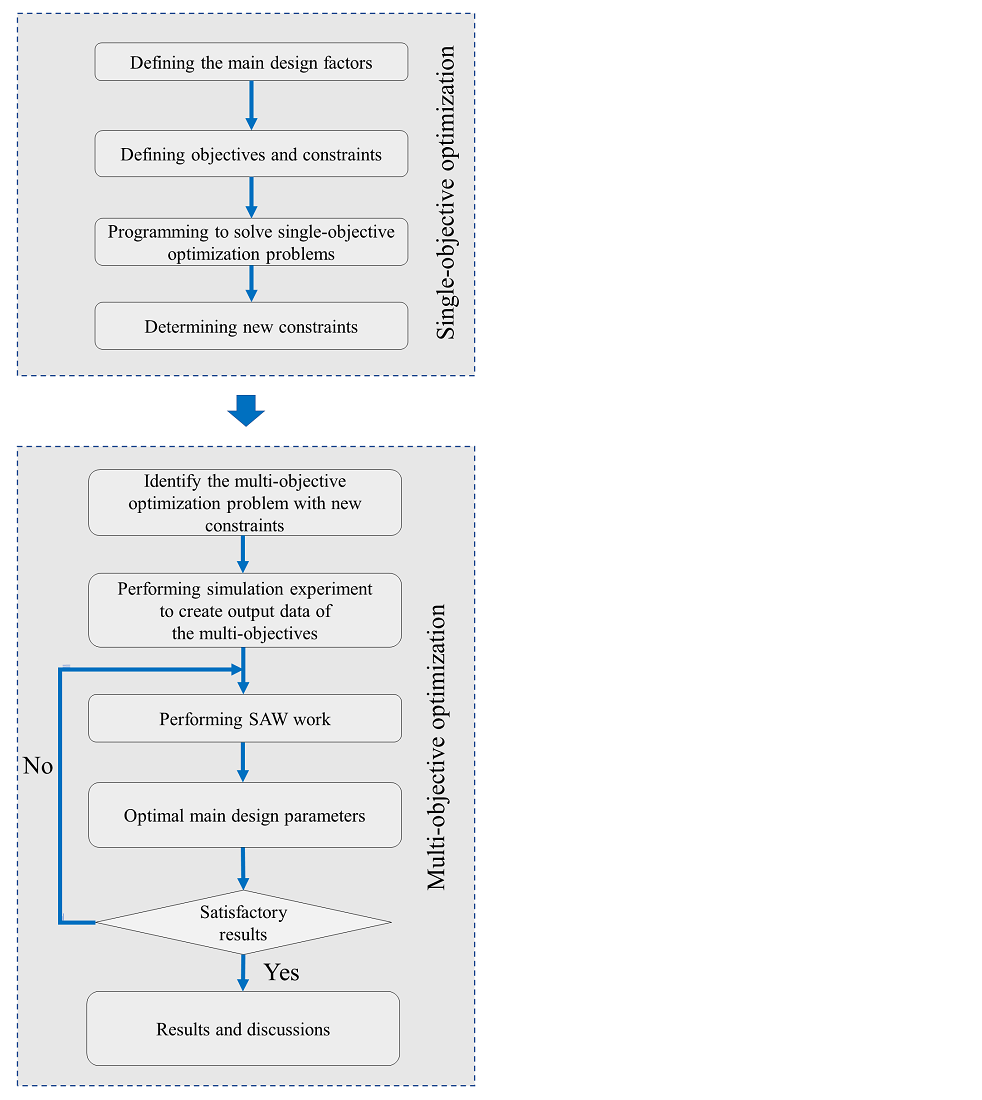
Two-stage helical gearboxes featuring two gears in the second stage are widely used across various industries. This gearbox design helps enhanced load capacity, increases consistent force distribution, and minimizes operational noise. One significant challenge in the design of this type of gearbox is the simultaneous optimization of multiple design criteria, including transmission efficiency and overall size. Optimizing gearbox design involves more than selecting an appropriate gear configuration; it necessitates a complete approach that balances performance with size, ensures sustainable operation, and minimizes manufacturing costs. This study was conducted to develop a method for solving the multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) related to the design of a two-stage helical gearbox (TSHG) containing double gears in the second stage (DGSS). The primary focus is on two single-objective functions: maximizing gearbox efficiency and minimizing the gearbox bottom area. This study investigates three primary design parameters: the gear ratio of the first stage (u1), the gear width coefficient of the first stage (Xba1), and second stage (Xba2). The optimization process was carried out in two distinct stages. The initial phase focused on the single-objective optimization problem aimed at minimizing the gap among the variable levels. The second stage concentrated on dealing with the MOOP to identify the optimal design parameters. The Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) method was employed to solve the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problem, while the MEREC technique was utilized to establish the weights of the criteria. The implementation of SAW in this context introduces a novel methodology that streamlines the identification of the optimal solution while enhancing the precision of the outcomes. Moreover, addressing the MOOP problem in a two-stage approach reduces the solution process and enhances the precision of the outcomes. The proposed optimized values of the primary design parameters aim to enhance gearbox efficiency and maximize installation space, thereby facilitating potential applications across diverse industries
References
- Khai, D. Q., Linh, N. H., Danh, T. H., Tan, T. M., Cuong, N. M., Hien, B. T. et al. (2022). Calculating Optimum Main Design Factors of a Two-Stage Helical Gearboxes for Minimum Gearbox Mass. Advances in Engineering Research and Application, 314–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22200-9_34
- Jelaska, D. (2012). Gears and Gear Drives. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118392393
- Le, X.-H., Vu, N.-P. (2023). Multi-Objective Optimization of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox Using Taguchi Method and Grey Relational Analysis. Applied Sciences, 13 (13), 7601. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137601
- Vu, D.-B., Tran, H.-D., Dinh, V.-T., Vu, D., Vu, N.-P., Nguyen, V.-T. (2024). Solving a Multi-Objective Optimization Problem of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox with Second-Stage Double Gear Sets Using the MAIRCA Method. Applied Sciences, 14 (12), 5274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125274
- Dinh, V.-T., Tran, H.-D., Vu, D.-B., Vu, D., Vu, N.-P., Do, T.-T. (2024). Multi-Objective Optimization for Finding Main Design Factors of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox with Second-Stage Double Gear Sets Using the EAMR Method. Symmetry, 16 (7), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16070783
- Dinh, V.-T., Tran, H.-D., Tran, Q.-H., Vu, D.-B., Vu, D., Vu, N.-P., Nguyen, T.-T. (2024). Multi-Objective Optimization of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox Using MARCOS Method. Designs, 8 (3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8030053
- Abuid, B. A., Ameen, Y. M. (2003). Procedure for Optimum Design of a Two-Stage Spur Gear System. JSME International Journal Series C, 46 (4), 1582–1590. https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmec.46.1582
- Wang, H., Wang, H.-P. (1994). Optimal engineering design of spur gear sets. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 29 (7), 1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/0094-114x(94)90074-4
- Yokota, T., Taguchi, T., Gen, M. (1998). A solution method for optimal weight design problem of the gear using genetic algorithms. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 35 (3-4), 523–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-8352(98)00149-1
- Huang, H.-Z., Tian, Z.-G., Zuo, M. J. (2005). Multiobjective optimization of three-stage spur gear reduction units using interactive physical programming. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 19 (5), 1080–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02984029
- Golabi, S., Fesharaki, J. J., Yazdipoor, M. (2014). Gear train optimization based on minimum volume/weight design. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 73, 197–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2013.11.002
- Patil, M., Ramkumar, P., Shankar, K. (2017). Multi-Objective Optimization of Spur Gearbox with Inclusion of Tribological Aspects. Journal of Friction and Wear, 38 (6), 430–436. https://doi.org/10.3103/s1068366617060101
- Liu, S., Li, B., Gan, R., Xu, Y., Yang, G. (2023). Multi-Objective Optimization of Two-Stage Helical Pairs in Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator Using Ensemble of Metamodels and NSGA-II. Actuators, 12 (10), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12100385
- Alam, J., Panda, S. (2021). A comprehensive study on multi-objective design optimization of spur gear. Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines, 51 (9), 5272–5298. https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2021.1996246
- Istenes, G., Polák, J. (2024). Investigating the Effect of Gear Ratio in the Case of Joint Multi-Objective Optimization of Electric Motor and Gearbox. Energies, 17 (5), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051203
- Hung, T. Q., Tung, L. A. (2023). Application of Taguchi Technique and Grey Relational Analysis for Multi-Target Optimization of Two-stage Helical Gearboxes. Advances in Image and Video Processing, 11 (6), 372–387. https://doi.org/10.14738/aivp.116.16104
- Huy, T. Q., Binh, N. V., Thanh, D. V., Danh, T. H., Trang, N. V. (2023). Optimization of a Two-stage Helical Gearbox with Second Stage Double Gear Sets to Reduce Gearbox Mass and Increase Gearbox Efficiency. Wseas Transactions on Applied and Theoretical Mechanics, 18, 287–298. https://doi.org/10.37394/232011.2023.18.27
- Dinh, V.-T., Tran, H.-D., Bui, T.-D., Vu, D.-B., Vu, D., Vu, N.-P., Truong, T.-T.-H. (2024). Multi-Objective Optimization of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox with Second Stage Double Gear-Sets Using TOPSIS Method. Processes, 12 (6), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12061160
- Chat, T., Uyen, L. V. (2007). Design and calculation of Mechanical Transmissions Systems. Vol. 1. Hanoi: Educational Republishing House.
- Dinh, V.-T., Tran, H.-D., Vu, D.-B., Vu, D., Vu, N.-P., Luu, A.-T. (2024). Application of a Multi-Criterion Decision-Making Method for Solving the Multi-Objective Optimization of a Two-Stage Helical Gearbox. Machines, 12 (6), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12060365
- Hartati, S., Harjoko, A., Wardoyo, R., Kusumadewi, S. (2006). Fuzzy multi-attribute decision making (Fuzzy MADM). Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu, 364.
- Keshavarz-Ghorabaee, M. (2021). Assessment of distribution center locations using a multi-expert subjective-objective decision-making approach. Scientific Reports, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98698-y
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Binh Duc Vu, Hung Quoc Tran, Thanh Van Dinh, Trang Van Nguyen, Minh Khac Nguyen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








