Densenet development with squeeze-and-excitation block for tomato plant disease classification
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.323176Keywords:
tomato classification, tomato leaf disease, DenseNet-SEGR, squeeze-and-excitation, growth rate, deep learningAbstract
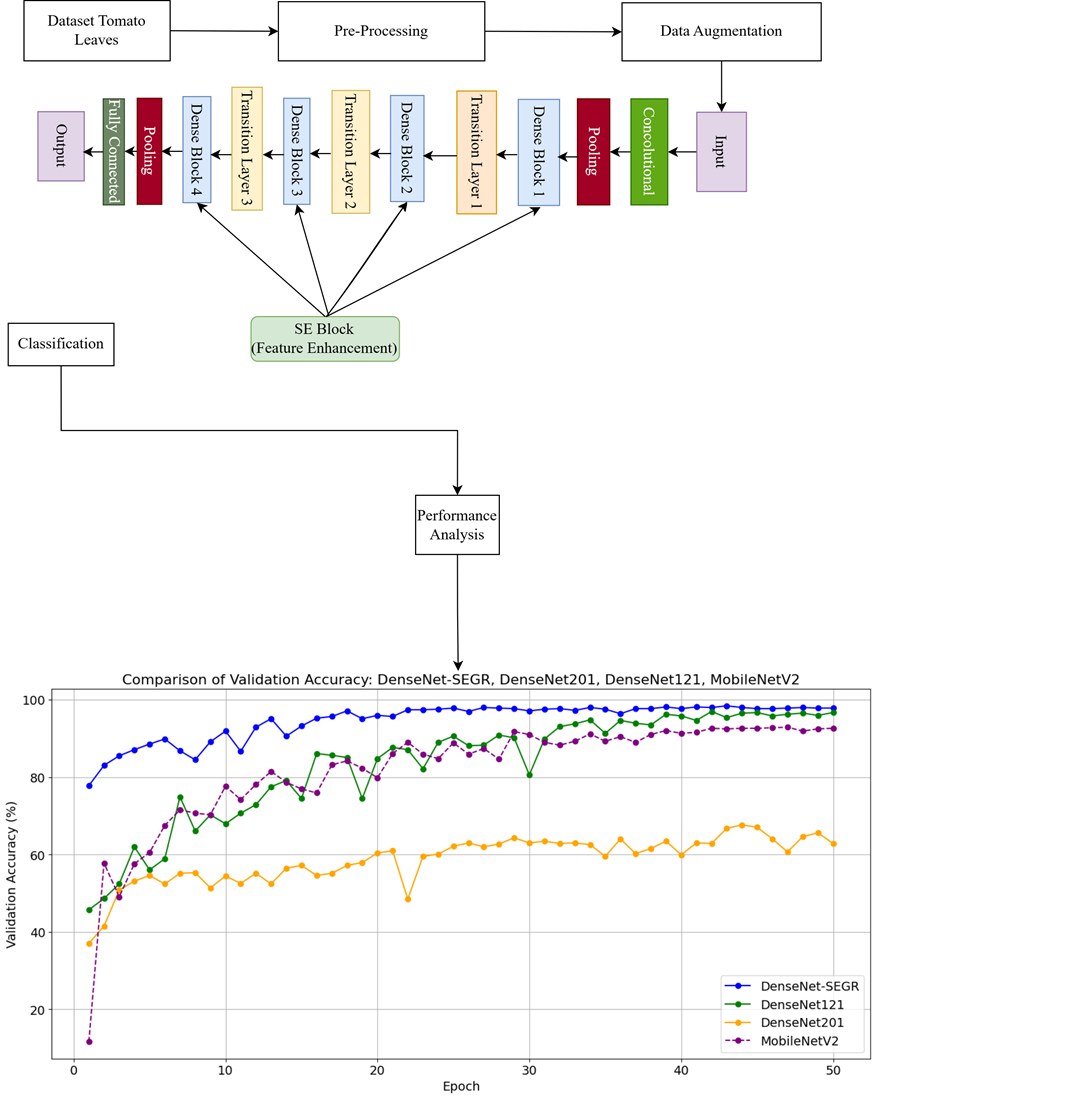
This study focuses on tomato leaf disease classification using an optimized deep learning architecture. This study proposes an improved architecture called DenseNet-SEGR, which integrates a novel Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) block with a customized growth rate of 48 to improve feature selection and classification accuracy. Unlike standard methods, this model replaces Global Average Pooling (GAP) with an integral-based squeeze method, thus enabling a more continuous and accurate feature representation. The use of SE blocks dynamically recalibrates the importance of features such as texture, color, and tissue patterns, thereby increasing sensitivity to disease symptoms. The model was trained using the PlantVillage dataset, which includes 12,246 images spanning 10 tomato leaf disease categories, such as bacterial spot, early blight, late blight, mosaic virus, and healthy leaves. Various augmentation techniques, including rotation, scaling, and contrast adjustment, were employed to strengthen generalization and improve robustness against environmental variations. Furthermore, batch normalization and adaptive learning rate scheduling were integrated to enhance model stability and prevent overfitting. As a result, the DenseNet-SEGR architecture is able to achieve a classification accuracy of 98.22 %, outperforming DenseNet-121, DenseNet-201, and MobileNetV2. This result is explained by the integration of adaptive attention mechanisms, sophisticated data augmentation strategies, and optimized architecture. The results can be effectively applied in real-world precision agriculture, especially in edge-based or mobile disease detection systems for early intervention and crop protection
References
- Bakr, M., Abdel-Gaber, S., Nasr, M., Hazman, M. (2022). Tomato disease detection model based on densenet and transfer learning. Applied Computer Science, 18 (2), 56–70. https://doi.org/10.35784/acs-2022-13
- Ahmed, S., Hasan, Md. B., Ahmed, T., Sony, Md. R. K., Kabir, Md. H. (2022). Less is More: Lighter and Faster Deep Neural Architecture for Tomato Leaf Disease Classification. IEEE Access, 10, 68868–68884. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3187203
- Khan, I., Sohail, S. S., Madsen, D. Ø., Khare, B. K. (2024). Deep transfer learning for fine-grained maize leaf disease classification. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 16, 101148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101148
- Arulananth, T. S., Prakash, S. W., Ayyasamy, R. K., Kavitha, V. P., Kuppusamy, P. G., Chinnasamy, P. (2024). Classification of Paediatric Pneumonia Using Modified DenseNet-121 Deep-Learning Model. IEEE Access, 12, 35716–35727. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3371151
- Zhu, H., Wang, L., Shen, N., Wu, Y., Feng, S., Xu, Y. et al. (2023). MS-HNN: Multi-Scale Hierarchical Neural Network With Squeeze and Excitation Block for Neonatal Sleep Staging Using a Single-Channel EEG. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 31, 2195–2204. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2023.3266876
- Yuan, Z., Li, X., Hao, Z., Tang, Z., Yao, X., Wu, T. (2024). Intelligent prediction of Alzheimer’s disease via improved multifeature squeeze-and-excitation-dilated residual network. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62712-w
- Zhu, C., Wang, L., Zhao, W., Lian, H. (2024). Image classification based on tensor network DenseNet model. Applied Intelligence, 54 (8), 6624–6636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05472-4
- Cui, X., Yu, Z., Li, J., Jiang, B., Li, S., Liu, J. (2023). Research on RFID Localization Algorithm of Refrigerator Foods Based on Improved DenseNet Model. IEEE Networking Letters, 5 (2), 135–139. https://doi.org/10.1109/lnet.2023.3258458
- Mugume, E., Tumwesigye, A., Muhangi, A. (2021). A spatio-temporal sleep mode approach to improve energy efficiency in small cell DenseNets. SAIEE Africa Research Journal, 112 (3), 134–141. https://doi.org/10.23919/saiee.2021.9513627
- Lu, T., Han, B., Chen, L., Yu, F., Xue, C. (2021). A generic intelligent tomato classification system for practical applications using DenseNet-201 with transfer learning. Scientific Reports, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95218-w
- Asker, M. E., Güngör, M. (2024). A hybrid approach consisting of 3D depthwise separable convolution and depthwise squeeze-and-excitation network for hyperspectral image classification. Earth Science Informatics, 17 (6), 5795–5821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01469-2
- Roy, K., Chaudhuri, S. S., Frnda, J., Bandopadhyay, S., Ray, I. J., Banerjee, S., Nedoma, J. (2023). Detection of Tomato Leaf Diseases for Agro-Based Industries Using Novel PCA DeepNet. IEEE Access, 11, 14983–15001. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3244499
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Li, Z., Li, X., Wang, Z. (2024). Hierarchical intelligent lithology recognition for thin section images using enhanced DenseNet. Earth Science Informatics, 18 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01663-2
- Bouni, M., Hssina, B., Douzi, K., Douzi, S. (2024). Synergistic use of handcrafted and deep learning features for tomato leaf disease classification. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-71225-5
- Umar, M., Altaf, S., Ahmad, S., Mahmoud, H., Mohamed, A. S. N., Ayub, R. (2024). Precision Agriculture Through Deep Learning: Tomato Plant Multiple Diseases Recognition With CNN and Improved YOLOv7. IEEE Access, 12, 49167–49183. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3383154
- Cheng, Y.-H., Kuo, C.-N., Lin, Y.-D. (2024). An Artificial IoT-Enabled Smart Production Line for 360° Visual Defect Detection and Classification of Cherry Tomatoes. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 11 (10), 18082–18098. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2024.3360715
- Liu, H., Liu, S., Wen, C., Wong, W. E. (2022). TBEM: Testing-Based GPU-Memory Consumption Estimation for Deep Learning. IEEE Access, 10, 39674–39680. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3164510
- Mao, Y., Kim, J., Podina, L., Kohandel, M. (2025). Dilated SE-DenseNet for brain tumor MRI classification. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-86752-y
- Devassy, B. R., Antony, J. K. (2023). Histopathological image classification using CNN with squeeze and excitation networks based on hybrid squeezing. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 17 (7), 3613–3621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02587-y
- Al-Waeli, M., Shahmohammadi, N., Tavakoli, S., Dizadji, A., Kvarnheden, A. (2024). Infection of tomato in Iraq with tomato leaf curl Palampur virus and multiple variants of tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Journal of Plant Pathology, 106 (3), 1283–1294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-024-01682-4
- Romero-Rodríguez, B., Petek, M., Jiao, C., Križnik, M., Zagorščak, M., Fei, Z. et al. (2023). Transcriptional and epigenetic changes during tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection in tomato. BMC Plant Biology, 23 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04534-y
- Khan, M., Hossni, Y. (2025). A comparative analysis of LSTM models aided with attention and squeeze and excitation blocks for activity recognition. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-88378-6
- Zhou, L.-Q., Sun, P., Li, D., Piao, J.-C. (2022). A Novel Object Detection Method in City Aerial Image Based on Deformable Convolutional Networks. IEEE Access, 10, 31455–31465. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3156953
- Xu, J., Pan, S., Sun, P. Z. H., Hyeong Park, S., Guo, K. (2023). Human-Factors-in-Driving-Loop: Driver Identification and Verification via a Deep Learning Approach using Psychological Behavioral Data. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 24 (3), 3383–3394. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2022.3225782
- Sun, M., Yu, M., Lv, P., Li, A., Wang, H., Zhang, X. et al. (2021). Man-Made Threat Event Recognition Based on Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensing and SE-WaveNet. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 70, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2021.3081178
- Al Jbaar, M. A., Dawwd, S. A. (2023). SIMD implementation of deep CNNs for myopia detection on a single-board computer system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (9 (125)), 98–108. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289007
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Pandi Barita Nauli Simangunsong, Poltak Sihombing, Syahril Efendi, Fahmi Fahmi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








