Determination of the range of angular velocities of the auto-balancing mode for a vertical rotor system with a Leblanc-type balancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.324793Keywords:
passive auto-balancing, Leblanc-type device, vertical rotor, auto-balancing modeAbstract
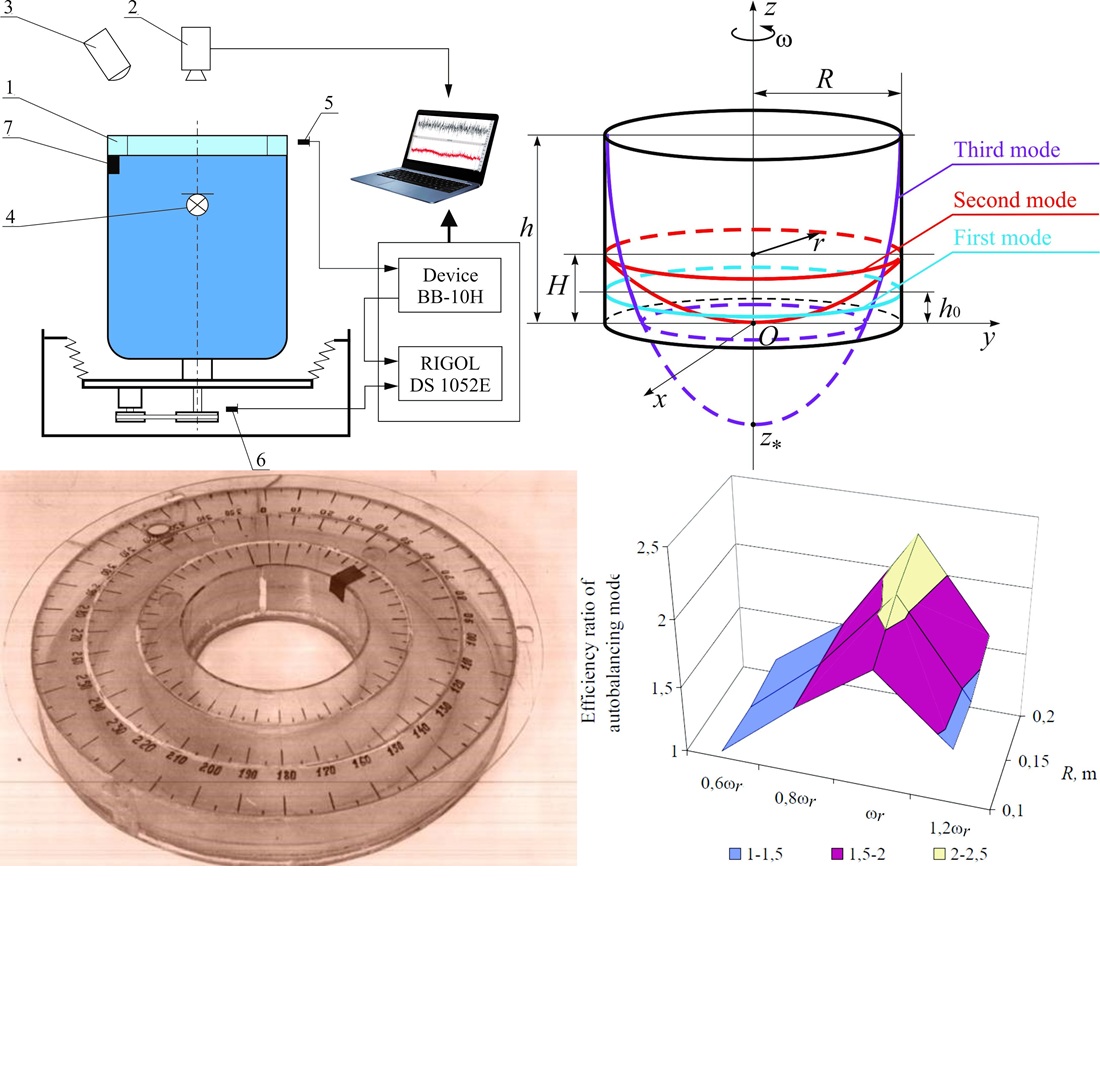
Automatic balancing devices (ABDs) of the Leblanc type – passive ABDs of the liquid type – are used in rotary machines to reduce their vibration level when the distribution of masses around the geometric axis of rotation changes during machine operation or during its restart. To redistribute the masses during balancing, the movement of the working (correcting) liquid in the direction opposite to the imbalance is used. The object of this study is the motion modes (qualitative states) of the working liquid in the chamber of the balancing device for the vertical rotor system. The study is aimed at substantiating the existence of the auto-balancing mode at subcritical angular velocities of the rotor system and investigating its conditions and features. This paper reports the results of modeling the motion modes of the working liquid in the cylindrical chamber of the Leblanc ABP at a subcritical range of rotation speeds taking into account the vector relationships of the force factors depending on the design parameters of the auto-balancing device, the volume of the working fluid, and the shape of its free surface. Estimates of the angular velocities of switching on the working liquid under the rotational motion and under the auto-balancing mode have been analytically and experimentally substantiated, constituting, respectively, 1/3 and 1/2 of the critical angular velocities of the rotor system. For the practice of balancing an elastically deformable rotor and a rotor on elastic supports, the results of the study expand the range of rotation speeds where the balancing of the imbalance by the liquid and the reduction of the amplitudes of vibration processes are observed. This could help increase the service life, reliability, and accuracy of the technological process of machines with variable rotor imbalance by monitoring their vibration resistance through the use of liquid ABDs
References
- Pan, X., Lu, J., Huo, J., Gao, J., Wu, H. (2020). A Review on Self-Recovery Regulation (SR) Technique for Unbalance Vibration of High-End Equipment. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 33 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-020-00514-7
- Osiński, Z. (Ed.) (2018). Damping of Vibrations. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315140742
- Ibraheem, A., Ghazaly, N., Abd el- Jaber, G. (2019). Review of Rotor Balancing Techniques. American Journal of Industrial Engineering, 6 (1), 19–25. Available at: https://www.sciepub.com/ajie/abstract/11311
- Li, L., Cao, S., Li, J., Nie, R., Hou, L. (2021). Review of Rotor Balancing Methods. Machines, 9 (5), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9050089
- Zhang, Z., Nielsen, S. R. K., Basu, B., Li, J. (2015). Nonlinear modeling of tuned liquid dampers (TLDs) in rotating wind turbine blades for damping edgewise vibrations. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 59, 252–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.09.006
- Cho, J.-S., Jeong, H.-Y., Kong, K.-C. (2014). Analysis of dynamic model of a top-loading laundry machine with a hydraulic balancer. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 15 (8), 1615–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0511-x
- Filimonikhin, G., Filimonikhina, I., Dumenko, K., Pirogov, V. (2017). Methods of balancing of an axisymmetric flexible rotor by passive auto-balancers. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (7 (87)), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.101832
- LeBlanc, M. (1912). Pat. No. US1209730A. Automatic Balancer for Rotating Bodies. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US1209730A/en
- Narkhede, C. N., Dhande, K. K. (2016). Review on vibration reduction of a vertical axis drum based washing machine. IJARIIE, 2 (3), 3842–3847. Available at: https://typeset.io/pdf/review-on-vibration-reduction-of-a-vertical-axis-drum-based-3lswicxnch.pdf
- Nilawar, S. G., Yerrawar, R. N. (2023). Numerical modeling of semi-automatic washing machine motion model. International Scientific Session on Applied Mechanics XI: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Applied Mechanics, 2949, 020032. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0168215
- Lozynskyi, V., Shihab, T., Drach, I., Ropyak, L. (2024). The Inertial Disturbances of Fluid Movement in the Chamber of a Liquid Autobalancer. Machines, 12 (1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12010039
- Spannan, L., Daniel, C., Woschke, E., Strackeljan, J. (2016). An evaluation of computational methods to specify the effects of liquid balancers. Proceedings of vibrations in rotating machinery – VIRM 11, 785–791. Available at: https://www.ifme.ovgu.de/ifme_media/DY/pdf/Veroeffentlichungen/2016/VIRM_paper_Spannan_final-p-2126.pdf
- Majewski, T., Ahearn, G. A. (2019). Extended Model of Automatic Balancer for Washing Machine. Advances in Mechanism and Machine Science, 3197–3206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20131-9_315
- Chen, H.-W., Zhang, Q.-J., Fan, S.-Y. (2011). Study on steady-state response of a vertical axis automatic washing machine with a hydraulic balancer using a new approach and a method for getting a smaller deflection angle. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 330 (9), 2017–2030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2010.11.006
- Haifei, W., Tian, Z., Guo, C. (2023). Boundary-value-problem examination of the stability of a symmetrical rotor partially filled with a viscous incompressible fluid. Physics of Fluids, 35 (4). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0147073
- Langthjem, M. A., Imura, M., Yamaguchi, K. (2023). The unbalanced rotating cylinder partially filled with fluid; multiple scales analysis of a forced Korteweg–de Vries–Burgers equation. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 140 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-023-10259-6
- Cunico, M. W. M. (2015). Characterization and Modelling of LeBlanc Hydrodynamic Stabilizer: A Novel Approach for Steady and Transient State Models. Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, 2015, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/729582
- Urbiola-Soto, L., Lopez-Parra, M. (2013). Liquid Self-Balancing Device Effects on Flexible Rotor Stability. Shock and Vibration, 20 (1), 109–121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/742163
- Drach, I., Bubulis, A., Mažeika, D., Kandrotaitė Janutienė, R., Juodvalkis, D. (2018). Investigation of Small Motions of Liquid in Cylindrical Chamber of Auto-Balancing Device. Mechanics, 24 (2). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.mech.24.2.20402
- Drach, I., Royzman, V., Bubulis, A., Juzėnas, K. (2021). Passive Balancing of the Rotor with an Auto-Balancing Device with a Viscous Incompressible Liquid. Mechanics, 27 (1), 45–51. https://doi.org/10.5755/j02.mech.23789
- Royzman, V., Drach, I., Tkachuk, V., Pilkauskas, K., Čižauskas, G., Šulginas, A. (2019). Operation of Passive Fluid Self-Balancing Device at Resonance Transition Regime. Mechanics, 24 (6). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.mech.24.6.22469
- Royzman, V., Drach, I., Bubulis, А. (2016). Movement of Working Fluid in the Field of Centrifugal Forces and Forces of Weight. Proceedings of 21th nternational scientific conference, MECHANIKA 2016, 222–224. Available at: https://elar.khmnu.edu.ua/items/73746ee0-fe74-46ad-98e4-641332f31c6e
- Dykha, A. V., Kuzmenko, A. G. (2016). Distribution of friction tangential stresses in the Courtney-Pratt experiment under Bowden’s theory. Journal of Friction and Wear, 37 (4), 315–319. https://doi.org/10.3103/s1068366616040061
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ilona Drach, Oleksandr Dykha, Serhii Matiukh, Maksym Dykha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








