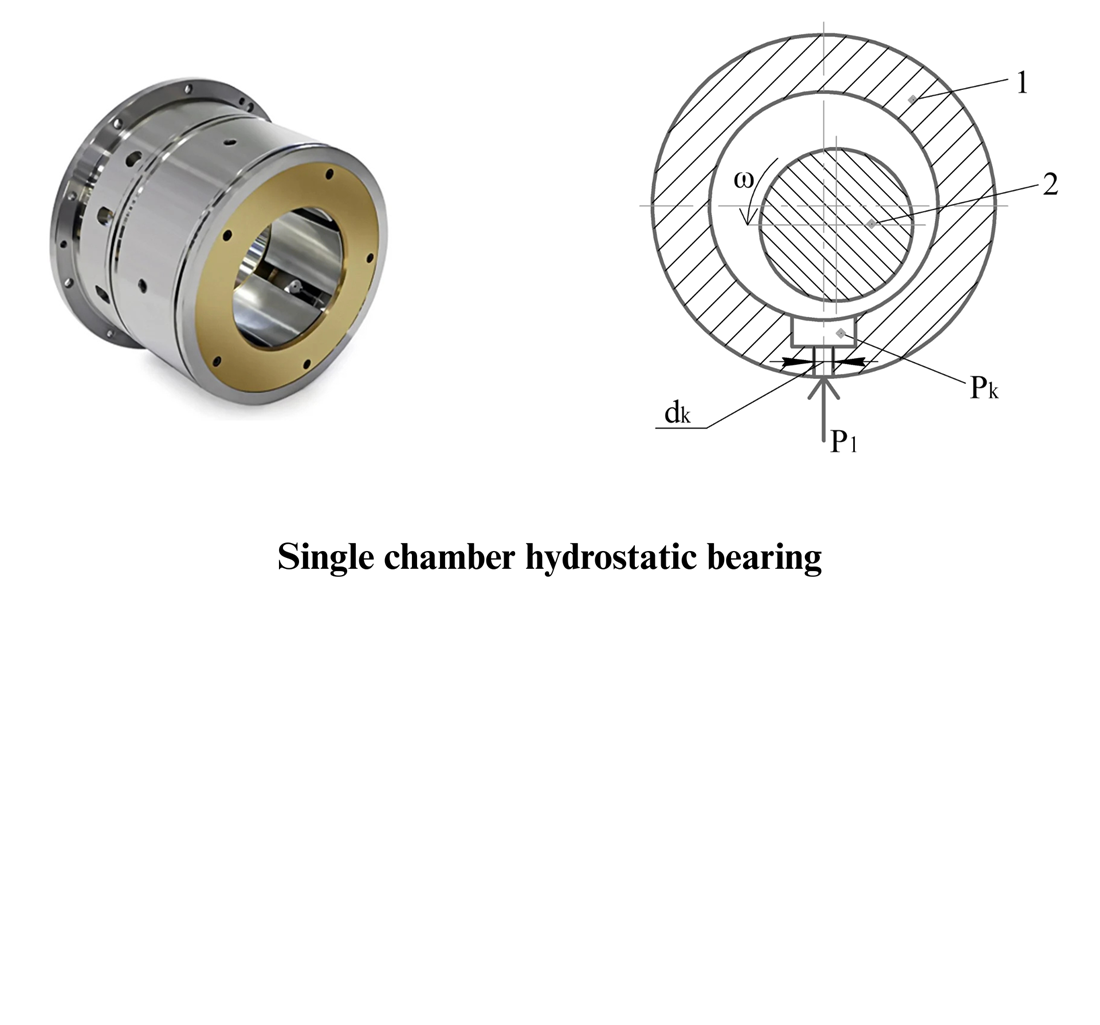
Determining the influence of working fluid temperature change on the characteristics of a single-chamber hydrostatic bearing at different values of design parameters
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325934Keywords:
single-chamber bearing, working fluid temperature, load carrying capacity, eccentricity, lubricant consumptionAbstract
The object of this study is hydrostatic processes in a single-chamber hydrostatic bearing of an aviation gear-type pump.
The task addressed is the influence of design parameters of a single-chamber bearing on its characteristics, taking into account changes in the temperature of the working fluid. The main characteristics considered are the carry-load capacity and flow rate of the working fluid. Determining these characteristics is associated with the joint solution of the Reynolds equations and the flow balance. The basic characteristics of the hydrostatic bearing were determined on the basis of the obtained pressure distribution function in the working fluid layer.
The influence of the eccentricity and diameter of the hydrostatic bearing on its characteristics has been studied, taking into account changes in the temperature of the working fluid.
It was found that at zero eccentricity the temperature of the working fluid increased by 5.6 °C and was 105.6 °C. At an eccentricity of 0.018 mm, the temperature of the working fluid increased by 15.6 °C and was 115.6 °C. With an increase in eccentricity from 0 mm to 0.018 mm, the maximum increase in the working fluid consumption in a single-chamber hydrostatic bearing due to an increase in temperature was 19 %. The maximum decrease in the bearing load carrying capacity due to an increase in the working fluid temperature was 17 %; and at a working eccentricity of 0.018 mm, it did not exceed 1.83 %.
With an increase in the bearing diameter, the working fluid temperature increased. At a bearing diameter of 14.5 mm, the increase in the working fluid temperature was 4.59 °C; and at a diameter of 43.5 mm, the working fluid temperature increased by 15.6 °C.
The results demonstrate that an increase in the working fluid temperature with an increase in eccentricity and bearing diameter has a negligible effect on its load carrying capacity and working fluid consumption
References
- Nazin, V. (2023). Identifying the influence of design parameters of a hydrostatic bearing in an aircraft fuel pump on its static characteristics. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (1 (125)), 28–34. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289426
- Nazin, V. (2023). Revealing the influence of structural and operational parameters of a hydrostatic bearing in a gear-type fuel pump on its main characteristics. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (1 (122)), 92–98. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.277755
- Nazin, V. (2024). Identifying the influence of design parameters of single-chamber hydrostatic bearing of fuel pump on its main characteristics. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (7 (127)), 30–36. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.298646
- Zhu, J.-X., Li, H.-C., Fu, J.-F., Liu, X.-W. (2020). Numerical Analysis of Non-Linear Transient Characteristics of Aviation Fuel Gear Pump Sliding Bearings, Tuijin Jishu/Journal of Propulsion Technology, 41 (2), 412–422. https://doi.org/10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190004
- Fiebig, W., Korzyb, M. (2015). Vibration and dynamic loads in external gear pumps. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 15 (3), 680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2014.11.003
- Yang, H. (2020). Gear Pump Bearings-Reverse Design of Journal Fluid Lubrication. 2020 5th International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT), 25–28. https://doi.org/10.1109/icectt50890.2020.00013
- Fu, J., Jiang, Y., Li, H., Zhu, J. (2021). Optimization Design of Sliding Bearing of Fuel Pump Based on CFD Method. 2021 12th International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAE), 546–551. https://doi.org/10.1109/icmae52228.2021.9522403
- Pham, H. T., Weber, J. (2019). Theoretical and experimental analysis of the effect of misaligned ring gear on performance of internal gear motors/pumps. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 33 (9), 4049–4060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0801-4
- Yang, G., Wan, J., Chen, P., Zhang, S., Zhu, X. F. (2011). Application Exploration of Self-adaptive Technology in the Modern Engineering Graphics Teaching. International Conference on Physical Education and Society Management ICPESM 2011, 131–134.
- Zhang, T., Yan, G., Liu, X., Ding, B., Feng, G., Ai, C. (2024). Hydrostatic bearing groove multi-objective optimization of the gear ring housing interface in a straight-line conjugate internal meshing gear pump. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62727-3
- Tacconi, J., Shahpar, S., King, A., Olufeagba, J. P., Khan, R., Sant, I., Yates, M. (2021). Elasto-Hydrodynamic Model of Hybrid Journal Bearings for Aero-Engine Gear Fuel Pump Applications. Journal of Tribology, 144 (3), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4052479
- Wu, Y., Ge, P., Bi, W. (2021). Analysis of axial force of double circular arc helical gear hydraulic pump and design of its balancing device. Journal of Central South University, 28 (2), 418–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4612-2
- Komagata, M., Ko, T., Nakamura, Y. (2019). Design and Development of Compact Ceramics Reinforced Pump with Low Internal Leakage for Electro-Hydrostatic Actuated Robots. Advances in Mechanism and Machine Science, 2439–2448. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20131-9_241
- Du, J. (2016). Analysis on Oil Film of Hydrostatic Bearing in Gear Pump Operating at High Pressures and High Speeds. International Journal of Simulation: Systems, Science & Technology. https://doi.org/10.5013/ijssst.a.17.43.25
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Vladimir Nazin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








