Identification the influence of increased pore water pressure and vertical deformation under the influence of the liquefaction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326558Keywords:
lateral resistance, group pile, sand soil, liquefaction, vertical loadAbstract
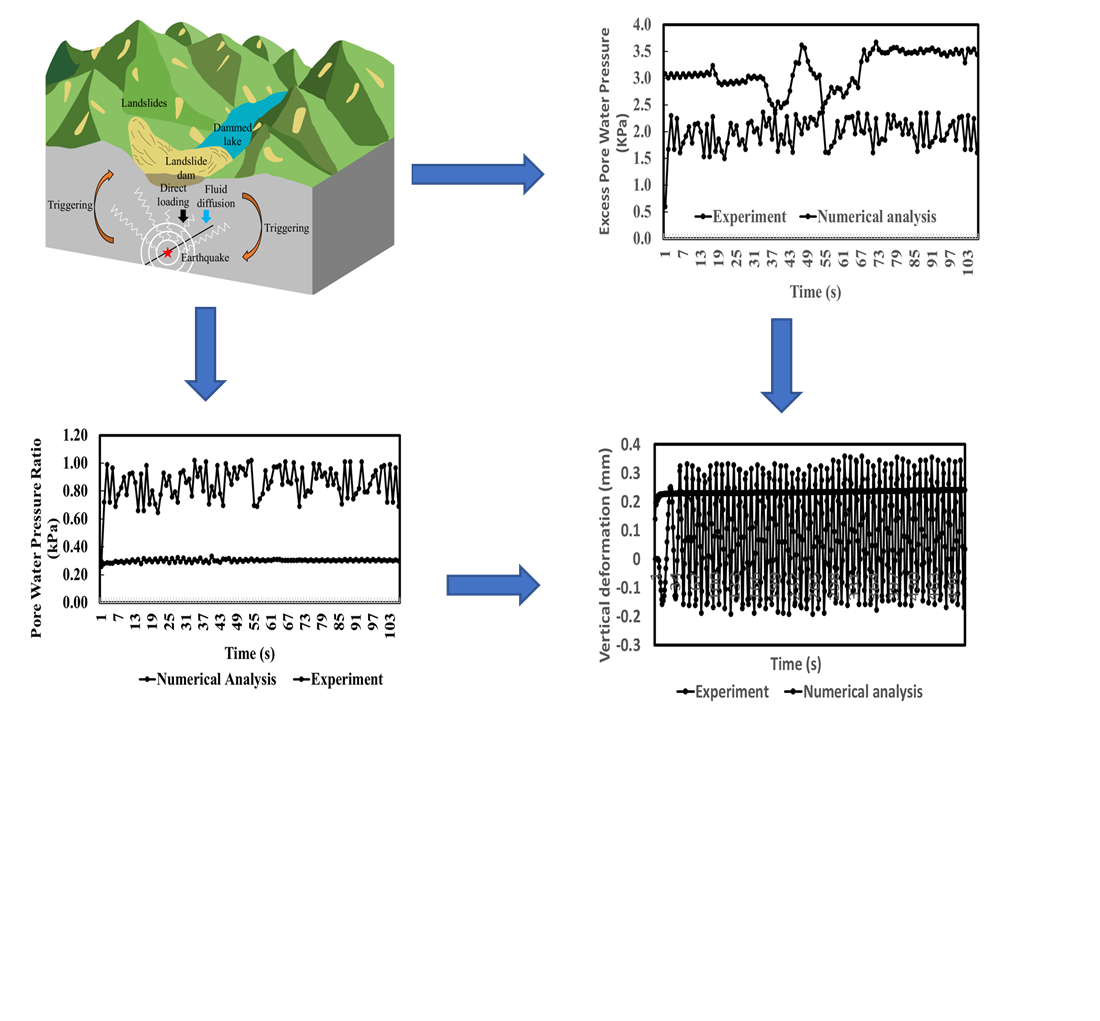
This study examines how increase in pore water pressure weakens the sand foundation, triggers liquefaction and lateral shift. This is related to the interaction of pressure, density, depth, and load through experiments and simulations to increase the foundation design. Numerical analysis using UBC3D-PLM 3D plaxis, while experimental tests are carried out with a 2.2 kW electric motor-powered table. Experiment uses an acrylic ground box 0.5×1×1.5 m3 which is strengthened by steel. The foundation model is in the form of a 2×2 pole group with four pillars and pile caps. The results of the study showed an increase in pore water pressure due to vertical and earthquake loads could trigger liquefaction and vertical deformation. Numerical analysis shows a surge in pressure in 20 seconds, in the case exceeding the 7.0 ratio, shows full liquefaction. The vibrating table experiment (relative density of 10 %) shows RU values close to 1, confirming the potential for liquefaction. Both experiments and simulations indicate rapid initial deformation before stabilization. Pore water pressure jumped to the critical level before stable, indicating the potential for full liquefaction. Non-linear vertical deformation confirms significant soil changes below the dynamic load. This study identifies the limit of the pressure ratio for partial and full liquefaction and soil response to vertical and seismic loads. The combination of numerical and experimental data allows the analysis of vertical deformation of foundation stability. This finding supports the design of earthquake resistant foundations and geotechnical risk assessment, although its application must consider soil conditions and limitations of numeric models, so it is necessary to be further calibration for prediction accuracy
References
- Yazdani, E., Wang, J., Evans, T. M. (2021). Case study of a driven pile foundation in diatomaceous soil. II: Pile installation, dynamic analysis, and pore pressure generation. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 13 (2), 446–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.10.005
- Hall, F. E., Lombardi, D., Bhattacharya, S. (2018). Identification of transient vibration characteristics of pile-group models during liquefaction using wavelet transform. Engineering Structures, 171, 712–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.06.028
- Ghiasi, V., Eskandari, S. (2023). Comparing a single pile’s axial bearing capacity using numerical modeling and analytical techniques. Results in Engineering, 17, 100893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2023.100893
- Lazuardi, L., Akhlis Rizza, M., Maryono, M. (2024). Application Planning Of Microhydro Electricity Generating Technology with 55 kW Power In The Mountains Using The River Flow Of Coban Rondo Waterfall, Krajaan, Pandesari, Kec. Pujon, Malang, East Jawa. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 01 (02), 61–69. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.vi.25
- Souri, M., Khosravifar, A., Dickenson, S., McCullough, N., Schlechter, S. (2023). Numerical modeling of a pile-supported wharf subjected to liquefaction-induced lateral ground deformations. Computers and Geotechnics, 154, 105117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2022.105117
- Asrori, A., Alfarisyi, M. F. S., Zainuri, Ach. M., Naryono, E. (2024). Characterization of the Bioenergy Potential of Corncob and Rice Husk mixtures in Biochar Briquettes. Evrimata: Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 01 (01), 14–20. https://doi.org/10.70822/evrmata.vi.22
- Liu, C., Wang, C., Fang, Q., Ling, X. (2022). Soil-pile-quay wall interaction in liquefaction-induced lateral spreading ground. Ocean Engineering, 264, 112592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112592
- Suhudi, S., Damayanti, F. (2024). Stability Analysis of Retaining Soil Walls Protecting Banu Canal, Ngantru Village, Ngantang District, Malang-Indonesia. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 02 (01), 95–103. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.vi.37
- Farag, R. (2014). Probabilistic pseudostatic analysis of pile in laterally spreading ground: Two layer soil profile. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 5 (2), 343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2013.12.010
- Puspitasari, E., Yudiyanto, E., Agustriyana, L., Alia, N. (2024). Small PLTS Off Grid 240 WP On Residential House Rooftop. Evrimata: Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 01 (03), 81–87. https://doi.org/10.70822/evrmata.v1i03.56
- Sahare, A., Ueda, K., Uzuoka, R. (2022). Influence of the sloping ground conditions and the subsequent shaking events on the pile group response subjected to kinematic interactions for a liquefiable sloping ground. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 152, 107036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.107036
- Ningrum, D., Nahak, A., Rasidi, N. (2023). Comparison Analysis of Equivalent Static Earthquake and Spectrum Response Dynamics on Steel Structure. Asian Journal Science and Engineering, 1 (2), 103. https://doi.org/10.51278/ajse.v1i2.548
- Fosoul, S. A. S., Tait, M. J. (2021). Soil-pile-structure interaction effects on seismic demands and fragility estimates of a typical Ontario highway bridge retrofitted with fiber reinforced elastomeric isolator. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 151, 106967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.106967
- Qiu, Z., Yu, Z., Su, L., Prabhakaran, A., Elgamal, A., Wang, X. (2023). Longitudinal seismic fragility assessment of an integral bridge-ground system in liquefaction-induced lateral spreads. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 168, 107838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.107838
- A Ibim, A. A. (2024). Adaptation to Climate Change, Conservation and Financial Feasibility in Heritage Buildings: A Nexus of Ideological Divergence in Post-Flood Disaster Reconstruction. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 02 (02), 150–157. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.v2i02.60
- Ahmed, K. S., Al-Moneim, A., Rashid, R., Siddika, N., Tamim, T., Islam, R., Khan, R. N. (2024). Numerical investigation for shear behavior of pretensioned spun precast concrete pile. Structures, 67, 106979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2024.106979
- Haeri, S. M., Rajabigol, M., Salaripour, S., Sayaf, H., Zangeneh, M. (2023). Effects of non-liquefiable crust layer and superstructure mass on the response of 2 × 2 pile groups to liquefaction-induced lateral spreading. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 15 (10), 2701–2719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.006
- Suhudi, S., Frida S, K., Damayanti, F. (2024). Analysis Of The Stability Plan For Kambaniru Weir, East Sumba District. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 02 (02), 138–143. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.v2i02.65
- Hirai, H. (2020). Analysis of cylindrical and rectangular bucket foundations subjected to vertical and lateral loads in sand using a three-dimensional displacement approach. Soils and Foundations, 60 (1), 45–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2020.01.001
- Zheng, G., Zhang, W., Forcellini, D., Zhou, H., Zhao, J. (2024). Dynamic centrifuge modeling on the superstructure–pile system considering pile–pile cap connections in dry sandy soils. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 187, 108979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108979
- Ningrum, D., Wijaya, H. S., Van, E. (2023). Effect of Treatment Age on Mechanical Properties of Geopolymer Concrete. Asian Journal Science and Engineering, 1 (2), 121. https://doi.org/10.51278/ajse.v1i2.544
- Chengcheng, Z., Zhongju, F., Cong, Z., Fuchun, W., Xiqing, W. (2024). Study on the seismic responses and differences between rock-socketed single pile and pile group foundations under different scour depths. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 187, 108971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108971
- Yamashita, K., Shigeno, Y., Hamada, J., Chang, D.-W. (2018). Seismic response analysis of piled raft with grid-form deep mixing walls under strong earthquakes with performance-based design concerns. Soils and Foundations, 58 (1), 65–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2017.12.002
- Pratama, A. Y., Widyasari, A., Fakhruddin, M., Muzaki, M., Firmansyah, H. I. (2024). Simulation Of The Effect Of Blank Geometry Toward The Mecanical Properties Of Strains And Stress On Deep Drawing Process Using Material Aluminum 7075. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 01 (02), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.vi.27
- Korre, E., Zeghal, M., Abdoun, T. (2024). Liquefaction in the presence of soil-structure interaction: Centrifuge tests of a sheet-pile quay wall in LEAP-2020. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 181, 108650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108650
- Putra, M. H. R., Utomo, E. B., Maulana, F. R., Huda, M. S. (2024). Improving the Quality of Frozen Chicken Sempol Products Using the Six Sigma Method at UMKM Suropati Pasuruan. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 02 (01), 104–111. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.vi.41
- Rasidi, N., Dora, M. P. I., Ningrum, D. (2022). Experimental Testing Comparison between Wiremesh Reinforcement and Plain Reinforcement on Concrete Slabs. Asian Journal Science and Engineering, 1 (1), 48. https://doi.org/10.51278/ajse.v1i1.405
- Xiao-ling, Z., Jun-yuan, X., Yan, H., Shong-loong, C. (2021). Model test study on horizontal bearing behavior of pile under existing vertical load. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 147, 106820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.106820
- Rajeswari, J. S., Sarkar, R. (2024). Adequacy of batter piles under seismic conditions: A review of past performances and investigations. Structures, 61, 106022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2024.106022
- Setiono, J., Rochman, T. (2022). Engineering and Financial Feasibility of Residential Housing Using Greenship Rating Tool Parameters. Asian Journal Science and Engineering, 1 (2), 60. https://doi.org/10.51278/ajse.v1i2.545
- Esfeh, P. K., Kaynia, A. M. (2019). Numerical modeling of liquefaction and its impact on anchor piles for floating offshore structures. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 127, 105839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.105839
- Zainal, M. Z. A., Susiloю S. H. (2023). Simulation of Heat Transfer Rate in Motorcycle Engine Cylinder with Variation of Distance Between Fins and Material. Evrimata: Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 01 (01), 01–08. https://doi.org/10.70822/evrmata.vi.12
- Eslami, A., Arjmand, A., Ardehe, A., Ebrahimipour, A., Nobahar, M., Mo, P.-Q. (2024). New approach for the numerical analysis of stiffened deep cement mixing columns and piles in coastal engineering through 1D elements. Ocean Engineering, 313, 119529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119529
- Machfuroh, T., Amalia, Z., Aida, F. (2023). Response of Vibration Reduction with Additional of Dual Dynamic Vibration to The Main System. Journal of Evrímata: Engineering and Physics, 01 (01), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.70822/journalofevrmata.vi.4
- Haeri, S. M., Rajabigol, M. (2023). Effects of liquefaction-induced lateral spreading on piles, an overview of physical modeling. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 173, 108111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.108111
- Ju, S.-H., Chiu, C.-S., Huang, Y.-C. (2025). Comparing traditional and suction piles in steel design of wind turbine structures. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 224, 109169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2024.109169
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 As’ad Munawir, Yulvi Zaika, Eko Andi Suryo, Nuril Charisma, Arief Alihudien

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








