Identifying the graph-based typology features for machine learning models in financial fraud detection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327410Keywords:
financial fraud, transaction patterns, machine learning, graph analysis, typology detection, classification, anomaly detectionAbstract
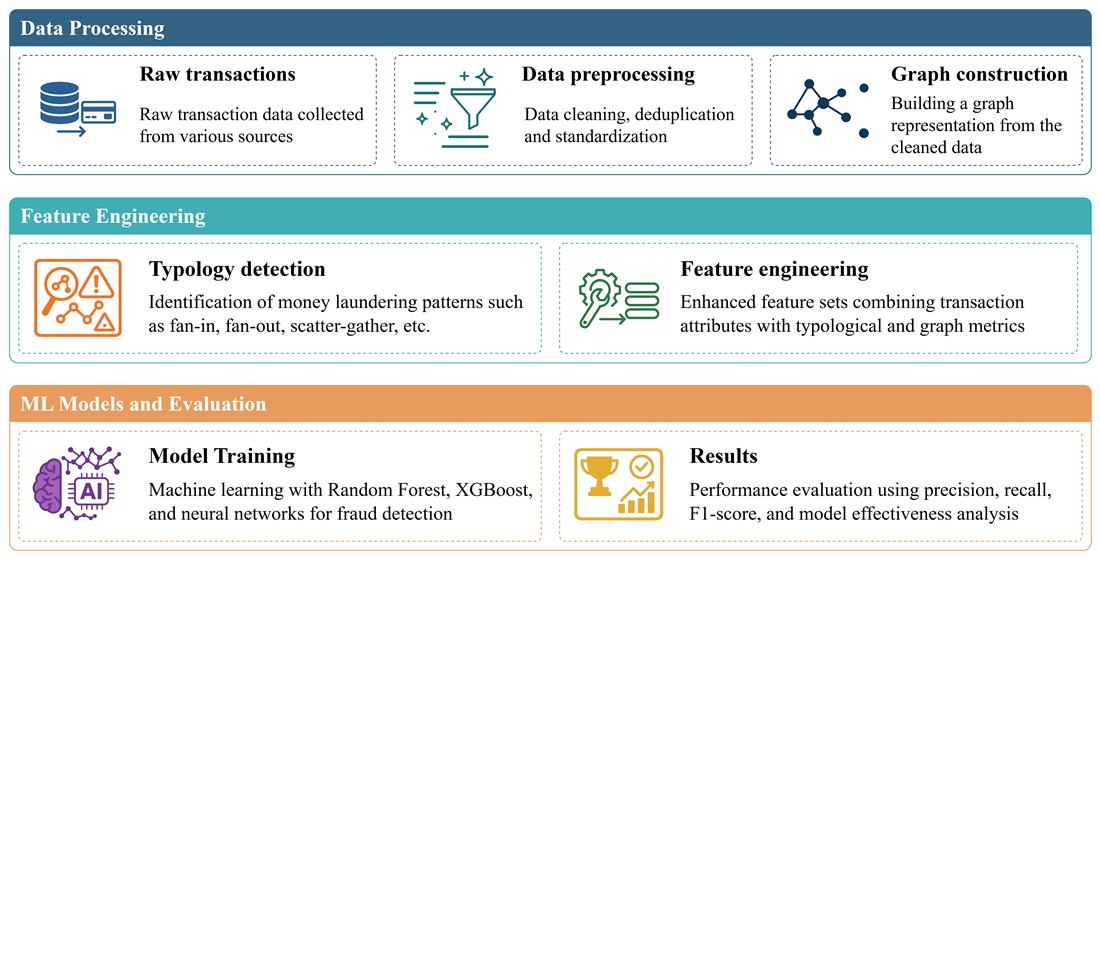
This article investigates fraud detection in financial transaction networks using machine learning and graph-based typologies. The object of the study is financial transaction data, analyzed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of identifying fraudulent activities. The problem addressed is the limited generalizability and low recall of traditional fraud detection models in complex, real-world settings.
To address this, a hybrid framework was developed that integrates Random Forests, neural networks, and graph-based typology indicators. Seven laundering typologies were extracted from a transaction graph – fan-in, fan-out, scatter-gather, gather-scatter, cycle, bipartite, and stacked bipartite – and used as additional features for classification. SMOTE was applied to correct class imbalance during training.
Experimental results show that adding typology features significantly improves model performance. The best results were obtained with Random Forest: 98.5% accuracy, 79.1% precision, 56.3% recall, and an F1-score of 65.7%. Adding typology-based flags raised recall by 9–11 percentage points compared to models without them. Graph patterns like fan-in and fan-out were detected in 3.5–5.1% of transactions, while more complex structures such as cycle and scatter-gather appeared less frequently but correlated more strongly with known fraud.
Unsupervised methods also showed promise: an autoencoder captured 60% of fraud cases among the top 2% anomalous transactions, while K-means identified 55% of fraud within flagged clusters. These methods proved useful for identifying emerging fraud types not yet labeled in training data.
The model is suitable for integration into financial security systems with minimal input requirements – account IDs, timestamps, and transaction amounts—alongside basic graph analytics. Its robustness across datasets suggests strong applicability across diverse financial institutions
References
- National Money Laundering Risk Assessment (2024). U.S. Department of the Treasury. Available at: https://home.treasury.gov/system/files/136/2024-National-Money-Laundering-Risk-Assessment.pdf
- Jarugula, S. (2025). The Evolution of Fraud Detection: A Comprehensive Analysis of AI-Powered Solutions in Financial Security. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 11 (2), 919–926. https://doi.org/10.32628/cseit25112430
- Ali, A., Abd Razak, S., Othman, S. H., Eisa, T. A. E., Al-Dhaqm, A., Nasser, M. et al. (2022). Financial Fraud Detection Based on Machine Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 12 (19), 9637. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199637
- Baisholan, N., Dietz, J. E., Gnatyuk, S., Turdalyuly, M., Matson, E. T., Baisholanova, K. (2025). FraudX AI: An Interpretable Machine Learning Framework for Credit Card Fraud Detection on Imbalanced Datasets. Computers, 14 (4), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14040120
- Li, X., Liu, S., Li, Z., Han, X., Shi, C., Hooi, B. et al. (2020). FlowScope: Spotting Money Laundering Based on Graphs. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34 (04), 4731–4738. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5906
- Blanuša, J., Cravero Baraja, M., Anghel, A., von Niederhäusern, L., Altman, E., Pozidis, H., Atasu, K. (2024). Graph Feature Preprocessor: Real-time Subgraph-based Feature Extraction for Financial Crime Detection. Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, 222–230. https://doi.org/10.1145/3677052.3698674
- Tümmler, M., Quick, R. (2025). How to detect fraud in an audit: a systematic review of experimental literature. Management Review Quarterly. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-024-00480-7
- Dumitrescu, B., Baltoiu, A., Budulan, S. (2022). Anomaly Detection in Graphs of Bank Transactions for Anti Money Laundering Applications. IEEE Access, 10, 47699–47714. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3170467
- Karim, Md. R., Hermsen, F., Chala, S. A., De Perthuis, P., Mandal, A. (2024). Scalable Semi-Supervised Graph Learning Techniques for Anti Money Laundering. IEEE Access, 12, 50012–50029. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3383784
- Karim, R., Hermsen, F., Chala, S., de Perthuis, P., Mandal, A. (2023). Catch me if you can: Semi-supervised graph learning for spotting money laundering. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.11880
- Islam, M. Z., Islam, M. S., Das, B. C., Reza, S. A., Bhowmik, P. K., Bishnu, K. K. et al. (2025). Machine Learning-Based Detection and Analysis of Suspicious Activities in Bitcoin Wallet Transactions in the USA. Journal of Ecohumanism, 4 (1). https://doi.org/10.62754/joe.v4i1.6214
- Rahman, A., Debnath, P., Ahmed, A., Dalim, H. M., Karmakar, M., Sumon, F. I., Khan, A. (2024). Machine learning and network analysis for financial crime detection: Mapping and identifying illicit transaction patterns in global black money transactions. Gulf Journal of Advance Business Research, 2 (6), 250–272. https://doi.org/10.51594/gjabr.v2i6.49
- Rahman, M. K., Dalim, H. M., Reza, S. A., Ahmed, A., Zeeshan, M. A. F., Jui, A. H., Nayeem, M. B. (2025). Assessing the Effectiveness of Machine Learning Models in Predicting Stock Price Movements During Energy Crisis: Insights from Shell’s Market Dynamics. Journal of Business and Management Studies, 7 (1), 44–61. https://doi.org/10.32996/jbms.2025.7.1.4
- Rahouti, M., Xiong, K., Ghani, N. (2018). Bitcoin Concepts, Threats, and Machine-Learning Security Solutions. IEEE Access, 6, 67189–67205. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2874539
- Podgorelec, B., Turkanović, M., Karakatič, S. (2019). A Machine Learning-Based Method for Automated Blockchain Transaction Signing Including Personalized Anomaly Detection. Sensors, 20 (1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010147
- Pham, H.-G. T., Pham, Q.-V., Pham, A. T., Nguyen, C. T. (2020). Joint Task Offloading and Resource Management in NOMA-Based MEC Systems: A Swarm Intelligence Approach. IEEE Access, 8, 190463–190474. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3031614
- Ali, A. H., Hagag, A. A. (2024). An enhanced AI-based model for financial fraud detection. International Journal of ADVANCED AND APPLIED SCIENCES, 11 (10), 114–121. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2024.10.013
- Pan, E. (2024). Machine Learning in Financial Transaction Fraud Detection and Prevention. Transactions on Economics, Business and Management Research, 5, 243–249. https://doi.org/10.62051/16r3aa10
- Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Cheng, J., Yan, H., Shi, K. (2023). Improved filtering of interval type-2 fuzzy systems over Gilbert-Elliott channels. Information Sciences, 627, 132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.01.053
- Tarjo, T., Anggono, A., Sakti, E. (2021). Detecting Indications of Financial Statement Fraud: a Hexagon Fraud Theory Approach. AKRUAL: Jurnal Akuntansi, 13 (1), 119–131. https://doi.org/10.26740/jaj.v13n1.p119-131
- Policy on Anti-Fraud, Corruption, Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing, and Domiciliation of BSTDB Counterparties. Available at: https://www.bstdb.org/Antifraud_policy.pdf
- Xia, Z., Saha, S. C. (2025). FinGraphFL: Financial Graph-Based Federated Learning for Enhanced Credit Card Fraud Detection. Mathematics, 13 (9), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13091396
- Duman, E., Ozcelik, M. H. (2011). Detecting credit card fraud by genetic algorithm and scatter search. Expert Systems with Applications, 38 (10), 13057–13063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.110
- Ren, Y., Zhu, H., Zhang, J., Dai, P., Bo, L. (2021). EnsemFDet: An Ensemble Approach to Fraud Detection based on Bipartite Graph. 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). https://doi.org/10.1109/icde51399.2021.00197
- Wójcik, F. (2024). An Analysis of Novel Money Laundering Data Using Heterogeneous Graph Isomorphism Networks. FinCEN Files Case Study. Econometrics, 28 (2), 32–49. https://doi.org/10.15611/eada.2024.2.03
- Cherif, A., Badhib, A., Ammar, H., Alshehri, S., Kalkatawi, M., Imine, A. (2023). Credit card fraud detection in the era of disruptive technologies: A systematic review. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 35 (1), 145–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.11.008
- Charizanos, G., Demirhan, H., İçen, D. (2024). An online fuzzy fraud detection framework for credit card transactions. Expert Systems with Applications, 252, 124127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124127
- Xiang, S., Zhu, M., Cheng, D., Li, E., Zhao, R., Ouyang, Y., Chen, L., Zheng, Y. (2023). Semi-supervised Credit Card Fraud Detection via Attribute-Driven Graph Representation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 37 (12), 14557–14565. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v37i12.26702
- Bolshibayeva, A. K., Uskenbayeva, R. K., Kuandykov, A. A., Rakhmetulayeva, S. B., Astaubayeva, G. N. (2021). Development of Business Process Design Methods. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 99 (10), 2344–2358. Available at: https://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol99No10/14Vol99No10.pdf
- Mohammed, H. N., Malami, N. S., Thomas, S., Aiyelabegan, F. A., Imam, F. A., Ginsau, H. H. (2022). Machine Learning Approach to Anti-Money Laundering: A Review. 2022 IEEE Nigeria 4th International Conference on Disruptive Technologies for Sustainable Development (NIGERCON), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/nigercon54645.2022.9803072
- Soltani, R., Nguyen, U. T., Yang, Y., Faghani, M., Yagoub, A., An, A. (2016). A new algorithm for money laundering detection based on structural similarity. 2016 IEEE 7th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/uemcon.2016.7777919
- Martínez-Sánchez, J. F., Cruz-García, S., Venegas-Martínez, F. (2020). Money laundering control in Mexico. Journal of Money Laundering Control, 23 (2), 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmlc-10-2019-0083
- Altman, E. (2019). IBM Transactions for Anti Money Laundering (AML). Available at: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/ealtman2019/ibm-transactions-for-anti-money-laundering-aml
- Labanca, D., Primerano, L., Markland-Montgomery, M., Polino, M., Carminati, M., Zanero, S. (2022). Amaretto: An Active Learning Framework for Money Laundering Detection. IEEE Access, 10, 41720–41739. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3167699
- Rocha-Salazar, J.-J., Segovia-Vargas, M.-J., Camacho-Miñano, M.-M. (2021). Money laundering and terrorism financing detection using neural networks and an abnormality indicator. Expert Systems with Applications, 169, 114470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114470
- Gaviyau, W., Sibindi, A. B. (2023). Global Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorism Financing Regulatory Framework: A Critique. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 16 (7), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm16070313
- Alkhalili, M., Qutqut, M. H., Almasalha, F. (2021). Investigation of Applying Machine Learning for Watch-List Filtering in Anti-Money Laundering. IEEE Access, 9, 18481–18496. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3052313
- Duisebekova, K. S., Kozhamzharova, D. K., Rakhmetulayeva, S. B., Umarov, F. A., Aitimov, M. Zh. (2020). Development of an information-analytical system for the analysis and monitoring of climatic and ecological changes in the environment. Procedia Computer Science, 170, 578–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.128
- Yang, G., Liu, X., Li, B. (2023). Anti-money laundering supervision by intelligent algorithm. Computers & Security, 132, 103344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2023.103344
- Lokanan, M. E. (2023). Predicting money laundering sanctions using machine learning algorithms and artificial neural networks. Applied Economics Letters, 31 (12), 1112–1118. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2023.2176435
- Rakhmetulayeva, S., Kulbayeva, A. (2022). Building Disease Prediction Model Using Machine Learning Algorithms on Electronic Health Records’ Logs. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Digital Technologies in Education, Science and Industry (DTESI 2022). Available at: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3382/Paper19.pdf
- Zhang, Y., Trubey, P. (2018). Machine Learning and Sampling Scheme: An Empirical Study of Money Laundering Detection. Computational Economics, 54 (3), 1043–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-018-9864-z
- Chen, Z., Soliman, W. M., Nazir, A., Shorfuzzaman, M. (2021). Variational Autoencoders and Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks for Improving the Anti-Money Laundering Process. IEEE Access, 9, 83762–83785. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3086359
- Domashova, J., Mikhailina, N. (2021). Usage of machine learning methods for early detection of money laundering schemes. Procedia Computer Science, 190, 184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.06.033
- Konyrbaev, N., Nikitenko, Y., Shtanko, V., Lakhno, V., Baishemirov, Z., Ibadulla, S. et al. (2024). Evaluation and optimization of the naive bayes algorithm for intrusion detection systems using the USB-IDS-1 dataset. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (132)), 74–82. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.317471
- Aloev, R., Berdyshev, A., Akbarova, A., Baishemirov, Z. (2021). Development of an algorithm for calculating stable solutions of the Saint-Venant equation using an upwind implicit difference scheme. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (112)), 47–56. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.239148
- Urmashev, B., Buribayev, Z., Amirgaliyeva, Z., Ataniyazova, A., Zhassuzak, M., Turegali, A. (2021). Development of a weed detection system using machine learning and neural network algorithms. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (114)). https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.246706
- Bolshibayeva, A., Rakhmetulayeva, S., Ukibassov, B., Zhanabekov, Z. (2024). Advancing real-time echocardiographic diagnosis with a hybrid deep learning model. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (132)), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.314845
- Kulbayeva, A. K., Rakhmetulayeva, S. B., Bolshibayeva, A. K., Yasar, A.-U.-H. (2024). Data Processing Methods for Financing Terrorism: The Role of Microsoft Power BI in Money Laundering Detection. Procedia Computer Science, 238, 528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.06.056
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sabina Rakhmetulayeva, Aliya Kulbayeva, Aigerim Bolshibayeva, Vassiliy Serbin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








